Venus Protocol is a decentralized money market protocol for lending and borrowing cryptocurrencies. It provides low-cost, fast transactions and allows users to take out loans with fast issuance and no credit check.
Unlike centralized lenders, such as BlockFi and Celsius —who declared bankruptcy and froze user withdrawals in 2022—users don’t need to sign up with the typical CeFi log-in credentials; Venus Protocol users connect crypto wallets like MetaMask.
The following guide explores the Venus Protocol in-depth, but if you’re looking for the best alternative centralized crypto lenders, check out these 5 crypto interest accounts that could fill the void left by Celsius.
What is Venus Protocol?
Venus is the second-largest lending protocol in the BNB Chain —only topped by accounting for roughly 30% of the total market share in terms of total value locked (TVL).
As of December 2022, the protocol has lent over $450 million in assets, and its TVL has been floating north of $700 million since mid-2022.
Venus Protocol’s standout advertised features include:
- Lending and borrowing loans in a matter of seconds
- Staking and earning rewards in crypto, up to 20%
- Liquidity pools offering up to 30% APY
- Mint synthetic stablecoins
- Participate in the community DAO
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency, and especially DeFi protocols like Venus Protocol are very risky. The following article is not and should not be considered a substitute for investment advice.
How Does Venus Protocol Work?
Venus was built exclusively for the BNB Chain (formerly known as the Binance Smart Chain (BSC)), therefore its native currency, XVS, uses the BEP-20 standard.
Venus supports multiple types of cryptocurrencies and stablecoins that can be used as collateral to borrow from the protocol’s pools or earn rewards by becoming a liquidity provider.
How to Borrow on Venus Protocol
Loans are over-collateralized, meaning users who wish to borrow must pledge collateral with a ratio depending on the current governance proposal, but they usually range from 50% to 70%. So, to hypothetically borrow $10,000, you’d need to post $15,000 of collateral, for example.
This collateral is then locked in a Venus Protocol smart contract for a specified period.
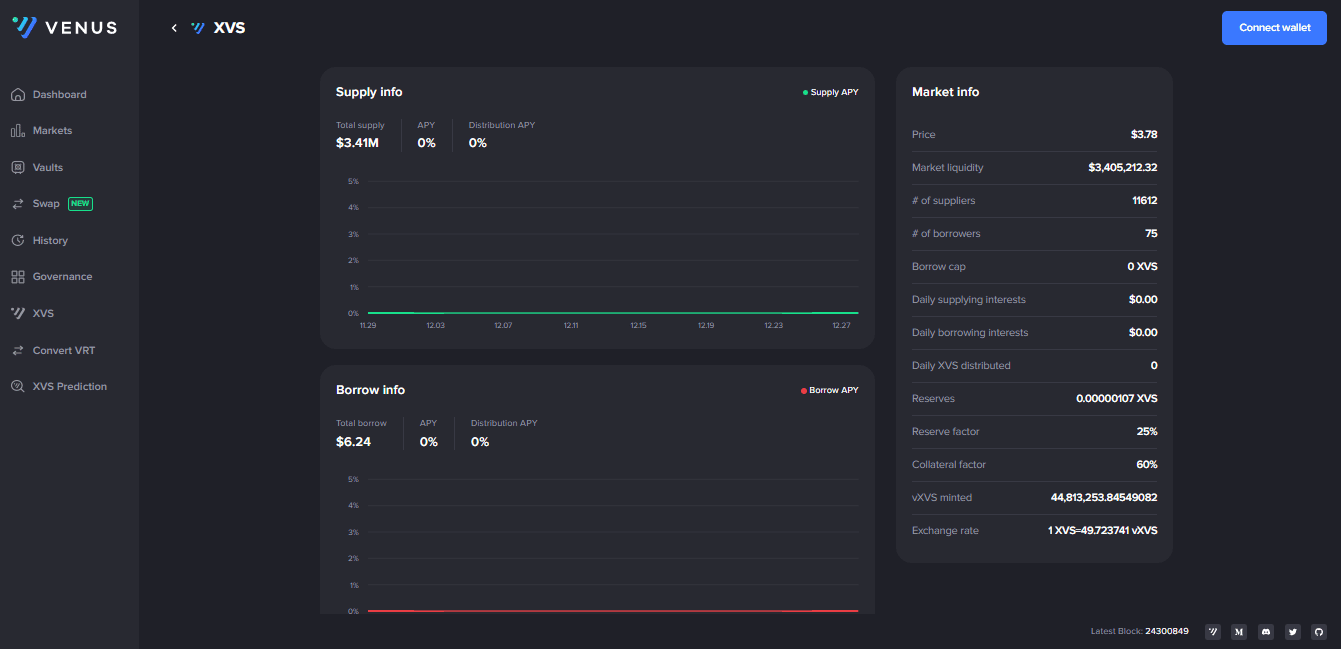
In the Market section, choose an asset, and you’ll be able to see the collateral factor (as well as market liquidity, number of suppliers and borrowers, APY, and more.)
Lending on Venus
Users can lend assets to Venus to earn yield, which varies on the type of asset.When a user loans cryptocurrencies to Venus, the funds are added to the lending pools. In exchange, depositors receive vTokens (for example, deposited BUSD becomes vBUSD).
Users can redeem these tokens for the underlying token.
Minting Stablecoins
Users can mint VAI, a synthetic stablecoin fixed at 1 USD (price will still fluctuate depending on market demand). This asset can be used for yield farming on other DEXs in the BNB ecosystem. Users can mint VAI using up to 50% of the remaining collateral value from previous vToken deposits.
The interest rates of VAI have yet to be determined (they are known as stability fees in other lending protocols like MakerDAO), so it depends on Governance and what the new V4 upgrade will bring.
Venus Protocol: History & Founders
The project was developed by Swipe, a cryptocurrency credit card issuer, officially launch in 2020. The team delegated control to the XVS community holders. Since then, multiple proposals have been submitted and put forward to change, upgrade and improve the Venus protocol.
Venus was born as a fork of Compound (COMP), a popular crypto lender built on the Ethereum network, and also took some inspiration from MarkerDAO. The protocol is essentially a mix of the two systems and their respective benefits. It was also audited by blockchain security firm CertiK in December 2020.
The team didn’t run a pre-mine for founders or the community. The only way to earn XVS was through the Binance LaunchPool project or by providing liquidity to the protocol during the early days.
Venus V4 Release
In November 2022, the Venus DAO unveiled its V4 upgrade after months of discussions. The upgrade seeks to enhance the network in three key areas:
- Risk management.
- Isolated markets: introduce new tokens of all kinds but pooled into their respective, separate lending pools. This has two significant benefits: 1) it protects users and the ecosystem from disaster since they are essentially segregating assets with potential risk into isolated pools; 2) it allows users to pick which pools to participate depending on their appetite for risk.
-
- Stable interest rate borrowing: a mechanism that will set stable interest rates for loans across all markets.
-
- Better risk management mechanisms: will provide a mechanism that will provide shortfall coverage for users, and a stability fee to keep VAI pegged to USD. This is especially important, as in 2021, VAI lost is peg due to oversupply and experienced a massive market sell-off.
- Decentralization
- Improved governance system: new governance roles have been assigned, longer intervals for contract upgrades and role reassignments,
-
- Price Feed Redundancy: allows Venus to support multiple blockchain oracles to avoid single points of failure.
- User experience:
- Partnership with DEXs: Venus has partnered with multiple DEXs in the BNB ecosystem, including PancakeSwap, to allow users to freely move funds between multiple protocols without leaving Venus. This makes Venus a DEX in which borrowing, lending, and swaps across multiple DEXs happen in a single UI.
- New tokenomics:
- Tokenomics 3.0: will bring new financial mechanisms to incentivize protocol retention. XVS becomes the core utility token, XVS emissions are cut, value is reinvested, and shortfall defense is added.
-
- The protocol will introduce the Venus Prime Soulbound Token (SBT), which users can earn if they stake a minimum of 1,000 tokens for 90 days in the Venus vault. The benefits of SBT are that it provides users with exclusive access to better yield across different markets, and dividends can be paid out in the supplied currency.
Venus Protocol: Tokenomics
XVS is the protocol’s utility token based on the BEP-20 token standard. XVS’s main uses cases are:
- Staking
- Voting
- Pay for transaction fees
The token has a max supply of 29 million tokens and a circulating supply of 12 million (or 41% of the total supply.)
XVS & Venus Governance
The Venus community runs a simple governance system: delegated and direct on-chain voting, where 1 XVS token = 1 vote. Whenever a protocol proposal is submitted through a Venus Improvement Proposal (VIP (similar to Ethereum’s EIP)), users can vote directly or delegate their voting rights to another user.
Proposals cost 300,000 XVS, which currently amounts to nearly $1 million. Once proposed, voting is active for three days. To be approved, the proposal must reach a voting quorum of 600,000 XVS. If successful, the proposal is timelocked for two days before implementation.
Final Thoughts: Future of Venus Protocol)
Venus Protocol has a TVL of $710 million, currently boasting $1 billion in liquidity as per its website and has borrowed over $450 million since its relatively short time in the industry.
Despite these numbers, Venus Protocol doesn’t really attract the same attention as platforms like PancakeSwap. Still, the protocol has managed to thrive along with the DeFi ecosystem, and the V4 upgrade brings better tokenomics, more risk management tools such as isolated pools, and an improved governance system to solidify decentralization.
The post What is Venus Protocol? appeared first on CoinCentral.