Key Insights:
- The FTX collapse caused a record-breaking volume of BTC to move from centralized exchanges into self-custodial wallets, leading to a decrease in BTC total exchange balance to levels unseen since April 2018.
- Bitcoin experienced an abnormally low correlation to equities this quarter while realized volatility continued to trend downwards.
- On-chain activity ticked upwards this quarter with active addresses growing 2% QoQ and the number of transactions recorded reaching a new high for 2022, likely attributed to the FTX crisis.
- Numerous public miners filed for bankruptcy or underwent significant restructurings during the quarter as their profit margins continued to be squeezed by the combination of rising hashrate, elevated power prices, and bitcoin’s price falling below the previous cycle high.
- While bitcoin’s price declined by 15% this quarter, numerous market indicators suggest a potential market bottom and a persistence of long-term investor confidence.
Primer on Bitcoin
Bitcoin is the first distributed consensus-based, peer-to-peer payment settlement network. Bitcoin (BTC), the native asset of the Bitcoin blockchain, is the world’s first digital currency without a central bank or administrator. Often referred to as digital gold, bitcoin has a predictable, stable monetary policy that operates autonomously, giving it the ideal store-of-value properties. To secure its network, Bitcoin uses a consensus mechanism known as Proof-of-Work (PoW) to solve the “double-spend problem.” PoW requires participants (miners) to contribute computing power to solve arbitrary mathematical puzzles in order to add a new block to the blockchain. Bitcoin is awarded to the miner who solves the puzzle first, thus minting new bitcoins.
Key Metrics
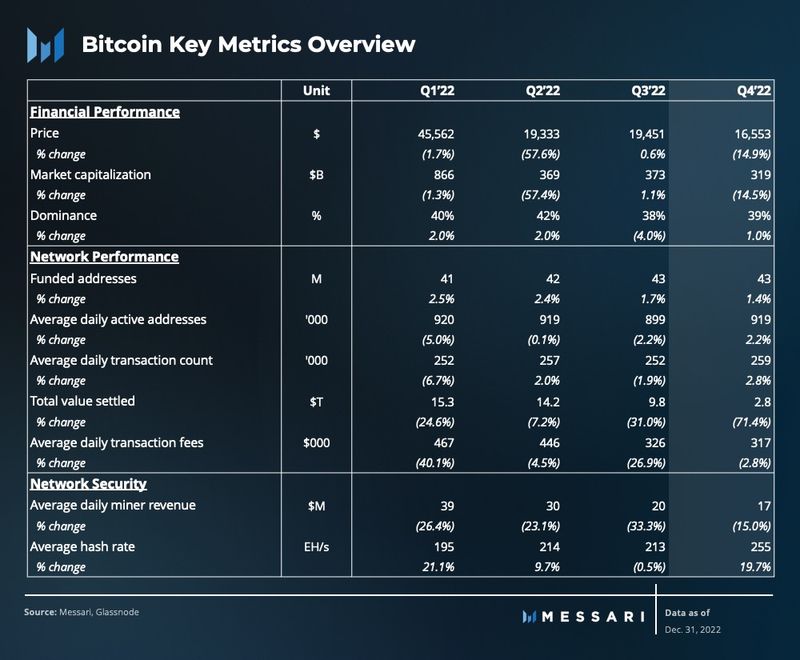
Performance Analysis
Quarter Highlights
2022 proved to be a challenging year for bitcoin. External factors, such as the unfavorable macroeconomic environment and the Terra/LUNA crisis and contagion, impacted bitcoin’s overall performance throughout the year.
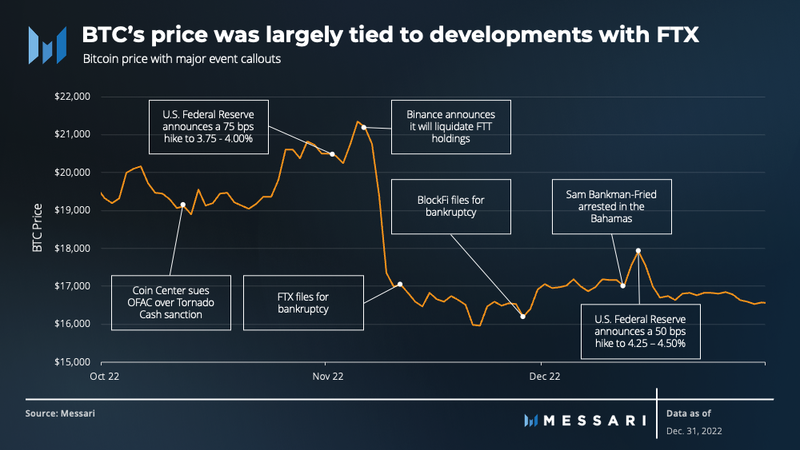
This trend continued into the fourth quarter. Bitcoin’s stability at $20,000 was quickly disrupted by the sudden collapse of FTX, and the market volatility that followed led to an unraveling in bitcoin’s price. It fell 25% in just 4 days, bringing about the bankruptcies of numerous centralized companies. Bitcoin ended the quarter at $16,533, a 15% QoQ decrease.
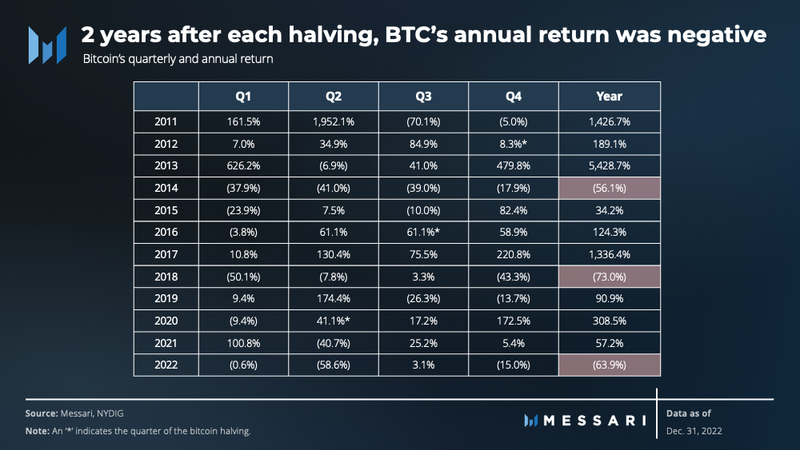
Overall, 2022 was bitcoin’s second-worst year in terms of annual performance, down 64%. Nevertheless, the price performance appears to be following a recurring pattern. As highlighted by NYDIG, bitcoin tends to excessively increase in price followed by a rapid decline approximately every four years, centered on the bitcoin halving event. This pattern occurred in 2014 (-56%), 2018 (-73%), and 2022 (-64%). However, in the fourth quarter, bitcoin strayed from the path of previous cycles as its price dropped below the previous cycle high from 2017.
Market Metrics
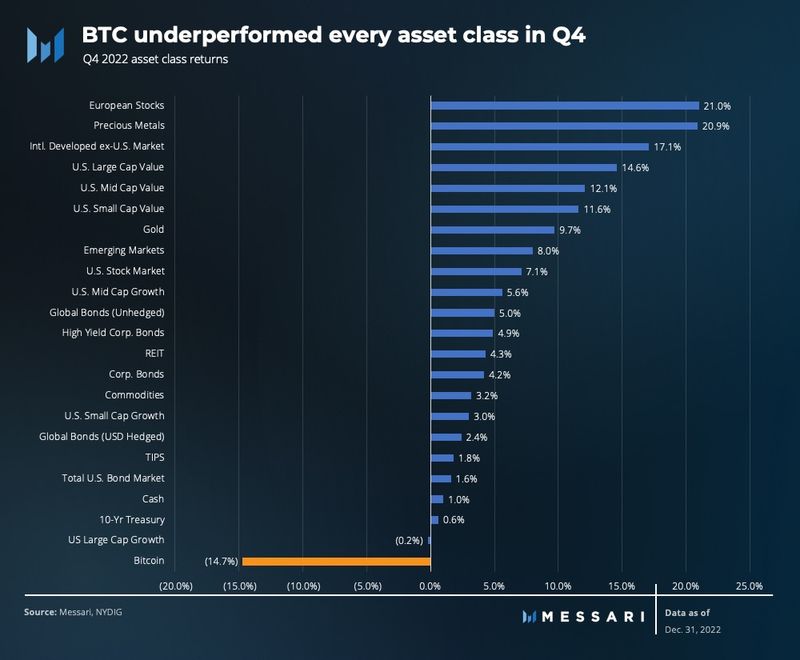
Overall, bitcoin was the worst-performing asset class this quarter. This poor performance can be largely attributed to the panic selling and contagion that followed the FTX collapse. The black swan event was in no way tied to the performance or integrity of the asset’s network.
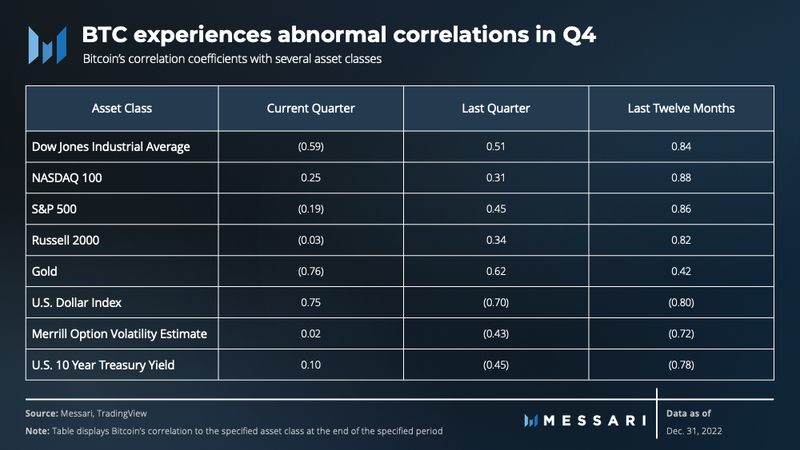
Bitcoin’s correlations were abnormal this quarter relative to Q3 and the last 12 months due to the systematic risk realized by FTX’s collapse. Despite this abnormal behavior, the digital asset maintained a strong positive 12 with the Dow Jones Industrial Average, NASDAQ 100, S&P 500, and Russell 2000 over the last twelve months. Conversely, it maintained a strong negative correlation with the U.S. Dollar Index and 10-Year Treasury Yield over the same period.
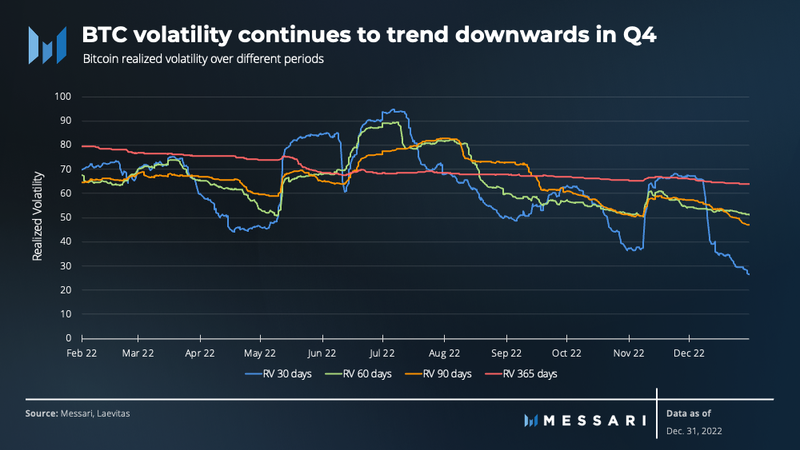
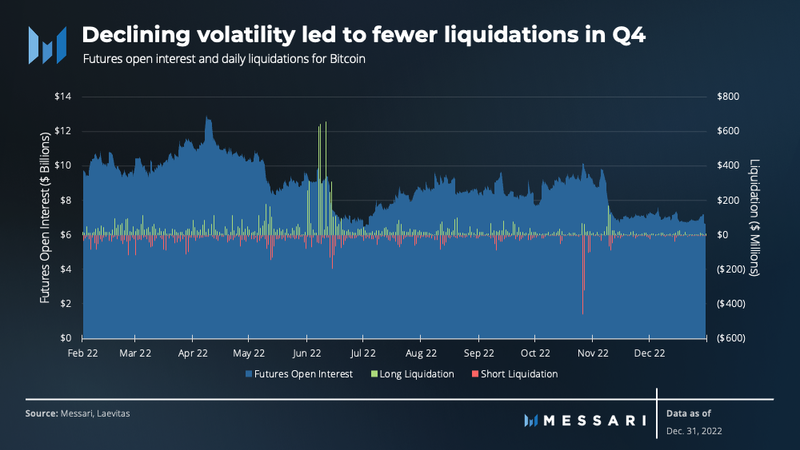
Bitcoin’s realized volatility continued its downward trend from Q3 with a temporary spike around FTX’s bankruptcy. This decline in realized volatility subsequently led to fewer liquidations in the quarter. The exceptions to this trend, outside liquidations surrounding FTX, were short liquidations on October 26 and 27, $460.82 million and $321.67 million, respectively. These liquidations in particular were due to spot prices breaking and holding above $20,000 which initiated a short squeeze. Notably, the second half of the quarter experienced futures open interest near annual lows, indicating a weakening bearish trend.
Network Overview
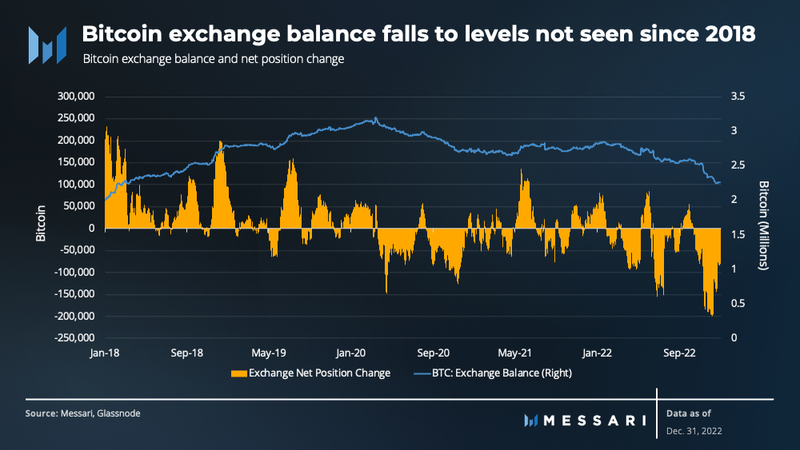
The collapse of FTX resulted in a record-breaking volume of BTC flowing out of centralized exchanges and into self-custody wallets. In Q4, the total amount of BTC held on exchanges decreased by 329,000, reducing the total exchange balance to 2.27 million BTC. This is the lowest exchange balance observed since April 2018 despite the increasing BTC supply.
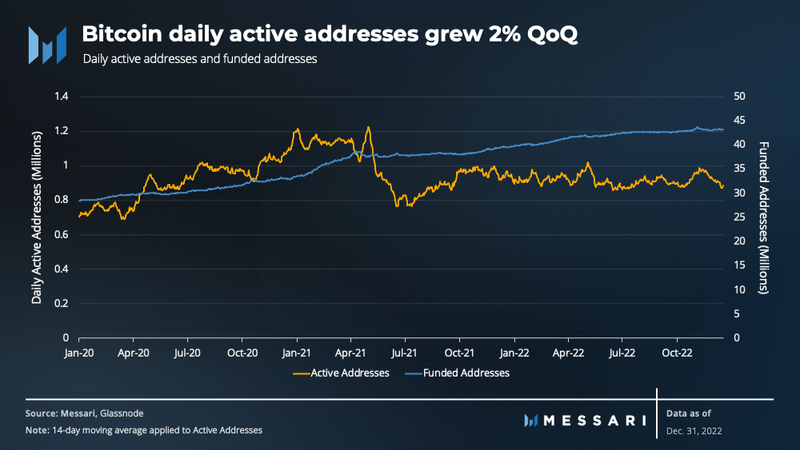
The slowdown in the growth of funded addresses continued in Q4, with the total number reaching 43.3 million, a mere 1% increase from the previous quarter. On the other hand, the daily number of active addresses saw a trend reversal, with a 2% increase after three consecutive quarters of decline. This boost in on-chain activity can be partially attributed to the FTX crisis, which prompted many holders to move their BTC from centralized exchanges to self-custody wallets.
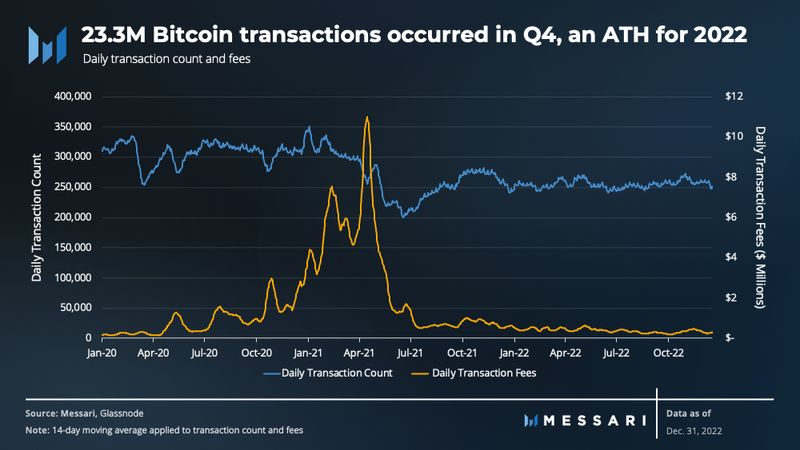
Over 23.3 million transactions were recorded in Q4, marking a new high for the year. On average, there were 259,000 daily transactions, a 3% increase compared to Q3. This rise in transactions can be attributed largely to the FTX crisis. The average daily amount of transaction fees generated dropped by 3% to $317,000.
Mining
Bitcoin miners faced the perfect storm in 2022: Bitcoin’s price dropped 64%, power prices reached their highest points in 41 years, and Bitcoin’s hashrate continued to push higher. These factors placed significant pressure on miner profitability. As a result, several public mining companies, such as Core Scientific and Compute North, were forced to file for bankruptcy, while others underwent major restructuring efforts to remain operational. Despite these challenges, $1.1 billion was raised in distressed mining funds during the second half of 2022 to support struggling miners.
Miners specifically struggled with the 20% increase in hashrate. This increase was mainly caused by the ASIC purchase orders placed in 2021 that were delivered in 2022.
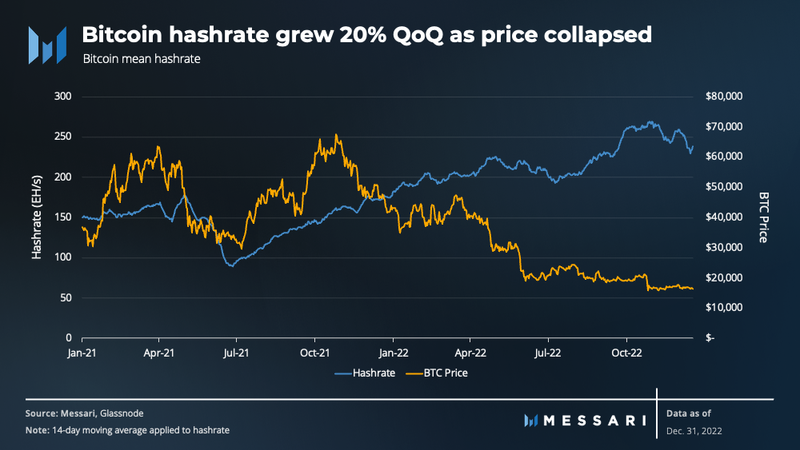
The Ethereum Merge that took place on September 15 is also believed to have played a role in the rise of the hashrate in Q4. With Ethereum mining obsolete, miners previously mining ethereum were likely motivated to switch to mining bitcoin as a way to make use of their existing mining infrastructure, such as industrial rack space and power purchase agreements.
Miner Revenue
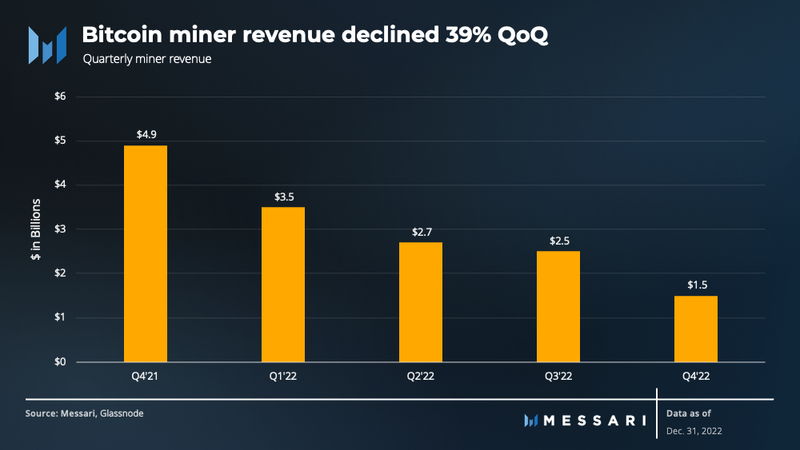
Miner revenue continued to trend downwards in the fourth quarter, declining 39% QoQ to $1.5 billion. Compared to 2021, miners generated $10.2 billion in revenue in 2022, a decrease of 43% that can be directly attributed to bitcoin’s price declining.
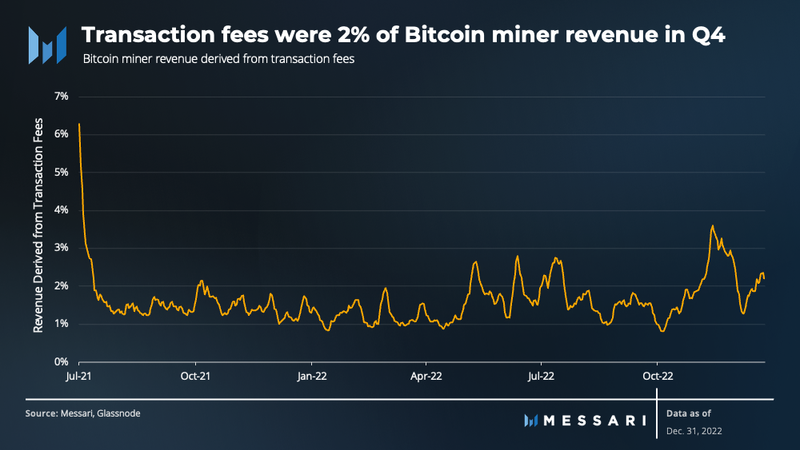
The majority of miner revenue continued to originate from block rewards in Q4, with only 2% coming from transaction fees in Q4. However, this may change in the coming quarters. In January 2023, an NFT protocol on Bitcoin emerged called Ordinals, which was enabled by a design quirk in Taproot and SegWit. As individuals mint NFTs, Bitcoin blocks have been rapidly filling up, driving higher demand for blockspace. As NFTs on Bitcoin increase in popularity, transaction fees are likely to increase, benefiting miners.
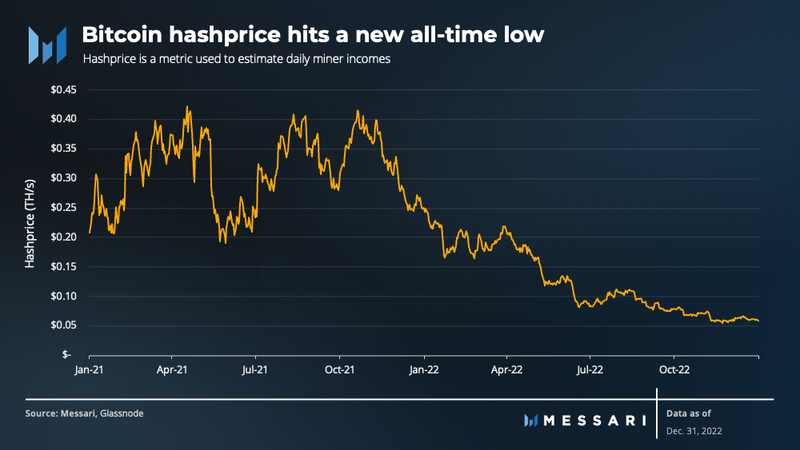
The intensifying competition in the mining landscape, driven by the growth in hashrate, caused the hashprice — a metric to estimate daily miner incomes — to hit a new low in the history of the network. In Q4, the average hashprice was $0.07 per TH/s per day, a 22% decrease from Q3. The average hashprice for 2022 was $0.22, compared to $0.32 in 2021.
Public Miners
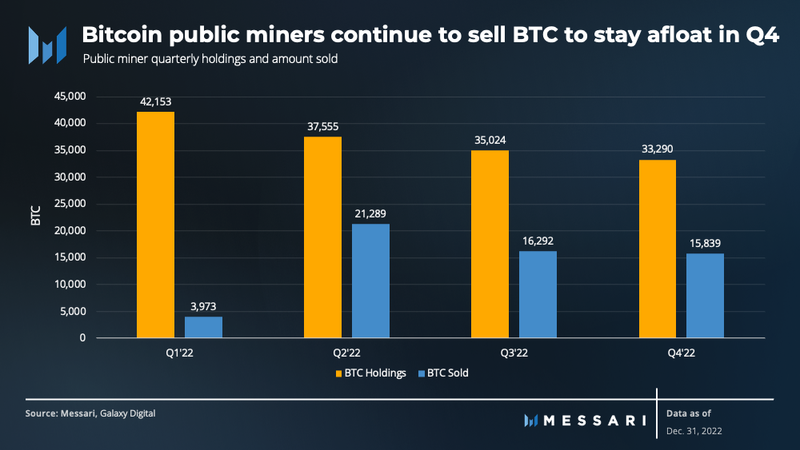
Public miners tend to follow the widespread practice of holding onto the bitcoin they mine, known as the HODL strategy. In 2022, however, this strategy proved less successful than in 2021. Due to the squeezing of miners’ profits, many were forced to sell off their bitcoin holdings in order to stay afloat, which added to the downwards price pressure in the market. In Q4, public miners sold 15,839 BTC, 3% less than the previous quarter. Total public miner holdings decreased 5% over the quarter to 33,290 BTC.
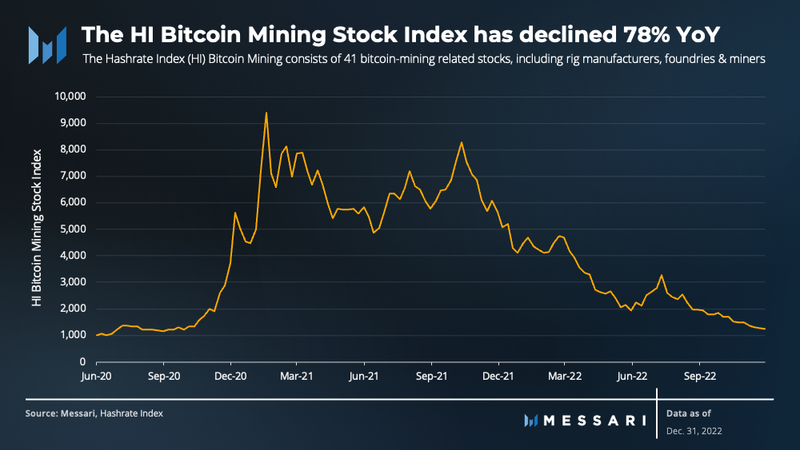
The Hashrate Index (HI) Bitcoin Mining Stock Index consists of 41 bitcoin-mining-related stocks, including rig manufacturers, foundries, and miners. These stocks offer investors high beta exposure to bitcoin. During 2022, the HI index had a daily correlation of 0.96 with the price of bitcoin, resulting in the index declining 78% YoY.
The stock performance of miners was particularly grim, with public mining stocks declining by an average of 91% in 2022. In November 2021, the total market cap of mining stocks was over $30 billion, but it plummeted below $3 billion by the end of 2022.
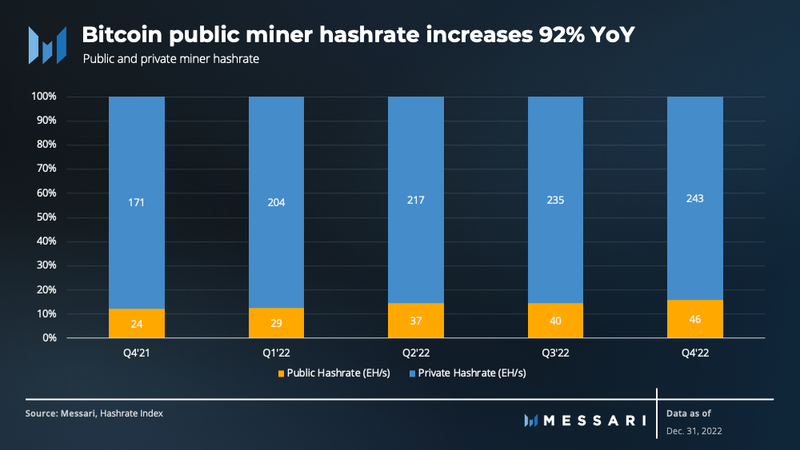
Despite the sharp decline in their valuation, public miners continued to grow their hashrate in Q4 due to the delivery of ASICs they ordered in 2021. By the end of Q4, public miners accounted for 19% of the total network hashrate. Their cumulative hashrate increased 92% over the year, surpassing the 42% increase seen with private miners. This trend shows that hashrate growth is largely driven by public companies.
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a Layer-2 payment channel network anchored to the bitcoin protocol. It increases the network’s throughput while decreasing transaction settlement time. First introduced in 2015, Lightning’s scaling approach has gained popularity over time and is now the de facto scaling solution for bitcoin.
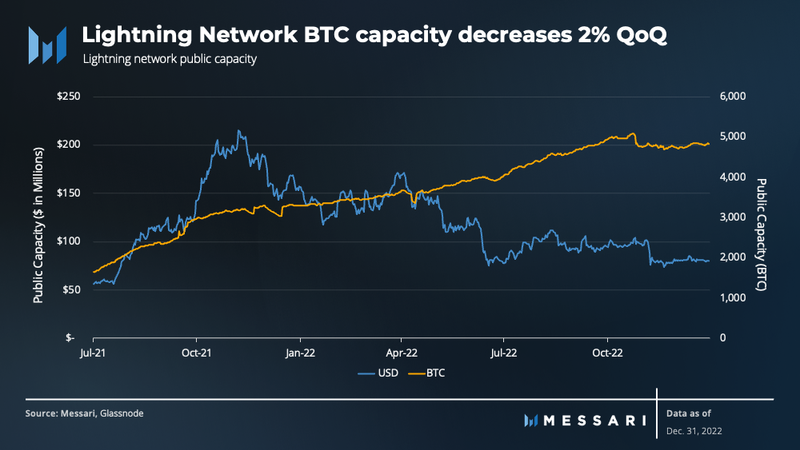
During the fourth quarter, the amount of bitcoin held in public channels on the Lightning Network decreased by 2% after a period of strong growth in the first three quarters of the year. Despite this, the overall annual growth was still 46%.
As the Lightning Network matures, Galaxy Digital predicts that miners may use it to earn interest on their bitcoin while minimizing counterparty risk. Given that miners typically hold a large amount of bitcoin on their balance sheets, becoming Lightning node operators could be a logical next step for them. By operating Lightning nodes, miners could potentially earn up to a 5% annual percentage yield through the leasing of channel liquidity. Not only would this benefit miners, but operating Lightning nodes would also contribute to the overall growth of the Bitcoin ecosystem. For further insights on this topic, we encourage you to read our report on earning yield on bitcoin with Lightning.
Sentiment Analysis
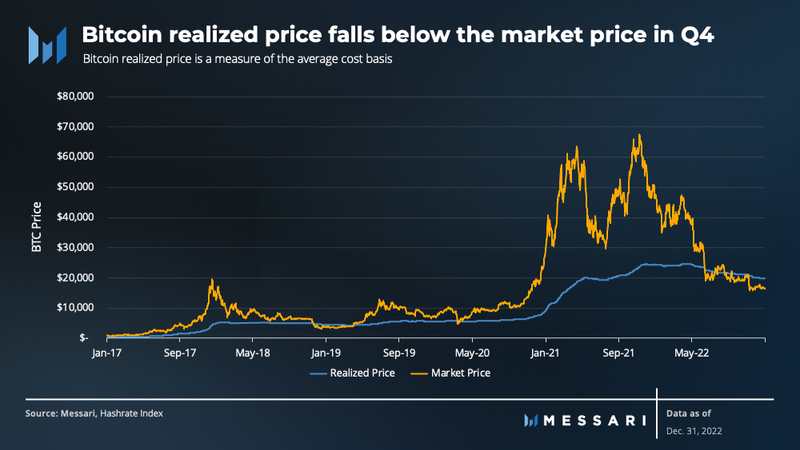
The bitcoin realized price is a measure of the average cost basis for all bitcoin in circulation, providing insights into the market sentiment towards bitcoin. If the market price of BTC is higher than its realized price, then market participants are, on average, in profit. Conversely, if the market price is lower than the realized price, market participants are, on average, holding paper losses.
Between June and November of 2022, the market price of BTC fluctuated around the realized price. However, the significant drop in price in November caused the market price to fall significantly below the realized price, signaling market distress. Historically, such occurrences have coincided with major market bottoms.
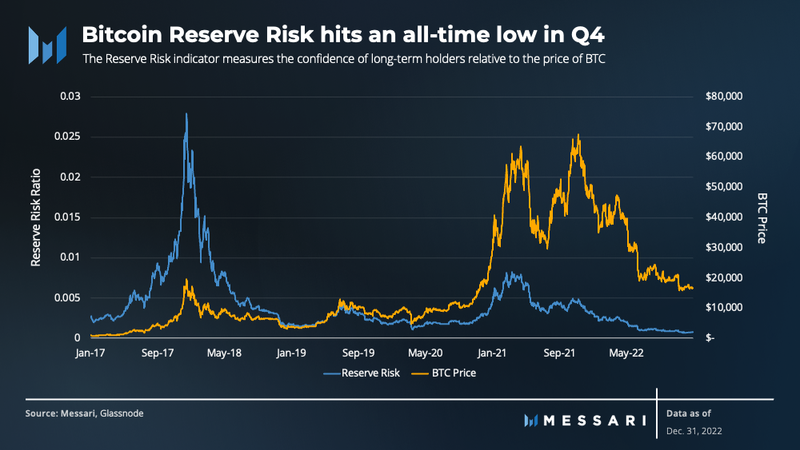
The Reserve Risk indicator measures the confidence of long-term holders (HODLer) relative to the price of bitcoin. A low Reserve Risk means that there is high confidence among HODLers during a period of low market price, creating a favorable risk-reward situation for investors.
During the fourth quarter, the Reserve Risk hit an all-time low, suggesting that bitcoin is undervalued and might be approaching a major cycle bottom.
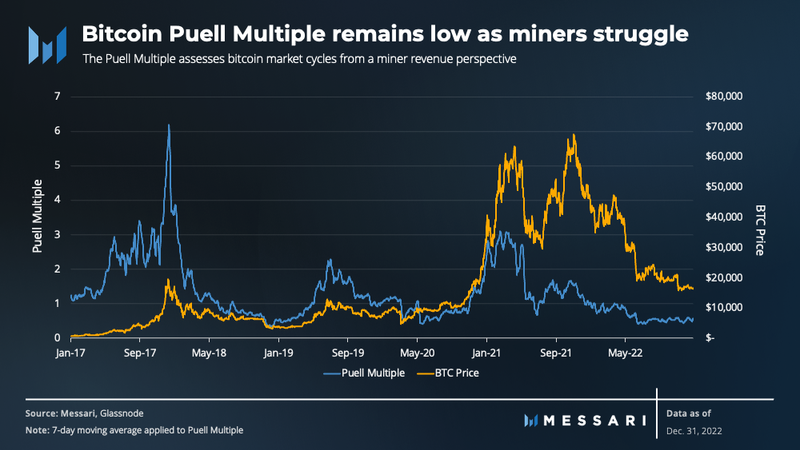
The Puell Multiple assesses bitcoin market cycles from a miner revenue perspective. A high Puell Multiple indicates miner profitability is above average, while a low Puell Multiple signals a difficult time for miners in terms of profitability.
During the second half of 2022, the Puell Multiple remained near historic lows, accompanied by capitulation and bankruptcies amongst miners. However, this period of low Puell Multiples can be beneficial for the market, as it implies that weaker, unsustainable miners are removed from the market.
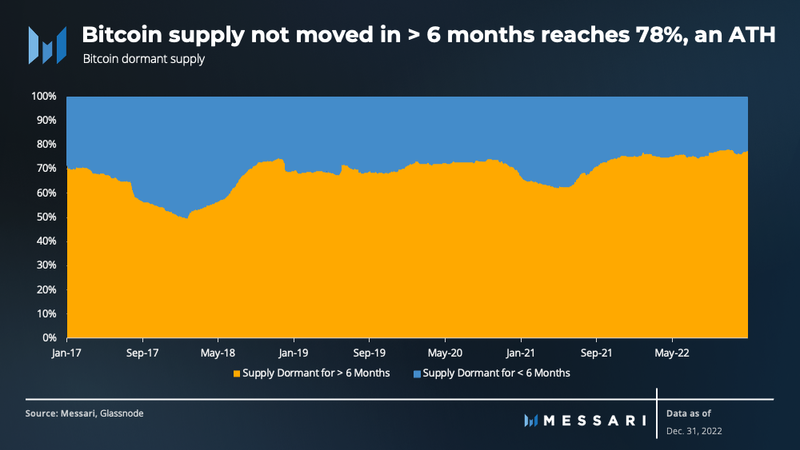
Despite the extreme market volatility experienced this quarter and the price of bitcoin falling below the previous cycle high, HODLer conviction continues to grow. The percentage of circulating coins that haven’t moved on-chain for more than 6 months reached a record high of 78% at the end of the quarter.
Qualitative Analysis
Regulation
Russia
Shortly after the war in Ukraine began in late February 2022, the United States and its allies continued to initiate sanctions targeting Russia’s economy and military–industrial complex. Russia responded to these measures in early October with an announcement from its Ministry of Finance stating it would “allow international settlements in cryptocurrencies for any industries without restrictions.” Two days later, the European Union announced it would be escalating its existing prohibitions on cryptoasset transactions from Russia by banning all cryptoasset wallets, accounts, or custody services, irrespective of the amount. The previous threshold was up to €10,000 per transaction.
Towards the end of the quarter, Russia’s Congressional finance committee chairman Anatoly Aksakov echoed the Ministry of Finance’s intent from October. He clarified that this legalization of transacting in bitcoin and cryptocurrency only applies to foreign trade and not to transactions within the territory of Russia. The chairman added that the legislation is expected to be passed in January 2023.
This legislation was a response to the steep decline in imports and import demand, with exceptions being from India, China, and Turkey. In mid-December 2022, the Financial Times reported that Russian imports have declined by 20-25% since the war in Ukraine began. This decline has lowered real GDP forecasts for 2023 to -4.0% and is expected to set the economy back several years.
Brazil
In other news, Brazil took significant steps towards maturing its blockchain economy this quarter. On November 29, 2022, lawmakers voted in favor of a comprehensive regulatory framework for cryptocurrency brokerages and the use of cryptocurrencies. Former President Bolsonaro signed the bill into law less than a month later, setting an effective date of June 20, 2023. The law defines crypto as the digital representation of an asset that can be traded, transferred, and used for payments or investments.
The law requires brokerages to abide by anti-money laundering best practices. They should prevent the concealment of assets, the financing of terrorist or criminal organizations, and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. These companies are also required to obtain explicit authorization from the federal government before operating in the country. Additionally, regulatory clarity is expected to come from the Central Bank of Brazil regarding payments and the Securities and Exchange Commission of Brazil in terms of investing activities.
U.S. Legislation
U.S. Senators Warren (D-MA) and Marshall (R-KS) proposed a bill on Dec. 14, 2022, titled “Digital Asset Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2022.” The bill requires custodial and self-custodial wallet providers, digital asset kiosk operators (i.e., bitcoin ATMs), and miners to implement know-your-customer (KYC) procedures. This requirement is due to their proposed designation as “money service businesses.” Additionally, it prohibits financial institutions from interacting with digital asset mixers, privacy coins, and other anonymity-enhancing technologies, as specified by the Treasury Secretary. This includes any digital assets that have been anonymized through technological means.
To enforce this rulemaking, the bill charges the Department of Treasury, SEC, and CFTC with the examination and review of entities under their jurisdiction no later than 2 years post-enactment. This enforcement is focused on anti-money laundering programs and reporting as well as compliance with anti-money laundering and requirements to counter the financing of terrorism.
The non-profit research and advocacy center Coin Center argues that the bill would face constitutional scrutiny if passed. It cites the First and Fourth Amendments as potential areas of violation since the bill would impede anonymous payments or messages essential to effective political assembly and expression. Moreover, it would deputize software developers and miners to collect and report private information without a warrant. The bill joins a growing list of proposed legislation in 2022 including the Digital Commodities Consumer Protection Act, the Responsible Financial Innovation Act, and the Stablecoin TRUST Act.
ESG
Q3 established a narrative of cryptocurrencies, particularly bitcoin, producing negative environmental impacts, which maintained its momentum going into Q4. The European Union announced in a draft proposal that it would be working with international partners to create a grading measure to encourage more environmentally friendly consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake. Additionally, the EU plans to produce a report that will evaluate the climate impact of the crypto mining industry by 2025 while encouraging member nations to cease tax breaks for miners.
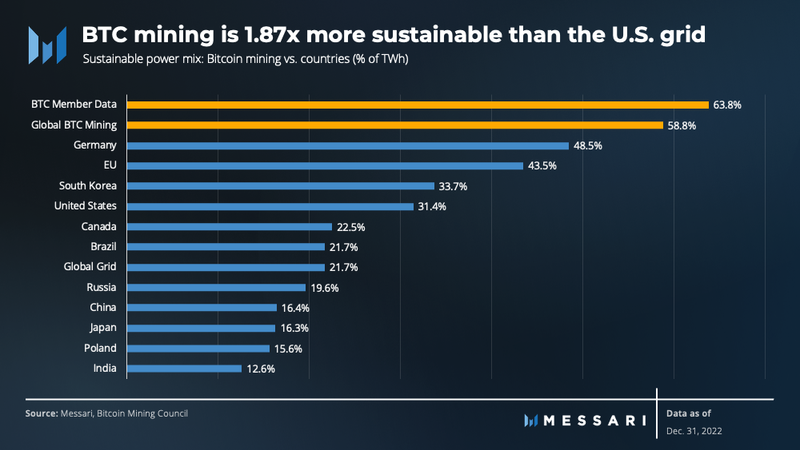
Industry participants recognize the potential for regulatory headwinds and have continued to implement sustainable energy. The Bitcoin Mining Council (BMC), a global forum of miners consisting of 54 mining companies across six continents, recently presented its Q4 2022 briefing. It reports that members’ sustainable power mix stands at 63.8% for the quarter versus the global Bitcoin network’s 58.9%. Over the last 12 months, the global Bitcoin network’s sustainable power mix has remained just below 60% (Note: The council’s reports are sourced by self-reporting).
As the BMC continues to utilize renewable energy, a few novel energy sources made headlines.
- The capture and elimination of methane emissions from landfills — Vespene Energy deploys self-sustaining microgrids to landfills of any size regardless of location which has been further incentivized by mining.
- The plasma gasification process — XcelPlus disposes of various waste types while producing fuel for clean mining.
- Surplus grid energy — Utility companies like the Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) are utilizing surplus grid energy to power their own mining operations.
To further incentivize renewable energy usage, Sustainable Bitcoin Protocol has created the Sustainable Bitcoin Certificate (SBC) an appreciable digital asset tied to verified clean energy use. SBC seeks to support institutional investors of bitcoin with ESG mandates, incentivize miner adoption of renewable energy, and reduce CO2 emissions.
The SBC process is as follows: miners verify their clean energy use, receive SBC for every bitcoin mined, and sell their SBC to buyers who wish to support sustainable mining. All the while, the protocol transparently records each SBC minted and ensures miners are following generally accepted renewable energy practices.
Protocol and Ecosystem Development
Despite the macroeconomic headwinds and FTX’s alleged embezzlement scheme, many developments were realized this quarter:
- Bitcoin Core 24.0 was released which notably included a replace-by-fee feature for transactions. Replace-by-fee allows senders to expedite their transactions by replacing an unconfirmed transaction in the mempool with one that has a higher transaction fee.
- Trezor hardware wallets enabled P2P transactions with trading platform Hodl Hodl.
- Stacks published its whitepaper for Stacks Bitcoin (sBTC) a smart contract digital asset backed 1:1 by BTC. The whitepaper claims this pegged asset will bring smart contracts to Bitcoin.
- Crypto Garage executed the first successful discrete log contract on the Lightning network. Discrete log contracts are transactions that execute smart contracts with data provided by an oracle.
Sustainable Bitcoin Protocol’s beta went live. It completed the world’s first end-to-end transaction monetizing clean energy bitcoin mining with bitcoin miner CleanSpark [CLSK].
Key Events
October
- Plan B Foundation onboards multiple businesses in Lugano, SZ, to accept BTC.
- Visa and FTX launch BTC debit cards in 40 countries.
- Google to accept BTC and crypto for cloud services in Coinbase partnership.
- BNY Mellon offers BTC custody services.
- 21Shares launches the Middle East’s first spot BTC ETP.
- Kazakhstan to establish legal framework for BTC and crypto.
- Hong Kong announces to legalize retail BTC trading.
November
- Fidelity debuts retail BTC trading accounts.
- U.S. DOJ seizes over $3.36 billion in BTC tied to Silk Road.
December
- Microstrategy announces launch of BTC lighting solutions in 2023.
- Microstrategy adds 2,500 BTC to holdings despite tax-loss harvesting.
- Hong Kong stock exchange’s first BTC futures ETF received $53 million in initial investment.
- Japan’s largest power company begins mining bitcoin.
Closing Summary
Despite the challenges Bitcoin faced in the fourth quarter, there were still some notable positive developments. Q4’s positive indicators include the movement of large amounts of bitcoin from centralized exchanges to self-custodial wallets, the growth of daily active addresses and transactions, and continued advancements in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
While bitcoin’s price declined by 15%, numerous market indicators suggest a potential market bottom and a persistence of long-term investor confidence. Although the hype surrounding bitcoin has diminished, the network has historically experienced a resurgence in popularity after periods of doubt.



















