Fantom is a blockchain protocol that provides high-speed transactions at a low cost and several tools for DeFi developers to build on its ecosystem.
Fantom is a Layer-1; a layer-1, also referred to as the mainnet or mainchain, is the base blockchain, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Binance Chain, Solana, Cardano, etc.
Layer-1s have their own infrastructure to process transactions and rely on their own security protocols. In contrast, a layer-2 is built on top of layer-1. Some popular examples are Polygon, Arbitrum, and Loopring, which are protocols built on top of Ethereum.
Fantom stands out from its competitors, like Solana, as one of the few layer-1s compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) allowing users to port their applications and projects from Ethereum to Fantom and vice versa.
Fantom is popular because it:
- Offers users high-speed transactions with settlement times of around 1 second
- Provides developers with several easy-to-use tools to create applications and smart contracts on its ecosystem
- It’s interoperable with the Ethereum network and the Binance Smart Chain
- Is home to several DeFi projects building on its ecosystem, including popular decentralized exchanges like SpookySwap and lending protocols such as Aave and Alchemix.
Fantom: How Does it Work?
Fantom allows users to transfer cryptocurrency seamlessly through Opera, the protocol’s main blockchain. Fantom has a utility token called FTM, which also has an ERC-20 version to use on the Ethereum blockchain and a BEP-2 to use on the Binance Chain.
Fantom provides developers with a stack of resources and tools to create smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), and even create their own blockchains with customizable aspects.
Let’s break down Fantom’s features and core components.
Lachesis: Fantom’s Consensus Algorithm:
Lachesis is Fantom’s consensus algorithm derived from the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus. In both mechanisms, validators must stake a certain amount of coins to validate blocks in a blockchain. The difference is that Lachesis uses a different mechanism called Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT.)
In simpler terms, the aBFT mechanism allows validators to execute commands (such as validating a block to process transactions) at their own pace without waiting for other validators to reach an agreement (consensus.) This allows a faster transaction throughput while maintaining decentralization and security (we’ll dive deeper into this last point in another section.)
Fantom says Lachesis is its attempt to solve the Blockchain Trilemma which states it’s practically impossible for a blockchain protocol to balance three specific traits in harmony: decentralization, security, and scalability. For example, if a blockchain has a high level of security due to decentralization, then it sacrifices speed.
Here are the key characteristics of Lachesis:
- Asynchronous: validators can process transactions at different times, resulting in efficient and fast transaction throughput.
- Leaderless: the aBFT consensus is a leaderless system as no participant plays a special role in the network
- Interoperable: all chains on Fantom are connected to Lachesis, allowing them to communicate with each other.
Fantom’s Multiple Chains
Users can create their own customizable blockchains to host their projects. These blockchains can communicate with each other and the Opera Chain as they’re plugged into the Lachesis consensus while maintaining their autonomy.
Developers can adjust blockchains according to their needs regarding use cases, tokenomics, governance, and more. We can describe Fantom then as a Layer-1 that hosts multiple Layer-2s.
Fantom and the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
Here we’re diving a bit deeper into Fantom’s technological stack, specifically on the Lachesis consensus layer. Let’s try to break it down: Lachesis’ underlying infrastructure is a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
A DAG is a data structuring system that processes transactions in a different way than a blockchain. Instead of blocks, a DAG consists of vertices and edges that allow transactions to be recorded on top of previous transactions. A DAG looks more like a tree-like graph instead of a, well… a chain of blocks.
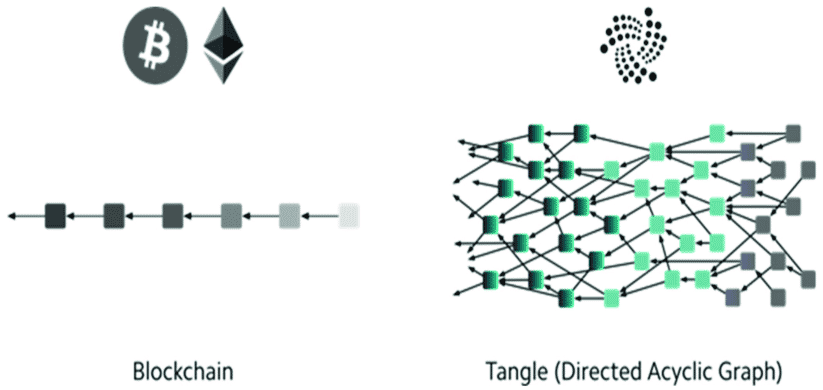
Blockchain basic infrastructure compared to Directed Acyclic Graph. Source: Research Gate
All transactions must reference a previous transaction to be successfully confirmed instead of being gathered in a block. DAGs can provide higher transaction speed as each node in the system can process transactions from more than one parent root. The rationale here is that nodes don’t have to wait for transactions to complete to process a new one.
The Fantom Token: (FTM)
Fantom’ has a utility token called FTM, used to pay for transaction fees, staking, and gain voting rights in Fantom DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization.) FTM has an ERC-20 and a BEP-2 version, which are not usable on the Opera Chain.
The total FTM supply is 3.175 billion, with over 2.5 billion FTM in circulation as of July 2022. The token distribution is as follows:
- 40.18%: public and private sale investors
- 38.76% vested for staking rewards, distributed daily until 2024. After that period, the protocol will introduce new ways to incentivize validators.
- 12%: advisors
- 7.49%: team and founders
- 1.57%: public investors
You only need a minimum of 1 FTM to start staking. You can lock up your FTM with a reward rate proportional to the lock-up period, which is up to 365 days and a maximum of 15% annual percentage yield (APY) as of July 2022. The minimum lock-up period is 14 days and a 4.96% yield.
Becoming a Validator
To become a validator, users must stake a minimum of 3,175,000 FTM. As of July 2022, the price of FTM is $0.26, so that’s roughly $825,000.
Where can you buy FTM?
You can buy FTM in almost any top crypto exchange like Binance, Coinbase or Kraken. Remember you can buy the ERC-20 and the BEP-2 versions of FTM as well.
Fantom: History & Founders
Michael Kong and Quan Nguyen founded the Fantom Foundation in 2018. The protocol was launched that year, raising over $40 million in an Initial Coin Offering (ICO.) Andre Cronje —a popular blockchain developer in the crypto community— participated in the launch of Fantom as a key advisor but departed on March 6, 2022. Cronje was known for his early work on several projects, including Yearn Finance, which is integrated into the Fantom ecosystem, and Sushiswap.
Fantom was designed to address several issues in the blockchain landscape. The Fantom Foundation has made several partnerships with other blockchain protocols to provide a multi-asset and cross-chain ecosystem. In May 2019, Fantom partnered with Binance Chain to introduce a new token standard for FTM and improve interoperability.
What Projects Are on Fantom?
There are over 200 decentralized projects from different fields on Fantom, including decentralized exchanges, cross-chain bridges, lending protocols and NFT platforms. Here are the top 3:
- SpookySwap (BOO): currently the most popular decentralized exchange and cross-chain bridge on Fantom, also compatible with Ethereum Binance, Avalanche, and other blockchains.
- Aave: originally built on the Ethereum network, Aave is also available for lending and borrowing crypto in the Fantom blockchain.
- Beefy Finance: a yield-generating protocol that allows users to earn compound interest on their cryptocurrency funds.
Final Thoughts: Fantom is a Layer-1 Dark Horse
Ethereum remains the number one protocol for decentralized apps of all kinds —yet the problem remains the same: the vast amount of network activity usually outweighs the network’s processing capacity.
Fantom is competing against some notable blockchains such as Solana, Cardano, and Avalanche. Fantom may not have the same sort of network activity as Ethereum, it has demonstrated an ability to seamlessly handle its current ecosystem with ease.
Fantom is home to a diverse array of decentralized applications projects building on its blockchain– all the same, stuff you’d see from another Layer-1 like DAOs, DEXs, to NFT and GameFi platforms.
Despite not commanding the same sort of mindshare of an Ethereum or Solana, the Fantom has been building for years, priming it as one of the top Layer-1s in crypto.
The post What is Fantom (FTM): A Guide on the Growing Layer-1 Blockchain appeared first on CoinCentral.



















