Key Insights
- Weekly NFT sales volume increased 131% QoQ to $20 million. This surge was primarily attributed to DraftKings’ Reignmaker NFT collection, which became the top collection on Polygon PoS.
- Immutable was the first to deploy a chain on testnet using the Polygon CDK. Following this, Astar Network and Canto’s core developers announced plans to develop zkEVM L2s with Polygon CDK.
- The POL token, an upgrade to the MATIC token, was activated on mainnet. POL will allow holders to contribute to network security across various chains in the Polygon ecosystem via a native re-staking protocol and features an inflationary model with an annual emission rate subject to community governance.
- Daily active addresses increased 1.4% QoQ to 364,000. The DeFi sector accounts for the majority of active addresses on the Polygon network.
- Polygon zkEVM reported an average of 44,000 daily transactions (+123% QoQ).
Primer on Polygon
Polygon Labs is a software company that develops Zero-Knowledge (ZK) scaling solutions for Ethereum, including Polygon Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network, Polygon zkEVM, and Polygon Miden. Announced this year, the Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK) is a collection of open source software components that makes it easy for developers to design and launch ZK-powered L2s on Ethereum.
In June 2023, Polygon Labs unveiled Polygon 2.0, a series of proposed upgrades to the Polygon ecosystem that aims to unify all Polygon protocols and blockchains using ZK-technology. As a part of the Polygon 2.0 roadmap, the Polygon PoS network will be upgraded to a zkEVM Validium network that shares security with Ethereum. Polygon 2.0 aims to become the “Value Layer of the Internet” and brings significant updates to protocol architecture, tokenomics, and governance. Polygon 2.0 is the future of the Polygon ecosystem.
Key Metrics
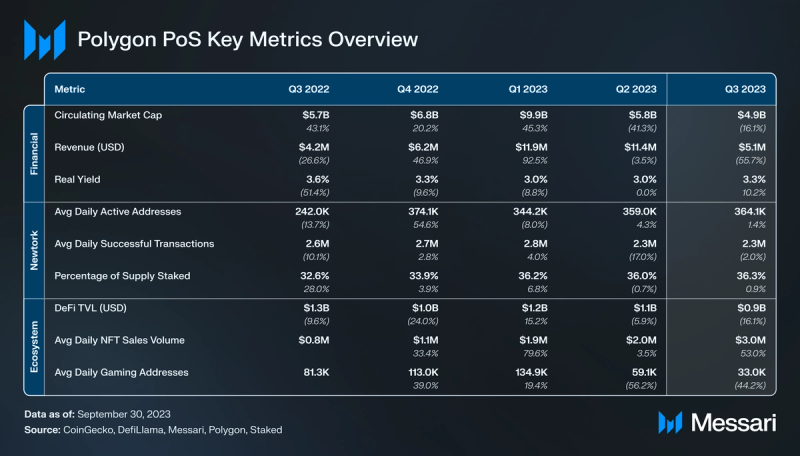
Financial Analysis
Market Capitalization
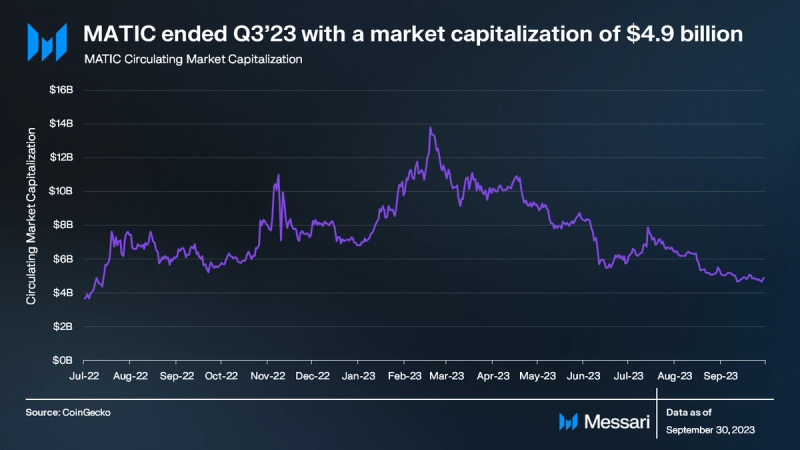
In Q3 2023, despite favorable court rulings for XRP and Grayscale, the overall crypto market experienced a moderate downturn. The total crypto market capitalization decreased by 5.8%, while BTC and ETH fell by 7.5% and 10.0%, respectively. MATIC’s market capitalization declined by 16% QoQ, closing at $4.9 billion, making it the 14th largest crypto token by market cap.
Revenue
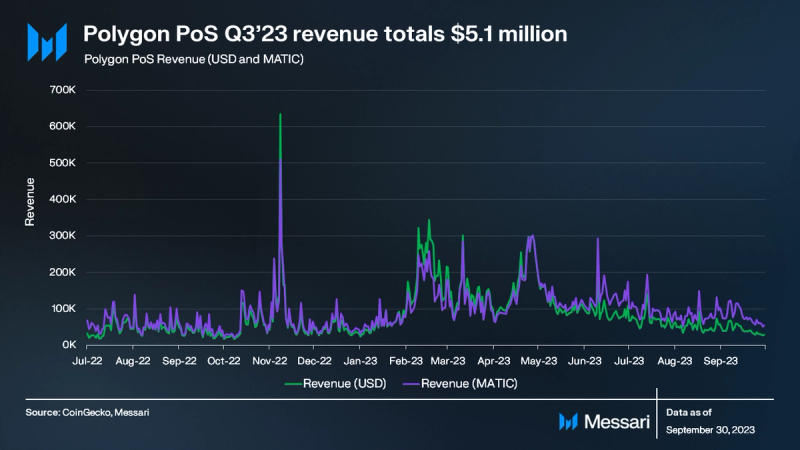
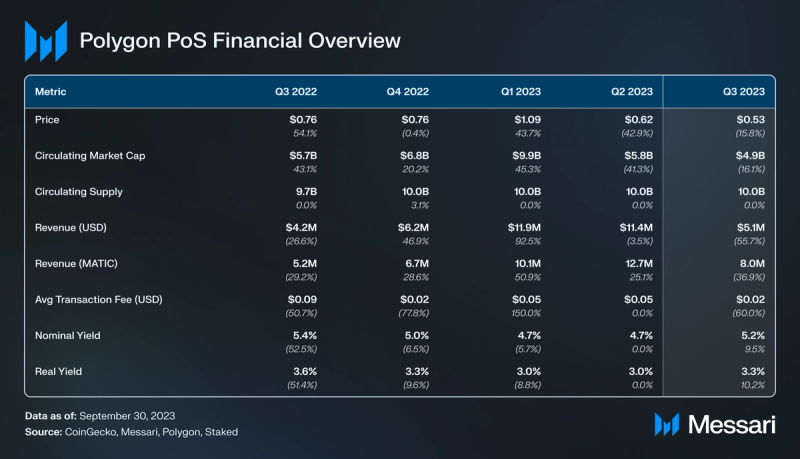
In Q3 ’23, Polygon PoS’s revenue declined by 56% QoQ to $5.1 million in USD terms and by 37% QoQ to 8.0 million MATIC. The primary factor behind the USD revenue drop was a 60% QoQ decline in the average transaction fee, going from $0.05 to $0.02. This reduction in the average transaction fee was attributed to a decrease in MATIC’s price and network transactions (-1.5% QoQ).
Polygon PoS follows EIP-1559, which burns a portion of every network transaction fee paid in native MATIC. The “base fee,” a fluctuating portion of the gas fee, is burned, while the remaining fee is distributed to the block’s proposing validator. To date, 25 million MATIC have been burned.
Supply
In Q3 ’23, MATIC remained the primary token within the Polygon ecosystem, serving functions including network fees, staking, and governance. It adheres to the EIP-1559 standard and has reached full vesting.
As part of the Polygon 2.0 upgrade, MATIC is expected to be phased out in favor of POL, an upgrade to MATIC. POL will enable its holders to contribute to network security on various chains in the Polygon ecosystem via a native re-staking protocol, earning rewards for diverse services. These services range from basic transaction validations to more advanced tasks like generating ZK-validity proofs. Each individual chain in the Polygon ecosystem can offer customized roles and rewards for its validators. Validators can choose to validate multiple chains at once to compound their rewards in a similar manner to EigenLayer’s restaking offering on Ethereum.
POL adopts an inflationary model with a yearly emission rate subject to community governance to incentivize validator participation and fund a community-governed treasury.
During Q3, the Polygon Labs team unveiled three Polygon Improvement Proposals for community consideration: PIP-17, PIP-18, and PIP-19. PIP-17 details the POL token and its relevant contracts. PIP-18 introduces the inaugural phase of the Polygon 2.0 upgrade. PIP-19 suggests transitioning the primary gas token on Polygon PoS from MATIC to POL, emphasizing an upgrade to the PoS Plasma Bridge Contract to facilitate the token transition. On October 25th, the POL contract was deployed on mainnet.
Network Analysis
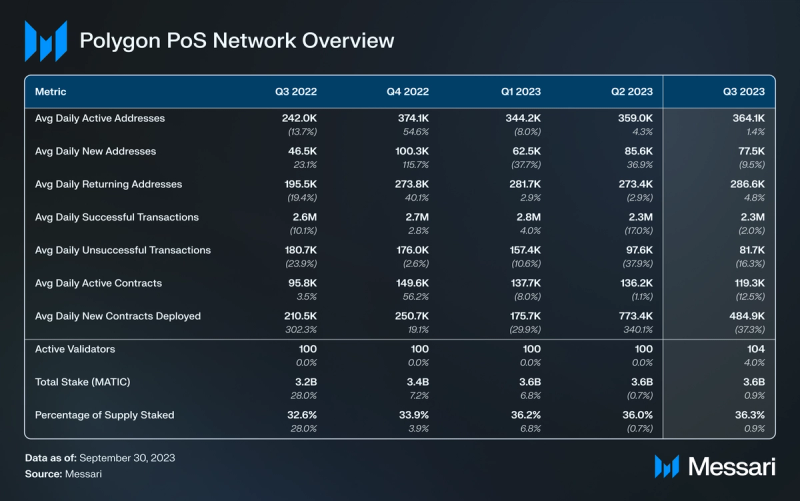
Usage
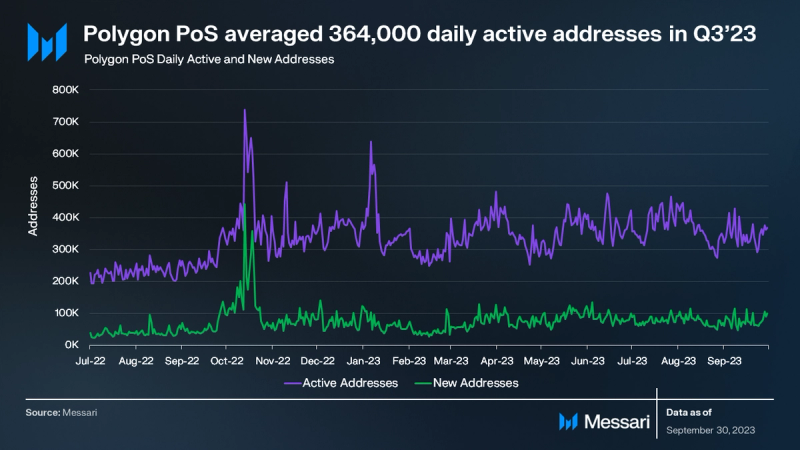
During Q3, Polygon PoS recorded 364,000 daily active addresses, representing a 1.4% QoQ growth. In parallel, the number of new addresses on Polygon PoS averaged 78,000, indicating a 9.5% QoQ decline.
For Q1 ’23, the gaming sector constituted 57% of Polygon PoS’s active addresses. However, by Q3 ’23, this percentage had decreased to 24%, with the reduction ascribed to Planet IX. In Q3 ’23, the DeFi sector led Polygon PoS in active address, capturing 57%. Trailing behind were NFTs with 10% and Social at 9%.

Transactions on Polygon PoS have been stable over the last year. In Q3 ‘23, Polygon averaged 2.3 million daily successful transactions (-2% QoQ) and 82,000 daily unsuccessful transactions (-16% QoQ). The average transaction fee fell 60% QoQ, going from $0.05 to $0.02.
The gaming sector is responsible for 51% of transactions on the Polygon PoS Network. It’s followed by DeFi at 34%, Social at 10%, and NFTs accounting for 5%. The disparity between active addresses and transactions across sectors is a result of the inherent characteristics of the respective sectors – gaming protocols typically demand higher activity, resulting in more transactions compared to DeFi protocols.
Development
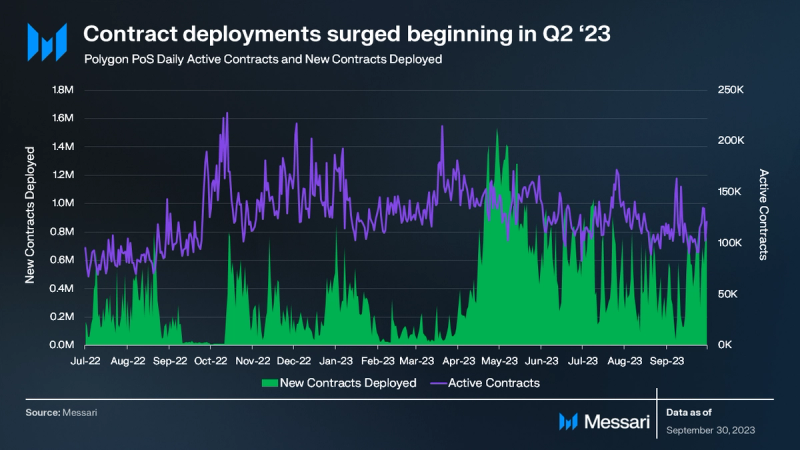
In Q2 ’23, the Polygon PoS chain saw a 252% QoQ surge in contract deployments, averaging 863,000 daily new contracts. By Q3, this number dropped by 34% QoQ to 568,000 daily contracts, though it remains notably above past averages.
As part of the Polygon 2.0 upgrade, the Chain Development Kit (CDK) was introduced, succeeding Polygon Edge and Supernets. This open-source framework aids in launching ZK L2s and transitioning current L1s to L2s. The CDK emphasizes:
- Sovereignty and Customizability: Developers can tailor their chains, adjusting components such as the virtual machine, operational mode, data availability solutions, sequencer types, gas tokens, and more, with full control over chain governance.
- Interoperability: All Polygon CDK chains will in the future be interconnected via Polygon’s Interop Layer, ensuring streamlined L2-to-L2 transactions and access to unified liquidity. The Interop layer serves as a proof aggregator for L2s in the Polygon ecosystem.
- Security: ZK proofs cannot be generated for an invalid state transition, which means secure bridging between Ethereum and Polygon CDK chains with no 7-day withdrawal delay.
- Ethereum Liquidity: A ZK bridge to tap Ethereum liquidity.
- ZK-tech: All Polygon ZK innovations will be directly accessible in Polygon CDK.
In August, Immutable became one of the first external teams to adopt the Polygon CDK, launching the Immutable zkEVM testnet. Following this, core developers from Astar Network on Polkadot and Canto announced their intentions to build zkEVM L2s with Polygon CDK. Other protocols integrating PolygonCDK include Aavegotchi, Accentrik, Arianee, CapX, Gameswift, Gnosis Pay, IDEX, Nexon, Nubank, Outerlife, Powerloom, and WireX.
In other developer-related news, Merokus V2 updated the DApp Store Kit, the DevX Global Tour visited South America twice and the US four times, and the Solution Provider Network was launched, aiming to pair developers with solution providers specialized in decentralized protocols.
Decentralization and Security
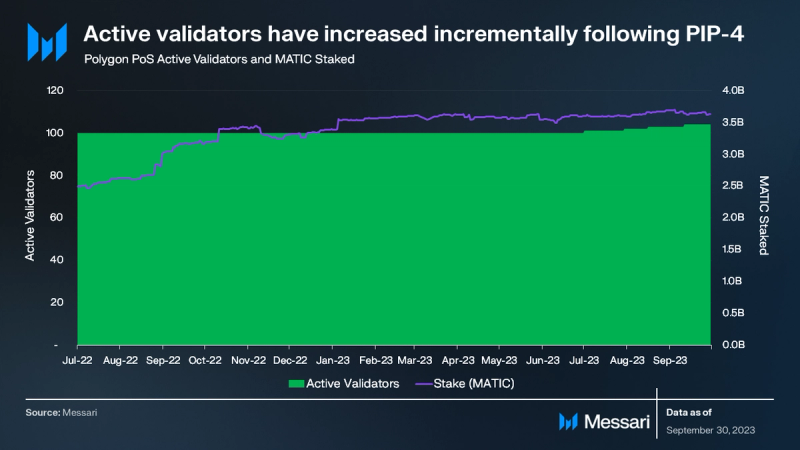
Polygon PoS operates as a Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) sidechain to Ethereum. Historically, the number of active validators on Polygon PoS was limited to 100. However, with the approval of Polygon Improvement Proposal 4 (PIP-4), the count of active validators expanded to 104 in Q3. Notably, Google Cloud is among the new additions to the validator list. In a move to enhance the validator onboarding procedure, Polygon validators implemented a revised validator admission form during Q3. By the close of the quarter, Polygon PoS boasted 104 active validators with a collective stake of 3.7B MATIC, representing 37% of the total supply.
With the proposed Polygon 2.0 upgrade, changes to the validator model are planned. The new model aims to place validators in roles with increased responsibilities, which will include securing network interoperability and staking. Future plans also involve validators functioning as decentralized sequencers, pending community approval. To engage in these roles, validators will be required to stake POL. As additional Layer 2s are integrated into the ecosystem, the interoperability layer will handle an increasing number of proofs, which is expected to result in increased network activity.
As part of the Polygon 2.0 upgrade, it is proposed for the Polygon Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chain to transition into a zkEVM validium. This change enables Polygon PoS to enhance its security, performance, and compatibility within the Polygon 2.0 ecosystem. With a zkEVM validium, transaction data is made available off-chain, resulting in lower fees compared to traditional rollups, while maintaining robust security guarantees.
Governance
Polygon Governance 2.0 introduces three main governance pillars for the Polygon ecosystem. Each pillar of governance will have its own unique governance framework, aiming to create scalable and efficient governance mechanisms.
- Protocol Governance: Facilitated by the Polygon Improvement Proposal (PIP) framework, providing a platform for proposing upgrades to Polygon protocols.
- System Smart Contracts Governance: Addresses upgrades of protocol components implemented as smart contracts. The Protocol Council, governed by the community, will be responsible for these upgrades.
- Community Treasury Governance: Establishes a self-sustainable ecosystem fund, the Community Treasury, to support public goods and ecosystem projects. The governance process involves two phases, starting with an independent Community Treasury Board and evolving into community-driven decision-making.
Community participation is encouraged by Polygon Labs through feedback and proposals. The PIP Bounty Program rewards exceptional submissions, with $40,000 allocated over one year. The framework covers core improvements, contracts on Ethereum, API specifications, and informational PIPs.
Additional Solutions
Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM, launched on March 27, 2023, is a Layer-2 rollup for Ethereum, aiming to facilitate secure, fast, and cost-effective transactions. As a ZK-rollup, it aggregates transactions into batches for off-chain execution. Post execution, Polygon zkEVM commits the transaction data on-chain. Alongside this data, it also submits a validity proof, providing cryptographic assurance of the data’s accuracy.
Throughout Q2, Polygon zkEVM announced notable collaborations and integrations with industry players such as Celer Network, Synapse, Balancer, and Uniswap (not yet live). Additionally, the Polygon Bridge to zkEVM debuted, enhancing connectivity within the ecosystem.
In Q3, several new protocols including Clearpool debuted on Polygon zkEVM. Furthermore, Polygon zkEVM underwent its first significant upgrade, Dragon Fruit. This upgrade introduced two key modifications: firstly, the integration of the PUSH0 opcode, aligning with the Shanghai hard fork, which ensures that the Polygon zkEVM Mainnet Beta remains synchronized with the latest Solidity version and maintains its parity with the EVM; secondly, it addressed a non-critical bug related to transaction parsing.
During Q3, Polygon zkEVM reported an average of 44,000 daily transactions (+123% QoQ). The stablecoin market capitalization on the network stood at $7 million. The TVL experienced a 30% QoQ dip, concluding at $19 million. QuickSwap was the leading protocol by TVL with $11 million, representing 57% of the zkEVM’s overall TVL.
Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK)
Polygon Labs has released the next component of the Polygon 2.0 vision with the Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK). Like the preceding updates, Polygon CDK represents an evolution of existing components, succeeding Polygon Edge and Supernets. Polygon CDK is an open-source development framework for launching ZK-L2 chains and transitioning existing L1s to L2s. Polygon CDK’s primary attributes focus on:
- Customizability: Developers can design their chain to meet their precise specifications by customizing different components like the virtual machine, operational mode, data availability solutions, sequencer types, gas tokens, and more.
- Interoperability: All Polygon CDK chains will link through Polygon’s Interop Layer, enabling seamless transactions and unified liquidity. The Interop Layer is a shared aggregate prover safeguarded by Polygon validators.
- ZK-tech: Polygon ZK advancements will automatically be made available in the CDK.
In August, Immutable became one of the first external teams to adopt the Polygon CDK, launching the Immutable zkEVM testnet. Following this, core developers from Astar Network on Polkadot and Canto announced their intentions to build zkEVM L2s with the Polygon CDK. Other protocols integrating the CDK include Aavegotchi, Accentrik, Arianee, CapX, Gameswift, Gnosis Pay, IDEX, Nexon, Nubank, Outerlife, Powerloom, and WireX.
Polygon Miden
Polygon Miden is an upcoming ZK L2 rollup utilizing the Rust-based Miden Virtual Machine (MVM) instead of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Miden aims for high-throughput, private applications using ZK-proofs, emphasizing privacy as a core feature for scalability. Additionally, Polygon Labs introduced Polylang, a TypeScript-based language for Miden VM.
On September 29th, Polygon Labs shared details about the development of Miden and announced plans for a testnet at some point in Q4 2023. Leading up to this Miden testnet launch, Polygon Labs has published a series of blog posts explaining Polygon Miden’s components.
- Transaction Model: Incorporates accounts, notes, and transactions to facilitate asset transfers, enabling concurrent computation, client-side proving, and public smart contracts.
- State Model: Combines account and UTXO-based models to manage state bloat and maintain privacy and throughput, utilizing ZK-proofs and user-centric data storage.
- Asset Model: Treats all assets natively, allowing creation and trading of fungible and non-fungible assets through specialized accounts, enhancing scalability and privacy in asset handling.
Polygon ID
Polygon ID is an open-source technology aimed at enabling a self-sovereign identity layer for Web3. It supports various identity verification methods, including document verification and biometrics, facilitating a decentralized identity framework. The structure of Polygon ID encompasses three key roles: issuers of credentials, identity holders, and verifiers, typically decentralized applications, which utilize user credentials for verification purposes.
In Q3, Polygon Labs released Polygon ID Release 4, which introduced technical upgrades to enhance the developer experience. Noteworthy features include the Explore Schema Builder, enabling developers to create and manage credential schemas, and an enhanced query builder for creating dynamic queries with ZK-proofs. Other enhancements include improvements in the Issuer Node, upcoming native iOS support for the Wallet SDK, and a new version of JS-SDK, simplifying the process of integrating Polygon ID.
Ecosystem Analysis

DeFi
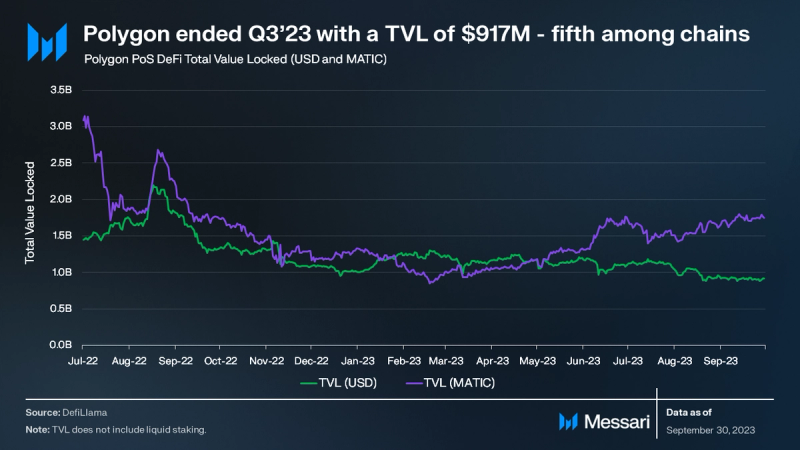
Polygon PoS’s Total Value Locked (TVL) decreased by 16% QoQ, concluding the quarter at $917 million. At the end of Q3, Polygon PoS ranked fifth among blockchains based on TVL. Polygon’s reduction in TVL is consistent with the broader market trend that started its decline after peaking in mid-2022.
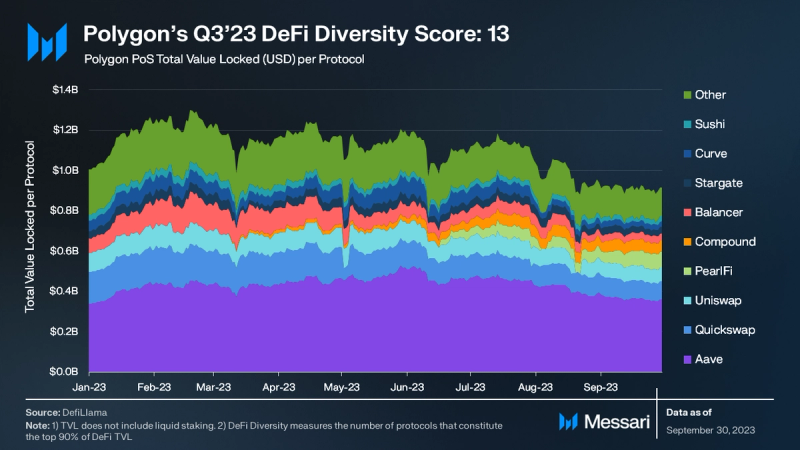
Aave remains the dominant protocol by TVL on Polygon PoS with $362 million or 40% of the aggregate value. Quickswap and PearlFi followed with TVLs of $89 million (9.7%) and $79 million (8.7%), respectively. PearlFi experienced a significant 91% QoQ increase in TVL, a result of its recent launch and the introduction of Pearl v1.5, which restructured its vote escrow contract and rewards claim system. Compound saw its TVL rise by 36% QoQ, after adding stMATIC as a collateral asset for the USDCv3 Polygon market in Q3.
The metric DeFi Diversity denotes the number of protocols comprising the top 90% of DeFi TVL. A wider spread of TVL across protocols can mitigate potential systemic risks from negative events. Polygon PoS concluded Q3 with a DeFi diversity score of 13. For comparison, the average DeFi Diversity score in Q2 ‘23 was eight, with Ethereum leading at 21 and Polygon ranking fourth.
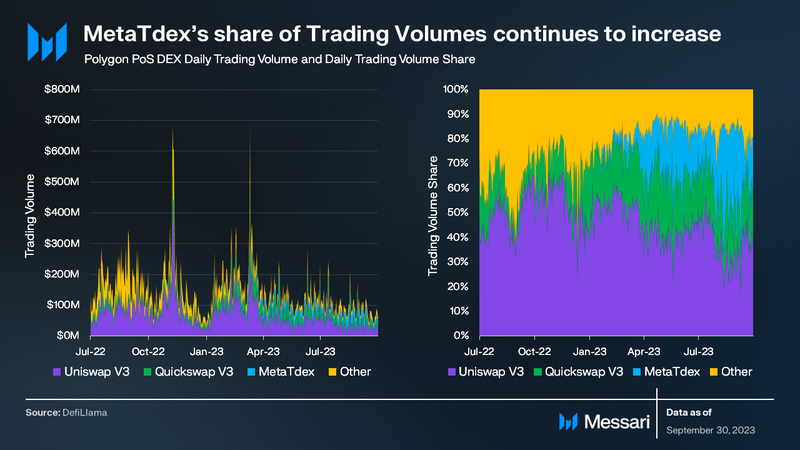
Polygon PoS recorded an average daily DEX trading volume of $95 million for Q3, a 24% decline QoQ. This trend mirrors the wider DEX market trajectory that began declining after its March peak (an outlier caused by the USDC de-peg event). Polygon PoS secured the fourth position in DEX trading volumes among blockchain networks.
Within the Polygon PoS ecosystem, Uniswap was responsible for 40% of the total DEX trading volume. MetaTdex followed with 23%, and QuickSwap with 21%. The combined volume of other DEX platforms on Polygon PoS constituted the remaining 17%.

Polygon PoS’s stablecoin market cap saw a 10% reduction, in-line with the broader crypto market, in Q3, ending at $1.3 billion. The main contributor to this decline was USDT, which decreased 25% QoQ. In contrast, USDC grew by 2% on Polygon PoS, finishing the quarter at $615 million, which constitutes 48% of the overall stablecoin market cap on Polygon PoS. Circle introduced native USDC on Polygon PoS in October.
In a broader context, this decline in Polygon PoS’s stablecoin market cap is in line with the general crypto market, which has been receding after its mid-2022 peak. Polygon PoS ranked sixth in stablecoin market cap among blockchain networks by the close of Q3.
NFTs
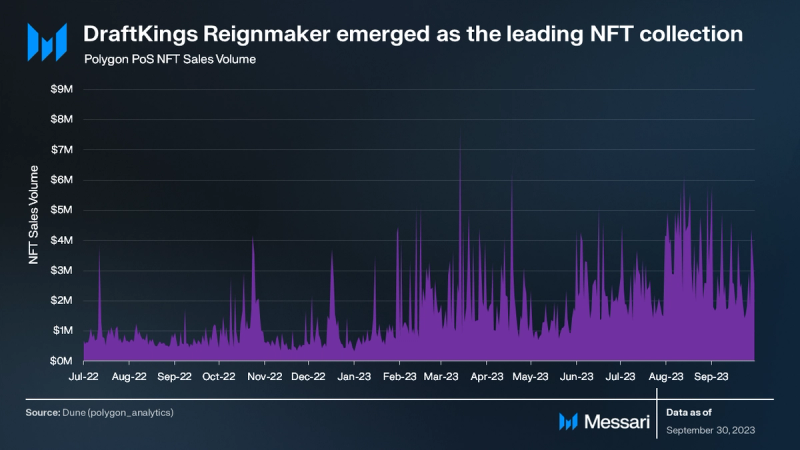
Throughout the NFT bear market, Polygon PoS’s NFT sector has maintained consistent performance. In Q3, there was a notable surge, with average weekly trading volumes witnessing a 131% QoQ increase, going from $8.6 million to nearly $20 million.
DraftKings’ NFT initiatives significantly influenced this growth. They released the Reignmaker NFT collection in August, which included officially licensed cards from the NFLPA, PGA TOUR, and UFC. This collection was the leading NFT sales collection on Polygon PoS and consistently ranked in the top five across all crypto networks as per CryptoSlam!. Its peak trading volume was $3.8 million on August 8th.
Y00ts announced a migration from Polygon PoS to Ethereum’s mainnet to unify the Y00ts and DeGods communities. They plan to repay a $3 million grant from Polygon Labs, which intends to redistribute $1 million of this to support the Polygon ecosystem’s developers and artists.
According to CryptoSlam!, Polygon PoS was ranked fourth in NFT Sales Volume. It should be noted that CryptoSlam! only includes secondary sales data, whereas the aforementioned figures also include primary sales.
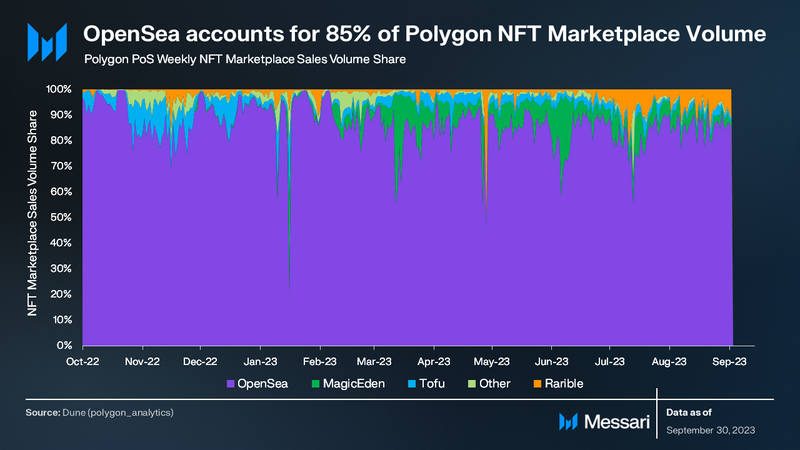
OpenSea remains the predominant NFT marketplace on Polygon PoS, representing 85% of Q3’s total NFT sales volume. Magic Eden, which was integrated into the network in Q1, held the second spot with 5.8% market share, followed by Rarible at 5.4%. Magic Eden has announced a $1 million NFT Creator Fund to further incentivize NFT activity.
Gaming

Polygon PoS’s gaming sector, which had the highest number of active gamers among all EVM chains, has reverted to its 2022 activity levels. The ecosystem is predominantly driven by key games such as Pixels, Arc8, Benji Bananas, Sunflower Land, Skyweaver, and IMVU.
The most significant gaming-related news for the quarter was the launch of the Immutable zkEVM testnet. Immutable zkEVM is one of the first external networks to utilize the Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK). This development is projected to attract a considerable number of gamers to the Polygon ecosystem. The Immutable zkEVM mainnet launch is slated for Q4 2023.
Closing Summary
In Q3 2023, the Polygon ecosystem experienced significant advancements and activity. Polygon Labs unveiled the Chain Development Kit (CDK) which succeeds Polygon Edge and Supernets, providing an open-source framework for the initiation of ZK L2s and the transition of current L1s to L2s. Immutable was the first chain deployed on testnet using the Polygon CDK, and this was closely followed by announcements from Astar Network and Canto’s core developers about their intentions to develop zkEVM L2s with the CDK.
The POL token, an upgrade from the MATIC token, was successfully activated on mainnet. Concurrently, as the Polygon 2.0 rollout progressed, the Polygon PoS chain maintained its activity. The NFT sales volume witnessed an increase of 131% QoQ, amounting to $20 million, largely driven by the Reignmaker NFT collection from DraftKings. This collection emerged as the leading collection on Polygon PoS. The network’s daily active addresses saw growth of 1.4% QoQ, reaching 364,000, with the DeFi sector the primary contributor. The Polygon zkEVM recorded an average of 44,000 daily transactions, marking a 123% increase QoQ.
Looking forward, the emphasis will be on the comprehensive rollout of Polygon 2.0, bringing forth significant enhancements to the network. A primary objective will be to collaborate with more teams for the CDK, especially as Polygon navigates a competitive landscape with modular EVM Layer2s. The engagement of high-caliber teams like Immutable, Astar, Canto, and others, is indicative of the traction the CDK is gaining. In summary, Polygon maintains its position at the forefront of the blockchain space, continuing its rapid developmental pace.



















