According to Footprint Analytics data, as of Feb. 7, Ethereum has burned 1,778,834 ETH since the London upgrade in August, equivalent to $5.5 billion at current prices. Polygon also announced the implementation of EIP-1559 in an upgrade to the main network on Jan. 18.
EIP-1559’s primary purpose is to get rid of the first-price auction mechanism in favor of a base fee plus a priority fee. The base fee fluctuates based on network conditions, making gas charges more visible, while the base fee will be burned.
The base fee will be locked to the burn contract on Polygon and the priority fee will be paid directly to the validators. The burn will start on Polygon and finish on Ethereum. Polygon provides a public interface that allows users to monitor the burn and initiate a burn once the cumulative MATIC to be burned exceeds 25,000. Polygon has currently burned 545,903 MATIC.
Why did Polygon Launch a Burn Mechanism
Polygon is a sidechain of Ethereum and aims to solve its scaling problems, like high fees, low TPS and poor user experience.
However, Polygon experienced a gas fee crisis at the beginning of January, which caused some validators to fail to submit blocks. An NFT game called Sunflower spiked gas fees, with 40% of the chain’s gas fees coming from this game. The average price of gas was 763 Gwei on Jan. 5.
The advantage Polygon claimed when it went live is diminishing compared to the average gas fee of only about 10 Gwei at the beginning of the year.
On Jan. 18, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin tweeted about the paper, Empirical Analysis of EIP-1559: Transaction Fees, Waiting Times, and Consensus Security, jointly published by Peking University and Duke University. It confirmed that EIP-1559 has indeed improved user experience—which can be seen as the leftward shift on the chart, indicating that waiting times have decreased.
Drawing on the results of the Ethereum London upgrade, Polygon hopes to bring improvements to everyone in the ecosystem with EIP-1559.
Effects of Polygon’s Upgrade
Polygon believes the London upgrade will have far-reaching implications.
- For Token Holders: Since MATIC is a fixed supply, the burning mechanism will contribute to deflation. According to simulations, the annual burnt MATIC will be 0.27% of the total supply.
- For Users: Enjoy lower gas fees than Ethereum while allowing for better fees prediction in the future.
- For Validators: Future return will be only priority fees, but the return will benefit from MATIC’s deflation. It will make both spam transactions and network congestion better in the future.
Here is how the Polygon London upgrade actually performs.
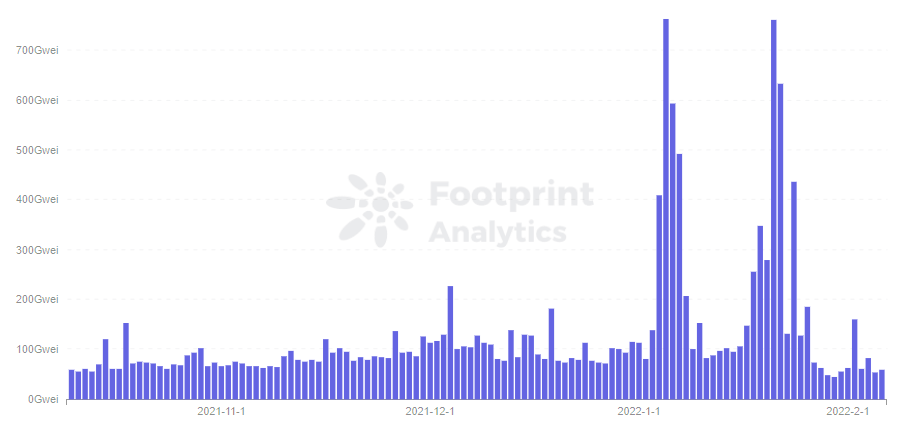
- Average Gas Price
Transaction fees are determined by supply and demand, the launch of EIP-1559 will not result in a significant improvement in the price of gas. It is true that after the upgrade the price did not drop significantly, but increased slightly. The average price has remained above 200 Gwei per day after update, with some decrease in late January.
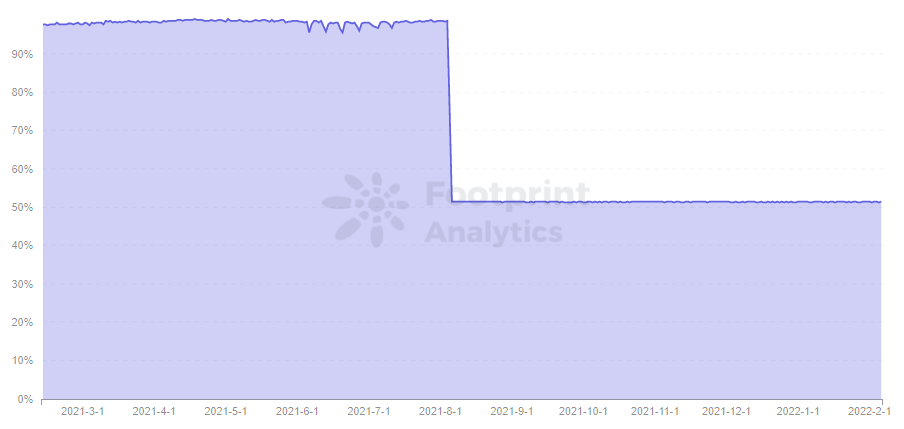
- Network Utilization
While there is no reduction in the price of gas, the London upgrade will make the base fee predictable. Gas fees increase in price as block usage rises and decrease in price as usage decreases.
Looking back at Ethereum since the London upgrade, there has been a huge drop in network utilization. From about 97% down to 51%, and the utilization rate is very stable, fluctuating not more than 1%.
Similarly, Polygon’s network utilization was between 60% to 90% prior to Jan. 18, dropping to below 50.7% instantly after the upgrade. The stability of fluctuating utilization rates has kept the overall network stable and transaction fees relatively stable.
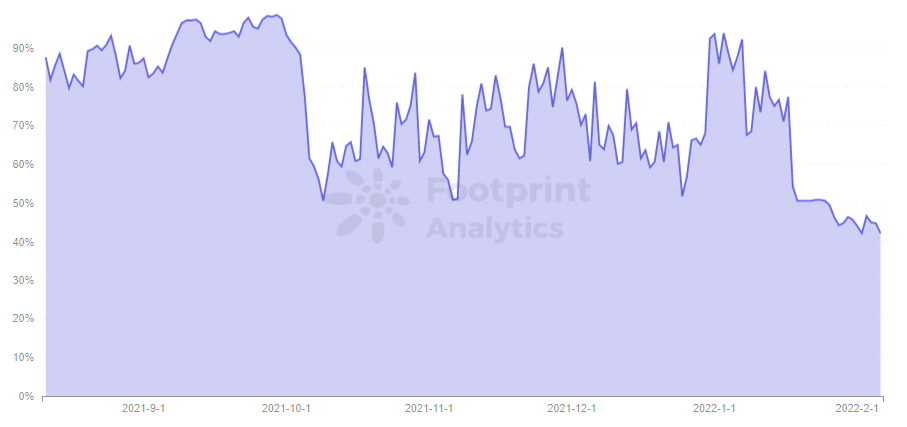
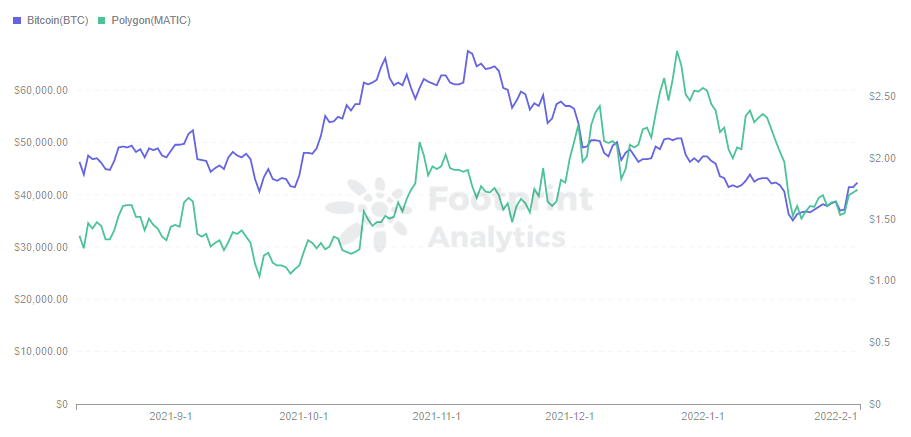
- Token Price
The price of ETH has increased after the London upgrade, while MATIC has decreased rather than increased. This is mainly because MATIC’s price is more influenced by the overall blockchain market. The price is highly correlated with BTC, whose price fell below $40,000 due to various factors.
Recently, the ESMA (European Securities and Markets Authority) called to ban PoW mining and the Bank of Russia published a report recommending a ban on cryptocurrencies. Countries have launched policies that are not conducive to the development of cryptocurrencies. At the same time, the Federal Reserve is expected to raise interest rates in March and funds are expected to start moving, which is also somewhat negative for blockchain. Many reasons have contributed to the recent turbulent downward movement of cryptocurrencies.
Summary
Polygon received a lot of attention for being a sidechain of Ethereum, and became the third largest blockchain by number of protocols after Ethereum and BSC. However, its market share has been gradually compressed since August, and TVL ranking has dropped from 3rd to 8th.
Without Ethereum’s first-mover advantage, this upgrade and optimization is imperative for Polygon to stand out among so many emerging chains.
Although MATIC has not yet been revived, the new burning mechanism may rekindle Polygon.
Date and Author: 17 Feb. 2022, Simon@footprint.network
Data Source: Footprint Analytics
What is Footprint Analytics?
Footprint Analytics is an all-in-one analysis platform to visualize blockchain data and discover insights. It cleans and integrates on-chain data so users of any experience level can quickly start researching tokens, projects, and protocols. With over a thousand dashboard templates plus a drag-and-drop interface, anyone can build their own customized charts in minutes. Uncover blockchain data and invest smarter with Footprint.
The post Will MATIC’s Burning Mechanism Help Polygon Stay on Top? appeared first on CryptoSlate.





















