Key Insights
- Chia Network is a decentralized Layer-1 blockchain with a sustainable and regulatory-compliant architecture.
- The protocol is led by Chia Network Inc., a private company led by BitTorrent founder Bram Cohen.
- Chia maintains one of the largest node networks in the crypto ecosystem.
- Notable regulatory entities have partnered with Chia, including the World Bank, the International Finance Corporation (IFC), and the Government of Costa Rica.
- In 2022, the network’s daily transaction volume has remained flat near all-time-lows.
In the past year, regulators and investors have increasingly criticized the sustainability standards of leading Layer-1 (L1) consensus mechanisms. Bitcoin has received scrutiny for the resource demands of its Proof-of-Work (PoW) design. Concerns about blockchain energy consumption have led legislators in New York to call for an outright ban on Bitcoin mining operations, citing potential electrical grid stress and heightened energy prices. Alternatively, Proof-of-Stake protocols such as Ethereum achieve consensus with a fraction of the energy expenditure of Proof-of-Work. However, research pointing to validator centralization risks has stoked heated debate over Ethereum’s censorship resistance.
Chia Network’s payment protocol attempts to answer the calls for a more sustainable, decentralized L-1 blockchain design. Chia combines facets of Bitcoin and Ethereum, offering smart contract functionality on top of a Nakamoto consensus architecture. Its unique Proof-of-Space-and-Time (PoST) consensus mechanism requires users to employ unused hard-drive space to coordinate block production and earn rewards. Compared to PoW, PoST has both lower hardware costs and less consumptive electricity demand. This low barrier-to-entry has enabled Chia Network to proliferate a high volume and geographically distributed node count compared to other protocols.
Chia sustainability and decentralization assurances have yet to result in significant network effects, but its project team maintains long-term goals to foster an ecosystem for peer-to-peer payments between users, along with enterprise and government integrations.
Background
On Aug. 1, 2017, Bram Cohen founded Chia Network. Cohen is also the co-founder and inventor of BitTorrent, a peer-to-peer file sharing network and one of the most widely used internet protocols in history.
In January 2018, Cohen co-wrote and published Chia Network’s first academic paper. Focusing on economic alternatives to PoW, the paper’s findings serve as the foundation for the network’s novel Nakamoto Consensus Algorithm, Proof-of-Space-and-Time (PoST).
Since its inception, Chia Network has raised over $75 million in financing, with the latest round led by Richmond Global Ventures and Andreessen Horowitz in May of 2021. In January 2019, the project team released open-source code for its Verifiable Delay Function (VDF), a cryptographic primitive used in PoST consensus. Later that year, Chia filed its first provisional patents and detailed the network’s comprehensive design in its Green Paper.
The Chia Mainnet went live on March 19, 2021, with transactions and its protocol coding language, Chialisp, being enabled on May 3, 2021. Since its launch, network development has been led by Chia Network Inc., a Delaware corporation.
The Company and its board maintain control over the Strategic Reserve, a treasury containing 21 million XCH created as part of the “pre-farm” token generation event at the mainnet launch. At the time of writing, XCH held in the Strategic Reserve makes up approximately 80% of the total token supply.
The Company has worked with the SEC to determine the classification of the Reserve and intends to proactively work with regulators over its equity structure, corporate governance (including over the Reserve), and potential IPO event. Jurisdictional control over the reserve is divided evenly between Chia’s U.S.-based parent company and its Swiss subsidiary.
Technology
Consensus Mechanism
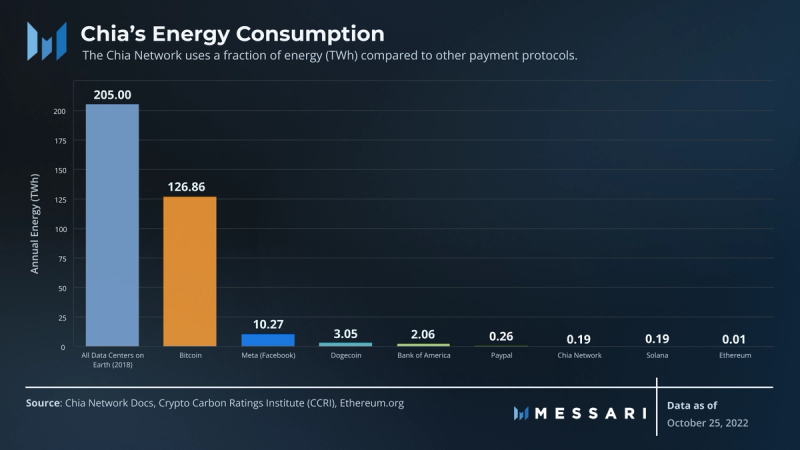
Chia Network leverages its PoST consensus mechanism to assure security and decentralization without costly resource demands. PoST is similar to Proof-of-Work (PoW), except PoST participants contribute disk space instead of computation power to verify cryptographic proofs. As a result, the network uses just 0.09% of the annual energy consumption of Bitcoin. At 0.19 TWh/yr, Chia Network uses a comparable amount of electricity as Proof-of-Stake protocols, with approximately the same annual electricity consumption as Solana (0.19 TWh/yr) and only nominally more consumption than Ethereum (0.01 TWh/yr).
Proof of Space
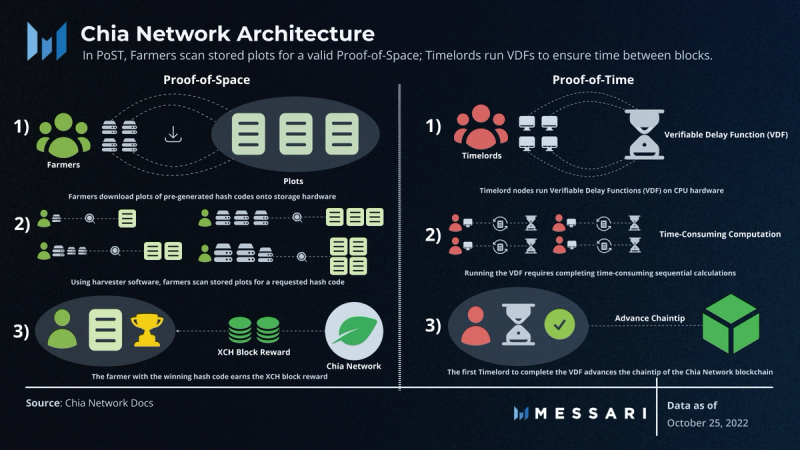
In Chia’s Proof-of-Space, users store large data files, known as “plots,” that contain collections of pre-generated hashes. These users, known as “farmers,” are tasked with scanning stored plots using software, known as a harvester, to find a hash code closest to the requested hash.
The process of “plotting” stored files onto storage hardware and “farming” plots for a requested hash requires a trivial amount of computation. Since plots can be reused, there’s no need to re-generate plots every time you scan for hashes. In Bitcoin’s PoW, on the other hand, miners regenerate hash permutations every single block, requiring significant computational power. Thus, PoST eschews the need to compete for computation power to generate new hashes. Instead, storage space is the prime commodity.
The probability of solving the challenge and earning block rewards is proportional to a farmer’s share of the total storage space being deployed to the network. To maintain a consistent rate of block creation, Chia Network also includes a difficulty adjustment. This mechanism algorithmically adjusts plotting demands so that 32 blocks are created with a target time of 10 minutes on average. The network’s consensus difficulty is adjusted every 4,608 blocks (approximately every 24 hours), with farming difficulty increasing when block production is too quick, and decreasing when blocks are completed slowly.
Chia’s permissionless nature allows any user with a hard drive and an internet connection to participate in farming. Farmers can also pool storage resources together to increase the likelihood of earning XCH rewards. Unlike in PoW and PoS, the farmer with the winning proof chooses the contents of a block, not the pool itself. This decreases the risk of centralized pools having adverse control on protocol activity.
Examples of hardware for storing and farming plots can be found here.
Proof of Time
Chia Network’s “proof-of-time” ensures that a specific amount of time has elapsed following the issuance of each challenge, and as a result, the creation of each block. In doing so, it nullifies the incentive for farmers to scan plots faster, and by association, invest in faster computation hardware.
Proof-of-time is achieved via Verifiable Delay Functions (VDFs), which are time-intensive cryptographic proofs required to advance the Chia Network chain. While VDFs take time to produce, they can be quickly verified without redoing the whole sequential calculation. This is analogous to how in PoW, one can easily determine the heaviest chain without repeating the work itself.
Without VDFs, additional challenges would be issued as fast as farmers could solve them, which would incentive farmers to invest in computation power to scan plots faster. This could also cause fluctuation in block times and an open attack surface for replay attacks in which transactions are fraudulently retransmitted. If an attacker presents a false alternate chain to the network, nodes can quickly invalidate it by checking whether blocks contain required VDFs.
VDFs are run by full nodes known as Timelords, which are also responsible for issuing challenges to the network. Though there is no monetary reward for running a VDF server, Timelords add redundancy and security to the network. Only one Timelord needs to be running to move the chain forward, and the Chia Company plans to run Timelords to ensure the network’s liveness.
Since each block on the Chia Network blockchain must include both a verified proof-of-space (VDF) and proof-of-time (scanned hash-code closest to challenge hash), Timelords only issue new challenges after the two space-and-time criteria are met.
UTXO Transactional Model
Another notable similarity to Bitcoin is Chia Network’s unspent transaction outputs (UTXO) model, known as the “coin set model.” Each coin represents an allocated amount of unspent XCH that can only be spent following the solving of a cryptographic puzzle.
Unlike in an accounts-based model, anyone can attempt to spend coins on the network, and there is no concept of coin ownership. A person is a coin’s de facto “owner” if they possess a certain public/private key pair for that transaction bundle.
Unlike Bitcoin’s UTXO model, in the coin set model, all transactions within a block occur simultaneously, which deters MEV opportunities like front-running, back-running, and sandwich attacks.
Computation
Chialisp is Chia Network’s native smart contract language. Chialisp is based on Lisp, a 60-year-old programming language that has historically served as the foundation for various expressive language iterations.
Chialisp works in tandem with the CAT2 token standard, which allows developers to build programmable, on-chain assets known as Chia Asset Tokens (CATs). CAT2 is similar to the ERC-20 token standard on the Ethereum Network and can accommodate stablecoins and limited supply tokens. Two notable differences between CATs and ERC-20 tokens are:
- CATs cannot be frozen or confiscated without the owner’s permission.
- Once a CAT has been distributed, it is impossible to change the asset’s functionality across the entire token supply. Attempting to do so would effectively replace the “old” version of the CAT with an entirely new supply of tokens.
Tokenomics and Governance
Tokenomics
Chia Network’s native token Chia (XCH) is used for payments, gas fees, and network security. Farmers earn transaction fees for including mempool transactions in published blocks. If the mempool is not full, however, transactions are not required to include a fee and farmers will only earn the XCH block reward. As of Nov. 14, 2022, the Chia Network only creates blocks that are 50% of the maximum size to prevent network throttling.
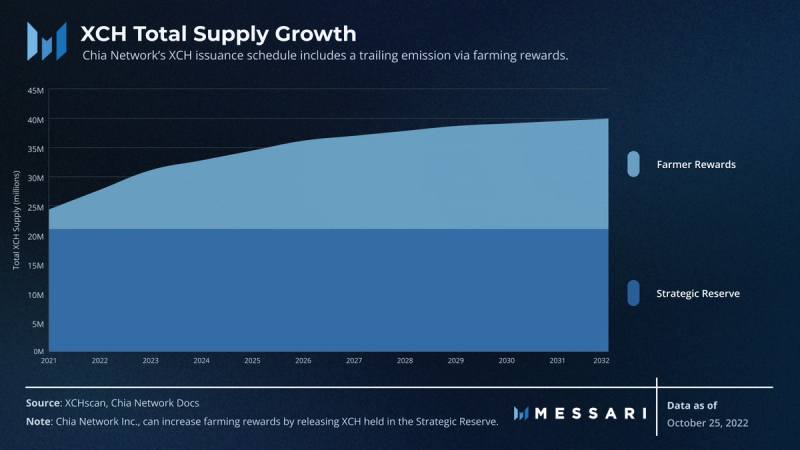
Upon the Chia Network’s Mainnet launch in March 2021, 21 million XCH were minted and allocated to a Strategic Reserve pool controlled by Chia Network Inc. As of Nov. 14, 2022, Chia Network Inc. retains the right to strategically distribute XCH from the Strategic Reserve into the Chia ecosystem. Given the protocol’s low transaction volume, it is possible that reserves could be deployed to attract users to the ecosystem. However, the project team has not expressed explicit plans to do so in the near future.
Additional XCH are minted and distributed via rewards for farmers. Currently, 64 XCH is created every 10 minutes. This amount will halve four times (in 2025, 2028, 2031, and 2033) until it permanently settles at 4 XCH every 10 minutes. Thus, unlike BTC, XCH does not have a fixed supply.
The fixed trailing emission is designed to ensure that the ratio of transaction fees to block rewards stays sufficiently balanced to deter farmers from overwriting blocks for higher rewards. Recent criticisms of Bitcoin’s capped supply have led some developers to suggest a similar trailing emission to be added to Bitcoin, as well.
Chia Network’s emission schedule projects that it will take approximately 21 years from mainnet launch for circulating farming rewards to equal the size of the Chia Network’s Strategic Reserve.
Corporate Governance
As of Nov. 14, 2022, Chia Network Inc. is a private company, but they are planning to go public in the future. The Company has expressed that it will not spend or allocate any of the XCH in the Strategic Reserve until after its transition to a public company. Once public, they will employ the Strategic Reserve for purposes such as:
- Lending XCH to credit-worthy governments, financial institutions, market makers, and enterprises to provide liquidity for Chia-related projects
- Repurchasing shares or distributing dividends to shareholders
- Investing in projects and technologies to promote Chia Network use case
Chia Network Inc. makes the following three assurances regarding its activities:
- The company will not sell XCH from the Strategic Reserve without providing 90-days’ notice to the public. This is enforced by a ruleset built into the Chia Network’s Strategic Reserve wallet, which requires that 90 days elapse after initiating the deployment of XCH from the wallet.
- The Company will not and has not compensated employees or those affiliated with the company with XCH.
- The Company will not fund or conduct XCH farming operations.
Current State of the Chia Network and Ecosystem
Network Activity
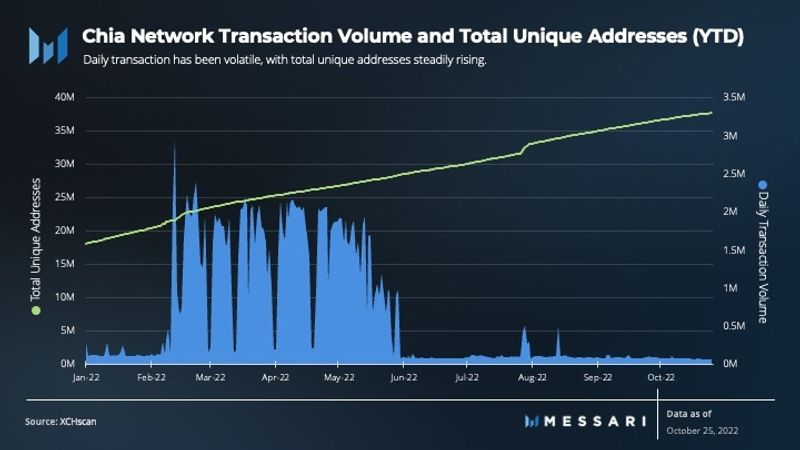
Daily transaction volume throughout 2022 has seen significant volatility. Since June 1, 2022, daily transaction volume has hovered around 90,000 daily transactions, an approximately 97% drawdown from its February high. Volume peaked on Feb. 12, 2022, with just under 3 million transactions, with large peaks and valleys in volume fluctuation up until June. This volatility may have been caused by “dust storms,” in which a user submits a wave of minute coin spends in an attempt to disrupt the network.
The number of unique addresses on the network has steadily risen since May 2021, with an average of about 50,000 new addresses added daily. According to CoinMarketCap, Chia Network’s circulating market cap currently ranks 145th among all cryptocurrencies, which is a significant improvement from its transaction volume peak on Feb. 12, 2022 (187th).
Chia Network currently boasts a L-1-leading 115,000 nodes verifying the Chia blockchain from around the world, including China (~18.5% of nodes), the U.S. (~14% of nodes), Germany (~7.6% of node), Russia (~7.1% of nodes), and others.
Ecosystem
Partnerships and Real-World Use Cases
Chia Network’s ecosystem development has primarily focused on furthering its mission to become a sustainable, compliant financial infrastructure stack. The Chia Network Inc. has achieved this by partnering with projects and organizations driving initiatives to better the planet.
Climate Warehouse: In November 2021, Chia Network announced its partnership with the World Bank’s Climate Warehouse to develop a data-sharing prototype for climate project information. Chia’s solution will connect independent and governmental registry systems to assist countries to meet carbon emission reduction targets. In October 2022, the International Emissions Trading Association (IETA), World Bank, and the government of Singapore announced a joint partnership to work with the Chia Network on a carbon-offset metadata sharing solution.
Tokenized Carbon Credits: This past August, the International Finance Corporation (IFC) announced that it would be partnering with Chia Network on the Carbon Opportunities Fund, a tokenized solution for verified carbon credits. Using Chia Network, the platform will enable a secure and transparent carbon market, while driving capital investment into climate change projects.
Partnership with Costa Rica: Chia announced a Memorandum of Understanding (an agreement between parties) with the Government of Costa Rica in November 2021. With the help of Chia Network Inc.’s technical expertise, Costa Rica is taking the helm on developing an open-source software platform to assist nations in managing climate registry information and carbon credit trading.
DeFi
Users can exchange Chia-native assets on decentralized exchanges (DEXes) such as Hashgreen and dexie. In addition to XCH, these DEXes offer support for CATs such as Stably USD (USDS), a US-dollar pegged stablecoin. Of note, at the time of writing, Hashgreen has had $0 in trading volume in the past 24 hours.
Offerbin is a peer-to-peer exchange that connects Chia Network users with mutual CAT-offer requests. Trading is accessible via Chia light wallet extensions such as Goby.
NFTs
Chia Network’s NFT1 standard allows users to mint, purchase, and sell NFTs on various platforms. According to SpaceScan, the Chia Network has over 330,000 total NFTs across over 1,700 NFT collections.
One of the network’s most popular NFT marketplaces is SkyNFT, which lists over 21,000 NFTs with over 2,846 XCH in volume (~$87,713 as of Nov. 14, 2022). While minting NFTs requires technical experience with Chia Network’s command line interface (CLI), users can curate NFTs using community tools like SkyNFT for a nominal fee.
One of the top Chia Network NFT collections is Chia Friends, which includes over 10,000 animated profile pictures. Chia Friends have been traded over 1,700 times for a total volume of approximately 15,250 XCH (~$470,000 as of Nov. 14, 2022). All on-chain royalties from the project are donated to the Marmot Recovery Foundation, an endangered marmot recovery effort.
Roadmap
Technical Improvements:
Chia Network’s roadmap for Q4 2022 includes technical improvements to transaction scaling, new primitive support, and Chialisp developer tools.
ZK OpCodes: To expand transaction throughput from a maximum of 40 tps to 1,000+ developers plan to implement OpCodes to its virtual machine to facilitate an L-2 smart contract network on top of the main chain. Increased throughput could be accomplished via zero-knowledge proof rollups (ZK rollups). As similar ZK rollup scaling solutions are being developed on Ethereum, Chia hopes to integrate OpCodes to support ZK transactions spent to the mempool from L2s. Additionally, there is potential for a Chia-native version of Lightning using Zero-Knowledge Rollup solutions.
Clawback support: When a user’s wallet is compromised by a malicious actor on any L-1, there is little they can do to recoup the funds. With the network’s proposed Clawback primitive, Chia wallet owners will be able to “rewind” a transaction after it has been settled into a receiving wallet. This is accomplished by providing the sender an additional key that can be used during a short recovery escrow period to correct a bad transaction. As of Nov. 14, 2022, Chia developers have yet to outline how a clawback primitive would affect block finality, however.
Wallet SDK: Chia Network developers are working to build a wallet SDK that makes tracking coin spends easier in decentralized applications (dapps). Developers that want to track Chia coin spends within an application are often required to build one from scratch using Chia Network’s python libraries, a time and resource-intensive process. To streamline wallet integration, rearchitecting core wallet capabilities will support Chialisp plugin features and allow developers to integrate their own graphical user interface (GUI) more easily.
Growth Strategy:
Beyond technical improvements done by the Chia Network developer community, Chia Network Inc. will look to grow its ecosystem and partnerships. In September 2022, the company announced partnerships with Akash Network, a peer-to-peer cloud computing provider, and Evergreen, a Chia plotting hardware producer. This joint initiative seeks to improve Chia Network’s user experience by allowing users to deploy idle storage space more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Chia Network Inc. also plans to go public and list the company’s equity on a national stock exchange. By explicitly delineating equity in Chia Network Inc. from XCH tokens, this will offer greater clarity to regulators around treating the company’s equity trades separate from the commodity application of Chia coins. The Chia Network Inc. team has not publicly disclosed a timeline for going public.
Chia Network Inc.’s go-to-market and revenue strategy will involve:
- Investing in development and services to support the use of XCH, Chialisp, and the issuance of CAT2 assets
- Earning interest on loans to credit-worthy entities, corporations, and developers
- Appreciation of XCH held on the Company’s balance sheet
Opening up the Chia Company to public shareholders will enable users, farmers, and developers to gain exposure to the network’s value appreciation beyond having to hold XCH. Shareholder governance could, for example, lead to Reserve tokens being sold, invested, or distributed via a dividend. Furthermore, the transparency and regulatory assurance that comes with a publicly-traded company may entice investors who would otherwise be deterred by the regulatory uncertainty endemic to other crypto ecosystems.
Summary
Chia Network attempts to straddle multiple fronts in the L-1 competitive landscape, borrowing both tried-and-true frameworks from leading blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum while attempting to mitigate their shortcomings. Chia’s PoST consensus mechanism mirrors Bitcoin’s robust decentralization while requiring less hardware-intensive inputs. Combined with its Chialisp smart transaction language, Chia weds its novel version of the UTXO transaction model with a similar programmability as Ethereum, while side-stepping centralization risks endemic to competing L-1’s running PoS. Competing chains such as Algorand, Cardano, and Solana each have less than 3,000 validators, while Chia maintains approximately 115,000.
Chia has shown signs of adoption through its partnerships with the World Bank, IFC, and Costa Rica. However, Chia Network has a long way to go in terms of increasing its user network effect. The network’s transaction volume has plummeted in recent months, and its NFT volume and DeFi stack have not gained traction compared to other protocols.
By the end of 2022, the Chia Network developer community plans to implement novel tools to attract builders to the network, which could help bolster network activity in the long term. The Chia Network Inc. team spoke with Bloomberg in June 2021 about plans to take the Company public, but there have not been any updates thus far in 2022, with current market conditions adding more uncertainty to the company’s timeline. Nonetheless, Chia Network’s foundational features have earned it recognition as a legitimate L-1 player, and leadership decisions in the works could spur the protocol to mature its standing in the crypto ecosystem.



















