Key Insights
- Axelar is a decentralized network that acts as an overlay network to deliver secure communication between blockchains.
- The Axelar project includes consensus-agnostic protocols, a dynamic validator set, and developer tools for building cross-chain dApps across various blockchains and networks, notably connecting Cosmos to EVM chains.
- The company launched in 2020 and its core offerings include the Cross-chain Gateway Protocol (CCGP), Cross-chain Transfer Protocol (CCTP), APIs, and an SDK, as well as a bridge app, satellite.money, used for transferring assets cross-chain.
- Axelar’s General Message Passing supports any payload cross-chain, going beyond bridged assets with function calls and arbitrary data.
- Circle recently partnered with Axelar to enable composable liquidity with the stablecoin USDC. This partnership is indicative of Axelar’s intention to deliver on use cases beyond cross-chain bridging, including composable liquidity, cross-chain governance, and cross-chain NFTs.
- In 2022, Axelar closed a Series B financing with a $1 billion valuation and launched its AXL token in September.
The current market offers limited options for developers that want to enable cross-chain capabilities across protocols that are built on blockchains with different consensus mechanisms. Blockchain networks like Cosmos and Polkadot built ecosystems of individual blockchains with similar consensus that can be interoperable with each other. However, the market does not offer comprehensive solutions for developers who want to enable one-click interoperability for their users, spanning multiple ecosystems. Axelar fills that market gap as a Web3 overlay network that offers comprehensive resources for developers who want to do just that. The Axelar project offers developers a secure cross-chain communication network accessible via APIs and an SDK. These developer resources are primarily easy-to-use plug-and-play integration solutions, making the protocol a great option for dApps that want to build out quick cross-chain capabilities.
Axelar Enables the Future
Because the Axelar project is consensus agnostic, it can brand itself as “Stripe for Web3 applications.” Axelar’s technology aims to allow more complex cross-chain functions than simply transferring wrapped assets to different blockchains. At its core, Axelar’s General Message Passing (GMP) advances the cross-chain communication of arbitrary data, enabling composable liquidity, cross-chain governance, and cross-chain transfer of assets that cannot be wrapped, such as NFTs.
General Message Passing (GMP)
General Message Passing (GMP) empowers developers building on the source chain to transfer any payload securely, cross-chain. For example, an application can call any function on any other connected chain. Here, any function refers to functions on the application and protocol layer, allowing for a wide range of development possibilities. At the highest level, a function is called from the source chain, the call is verified through Axelar’s DPoS network, and executed via a Gateway on the destination chain.
Composable Liquidity
Composable liquidity refers to the ability for Axelar to allow dApps on connected chains to share liquidity cross-chain. This functionality would have significant implications for many decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. Single-click, cross-chain transactions are a starting point. Further, imagine if multi-chain DEXs could rebalance their liquidity pools on one chain by borrowing asset liquidity on other chains. Such a capability could minimize slippage and impermanent losses. Composable liquidity may also pave the way for new DeFi inventions that progressively take on more risk as protocols feel that they have “backup” or “extra” liquidity on other chains.
Axelar Partners with Circle Finance for Composable Liquidity
Circle recently chose to employ Axelar’s General Message Passing (GMP) to support Circle’s Cross-chain Transfer Protocol (CCTP) for Composable USDC. Circle’s CCTP will mint and burn native USDC to “move” tokens across chains and add General Message Passing to couple those transactions with arbitrary data, such as a function call. This partnership will enable developers to seamlessly integrate cross-chain, native USDC into their dApps. Users will be able to move and swap across multiple blockchains using USDC, transacting in a single click, without wrapping their assets.
USDC plays a critical role in many DeFi protocols. The token exists in the most popular liquidity pools, is widely adopted in crypto-derivatives, and can be employed in the pegging mechanisms of other stablecoins. Composable USDC will empower blockchain ecosystems that do not currently have a reliable native stablecoin, while increasing competition for other native stablecoins.
Gas Services
Many multi-chain interoperability networks require users to maintain gas tokens on both source and destination chains. Axelar, however, allows gas fees to be paid once on the destination chain and with the destination token. Because Axelar is a blockchain connecting blockchains, it can handle smart-contract logic, and Axelar’s gas services conveniently handles all conversions required in the cross-chain transaction flow:
- AXL tokens are paid as fees to Axelar’s validators.
- AXL tokens are converted into the source-chain token for gas.
- The gas covers the action, like token mints or function calls, on the destination chain.
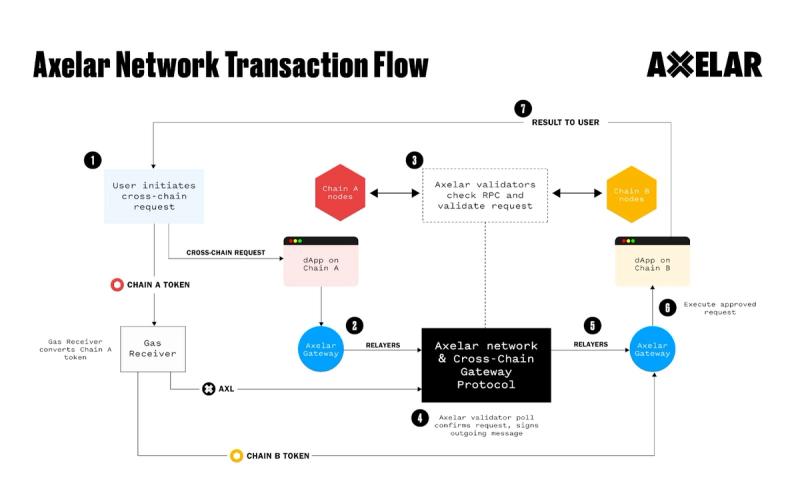
Source: Axelar
Axelar’s Popular Use Cases
Cross-chain Governance
Cross-chain governance allows a multi-chain Web3 protocol to submit a single governance proposal on one chain while the proposal’s result applies to the project’s governance on other chains. For example, a DAO can use Axelar to build on-chain governance that coordinates investments and activities across multiple chains, rather than limiting such decentralized governance to single-ecosystem activities.
Cross-chain NFTs
The implications of cross-chain NFTs go beyond simply recording ownership of an NFT on multiple blockchain networks. For example, cross-chain NFTs allow gamers to use their in-game NFT items on multiple blockchains, which could lead to more complex gaming on multi-chain GameFi platforms. Additionally, with the rise of “NFTFi,” which refers to the growing popularity of NFT lending/borrowing and derivatives, cross-chain NFTs could enable NFTs to be used as collateral for DeFi activities on another chain.
Token Transfers
Axelar’s Gateway smart contracts allow for cross-chain token transfer, which is the most widely used case for Axelar at the moment. Axelar is capable of much more than token transfers, but current market demand for cross-chain bridges is primarily driven by token asset transfers. As of this writing, Axelar has executed almost 300K token transfers with a cumulative volume of around $1.5 billion.
Axelar’s Architecture
The following is a brief summary of how Axelar works.
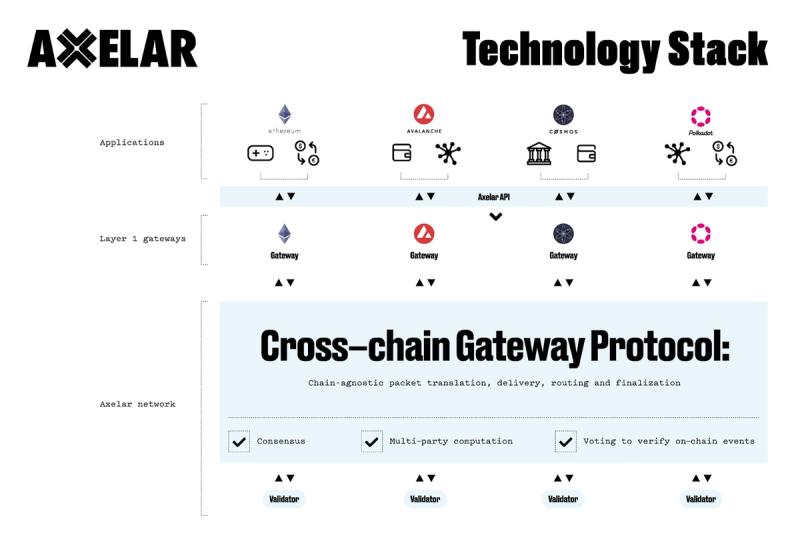
Source: Axelar
Cosmos SDK
Axelar’s Delegated Proof-of-Stake blockchain is built using the Cosmos Software Development Kit (SDK), which is an open-source toolkit with prebuilt modules that enable cross-chain interoperability. Cosmos SDK adopts the Tendermint consensus, which is the model Axelar adopts to validate requests on the source chain and confirm changes on the destination chain. Tendermint consensus provides instant finality and Byzantine fault tolerance. This specific consensus approach is used to verify cross-chain communication, but Axelar is able to connect diverse forms of consensus. For example, Axelar is one of a few cross-chain protocols to connect EVM and Cosmos chains.
Cross-Chain Gateway Protocol (CGP)
Axelar’s Cross-chain Gateway Protocol (CGP), operates like the internet’s Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). A BGP is essentially a relay center designed to securely pass data among internet networks, the way a post office sorts and delivers mail. Axelar’s CGP has two critical functions: state synchronization and asset transfers.
State synchronization is exactly what it sounds like: separate blockchains in different “states” where one blockchain has separate information from another. CGP would synchronize the information so that both blockchains reflect the same information.
Asset transfers refer to bridging assets across various chains. In both situations, a user request is posted via API and assets are deposited in an Axelar Gateway on a source chain. The deposit is validated after a number of validators reach an agreement, and equivalent tokens are minted on the destination blockchain.
Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol (CTP)
Similar to the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) for Web2, the Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol (CTP) is an application-level file transferring mechanism for Web3 that sits atop the CGP. CTP allows dApps to interact with various blockchains, enabling the transfer of assets and arbitrary messages across chains.
Axelar’s Network Security
Axelar’s Consensus Security
Axelar’s network uses a Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism. Axelar’s specific kind of Delegated PoS consensus achieves Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT), allowing up to one-third of validators to fail without compromising the security of the network. Holders of Axelar’s AXL token delegate stake to validators; the top validators by delegation are included in the active set. The number of validators in the active set is determined by on-chain governance, set at 70 validators as of this writing. Axelar keeps the barriers of entry low for validators, encouraging diverse software deployments (Ubuntu, Debian, etc.) and allowing any entity or individual to participate. Each validator would be assigned a weighted voting power based on their stake in the protocol, which they leverage to confirm the accuracy of cross-chain messages (along with other transaction requests) and produce blocks in the chain. The validators are rewarded for their services with newly-minted AXL tokens and transaction fees paid in AXL.
Every PoS consensus mechanism runs the risk of concentrating voting power among a few dominant stakers. Axelar mitigates this stake concentration risk with quadratic voting for its DPoS consensus mechanism. With quadratic voting, voting power does not increase linearly with stake. To increase their voting power, Axelar validators must increase their delegated stake exponentially.
Axelar’s chosen consensus mechanism allows validators to attract delegations from stakers and deposit these as collateral. In practice, on Delegated Proof-of-Stake chains such as Axelar, this discourages validators from acting maliciously. If a validator did act maliciously by misinforming the network, that collateral would be slashed and any lost funds would be paid out through the stake. In other words, Axelar’s DPoS design is inherently an economic model that renders malicious attacks unprofitable.
However, in cases where the collateral (in AXL) and hacked funds are different assets with varying price differences, the malicious actor may still be able to make a profit from the attack. Furthermore, users may not be paid out the full amount of any funds lost in cases where there is a significant difference in the collateral asset’s value versus the value of the hacked funds. These malicious actors may realize that together they could organize an attack that compromises the vote on external events, providing a significant difference in the value of the collateral and the value of the funds to be hacked. They could then proceed to pass through the insurance security layer. However, such an organized attack is unlikely, as it would cause reputational damage to the validator. Axelar validators maintain nodes on connected chains; many are staking and validating on those chains, as well. Such reputational damage would be costly beyond the impact within the Axelar ecosystem.
Enhanced Security Measures
To protect against losses from attacks, Axelar uses rate limits to cap the volume of assets that can be accessed during specified time periods, so the value of the hack could never exceed that specific threshold. The protocol has also built-in the ability to freeze transfers from any particular chain, should it become compromised or malicious. In the event of a total transfer freeze, neither incoming nor outgoing requests are permitted.
Validator security policies (e.g., mandatory key rotations), audits, and bug bounties are also included in the Axelar security approach, to further enhance security.
Axelar’s Tokenomics
The launch of Axelar’s native AXL tokens makes Axelar’s network permissionless, allowing any participant to accumulate delegated stake and participate in securing the network. The token’s primary function is to incentivize tokenholders to delegate stake on the Axelar chain, thus encouraging wider staking/voting power distributions and network security. Axelar’s block explorer and data dashboard, Axelarscan, identifies its network validators and reports real-time voting power distributions. As of this writing, there are 70 validators in the active set. Axelar also has a data dashboard on Metrika, showing block production, block generation, cross-chain activities, and more.
Transaction fees are paid to validators and stakers in AXL, with conversion and payment handled through Axelar ‘s Gas Services. New AXL tokens are minted to reward validators, which increases the total supply and makes AXL an inflationary token. However, AXL token mechanics may become deflationary in some instances, if “change” from Axelar Gas Services is used for buybacks or burns.
One billion AXL were issued at Axelar’s Genesis Block. Investors from the seed, Series A, and Series B rounds are allocated almost 30% of the token supply. 17% of AXL token supply is set aside for the core team, and 12.5% for company operations. Community programs are allocated almost 36% and the community sale accounts for 5% of the total token supply. Percentage breakdowns and vesting schedules are presented in the pie graph below. Release schedules for the team, company, backers, and community programs began three months after the token launch; community sale token release began earlier, on an accelerated schedule. A blog post on Axelar token economics provides full details of release schedules.
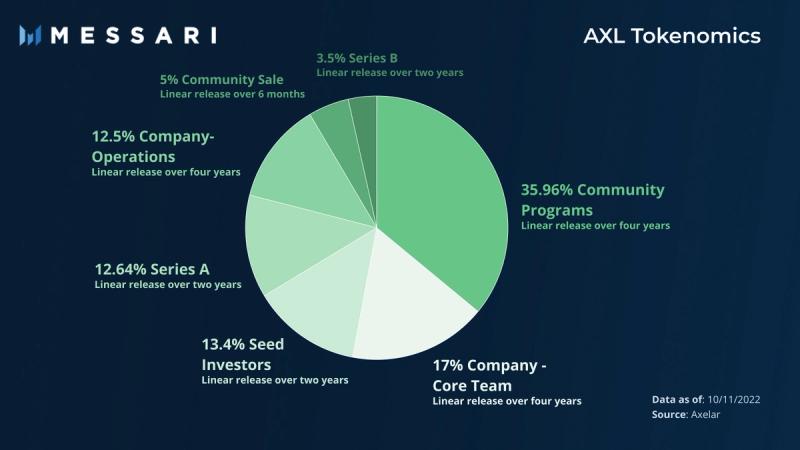
Axelar’s Ecosystem
Traction and Funding
One of Axelar’s main attractions is its ability to connect Cosmos networks with EVM chains. However, it also has the capability to connect with other non-EVM blockchains. Most recently, Axelar announced a partnership with Mysten Labs to provide General Message Passing functionalities on the Sui blockchain. The protocol’s existing and operating mainnet chain integrations number 30 at the time of writing and include Avalanche, BNB Chain, Ethereum, Polkadot, Polygon, and a variety of Cosmos-based chains.
As of this writing, more than 300,000 transactions have passed through Axelar. At this writing, Ethereum, Kujira, Osmosis, and Polygon are the top 30-day source and destination chains; AXL, ETH, and USDC are the top assets.
According to Crunchbase, Axelar raised $63.8 million across 28 investors. On Feb. 15, 2022, Coindesk reported that Axelar raised a total of $35 million in its Series B, raising its valuation to $1 billion. The majority of investors across all three rounds were crypto-native venture capital funds, including Dragonfly Capital, Polychain, Blockchange, Node Capital, North Island Ventures, and more. Polychain Capital also led Axelar’s Series A round, which closed at $25 million. Axelar’s ability to retain its investors across investment rounds (at higher valuations in more matured rounds) and particularly at the beginning of a market cooldown, suggests that the protocol has been successful in meeting strategic objectives.
Governance
AXL holders are also able to vote on proposals suggesting various protocol alterations, from product upgrades to changes in reward distribution and validation parameters. Some of the metrics that are governed by decentralized governance include the AXL gas fee price per transaction and the formula for determining gas fees. Also, Axelar allows its community to vote on technical requirements, including the minimum number of validators any blockchain must meet before being integrated with Axelar.
Final Remarks
The majority of Axelar’s cross-chain messages support token transfers due to the market demand for highly functional cross-chain capabilities. Axelar recently partnered with Circle to enable USDC composability, thereby creating opportunities for protocols to share liquidity across chains and develop novel DeFi applications. Beyond token transfers or composability, Axelar’s cross-chain arbitrary message-passing capabilities could pave the way for new innovations in the blockchain market from cross-chain governance to institutional-grade blockchain solutions. Axelar offers a robust solution, and its team is well-positioned (and well-funded) to pursue new partnerships and applications for cross-chain infrastructure.



















