Key Insights
- The Nym mixnet is bringing privacy to not just crypto users, but internet users in general. The Nym mixnet is a modular technology that can be integrated with any internet application to add transport layer privacy.
- Nym itself is not a blockchain, but it uses the Nyx blockchain for decentralization and incentivization.
- Nym and the Nyx blockchain together form a Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN). The focus is providing a private and secure communication infrastructure.
- Nym will soon be leveraged by the NymVPN, with a broad scope for user adoption. Currently, Nym can also be utilized by end users through interfaces like NymConnect or direct integrations like Aztec.
- Nym is comprised of three components to provide privacy for internet traffic: a mixnet, zk-nyms, and the NYM token.
Background
Nym Technologies SA, a Swiss company established in 2018, is dedicated to developing open-source privacy-enhancing technology. The organization is under the leadership of CEO Harry Halpin, COO Alexis Roussel, Head of Research Ania Piotrowska, and Chief Scientist Claudia Diaz. Nym Technologies cofounded the Universal Privacy Alliance, an industry alliance of crypto-related entities committed to advancing, educating about, safeguarding, and engaging with privacy technology to establish it as the industry standard.
Nym Technologies raised a total of approximately $18 million in funding rounds by a16z, Polygchain Capital, Figment, Binance Labs, and Digital Currency Group, and then did a token launch on Coinlist for $25 million. Venture capital firms backing Nym continue to support it via the Nym Innovation Fund. Advisors to the team include Aggelos Kiayias, Bart Preneel, Ben Laurie, George Danezis, Carmela Troncoso, and Andres Arauz.
At the core of Nym Technologies’ innovations is the Nym mixnet. Nym is an open-source, incentivized, and decentralized platform that protects privacy at the network level of any application, wallet, or digital service. Nym protects against traffic pattern analysis and metadata surveillance. Nym exists as a tool to facilitate private internet communication between any applications, like a VPN, and so, it is not exclusive to blockchain-related activities. However, it’s closely linked to the NYM token and the Nyx blockchain, which Nym uses as its Cosmos-based appchain to coordinate the NYM token.
The Nym mainnet was launched in 2021 as a network for anonymous communication over the internet. Nym has expanded to include multiple technologies, such as the zk-nym identity system based on zero-knowledge anonymous credential technology. In 2022, the NYM token, employed to incentivize the mixnet, was launched through an initial coin offering (ICO) on Coinlist, which served as an initial coin distribution to facilitate decentralized staking and node operations. Nyx, a sovereign Cosmos Layer-1 (L1) blockchain, supports the Nym mixnet. Nyx is expected to be de-permissioned in 2024.
The Privacy Problem
Application Layer vs. Transport Layer
Privacy in software technologies generally falls into two categories: the application layer and the transport layer.
The application layer focuses on user-facing functionalities, data processing, and data security/privacy. In the context of crypto, these categories encompass actions like token transfers, smart contract interactions, and blockchain messages. On social media platforms, this layer governs content logic and privacy settings.
The transport layer manages communication across networks, including data transmission between devices and systems. It handles routing, addressing, and packet forwarding. In the context of crypto, these actions include all communications between nodes and validators/miners, including RPC calls from a wallet to broadcast a transaction to the broader network. On social media platforms and other traditional websites, this layer also includes all messaging between the client and server.
In practical terms, user interactions with applications depend on data transmission across the internet, such as RPC calls and consensus-related broadcasting, which takes place at the transport layer. Even when end-to-end encryption is applied, the fact that users are communicating with a platform remains public. For example, a Telegram message may seem to only happen in the Telegram application, but those messages must be broadcast across the internet to Telegram’s servers and the correspondent’s device, which takes place on the transport layer. In the same way, a transfer of BTC on Bitcoin takes place on the application layer, but the broadcasting of that transaction to other nodes takes place on the transport layer of the internet.
This distinction highlights that privacy concerns exist in both layers, given that network communications over the internet inherently involve data leakage. Achieving default privacy at the transport level is essential for preserving privacy and is the precondition for autonomy and freedom in an increasingly digital world.
The State of Crypto Privacy
Privacy and security strategies on the application layer are fairly diverse in crypto. However, there is much to be desired from the current suite of privacy tools. Many protocols can be perceived as private due to the technologies they leverage, but in actuality, they are not. Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are a powerful cryptographic technique that is seeing widespread adoption in the crypto space; however, ZKPs are a misnomer in most cases. Rather than being used for the obfuscation of data, ZKPs are typically used for succinctness and compression of data. Most zero-knowledge rollups (better referred to as validity rollups) only use ZKPs to leverage cheaper execution environments while providing zero privacy benefits, with few exceptions (i.e., Aztec and Nightfall).
In protocols that are actually private, effectiveness is tightly correlated to the size of the protocol’s anonymity set. In a privacy protocol, an anonymity set is a group of users or entities from which it is difficult to discern the specific origin or identity of a particular transaction or action, enhancing privacy by obscuring individual contributions. At the application layer, anonymity sets are heavily fragmented across various protocols, reducing the strength of the sets. Even when privacy sets are unified and networks are interoperable, the setup would still only cover the application layer. While the content of the actions may be private and secure, the patterns of interaction with the application would still be insecure and, therefore, subject to censorship. Fundamentally, privacy is most effective when embedded at the lowest level, making transport layer privacy crucial for any protocol striving for application layer privacy.
One of the first steps towards bottom-up privacy involves RPCs. Remote procedure calls (RPCs) for wallets are a set of protocols or functions that allow external applications or services to interact with and control a cryptocurrency wallet remotely. They enable actions like sending and receiving funds, checking balances, and managing transactions programmatically. The centralization of RPC providers is a bottleneck for privacy, as major wallets, RPC providers, and protocols have engaged in collecting and monitoring data from users. MetaMask, the most popular Ethereum wallet, and Infura, a popular RPC provider, collect users’ IP addresses when they transact on Ethereum. zkSync, a popular Ethereum rollup, engaged in the same practice of collecting IP addresses, allegedly related to ensuring regional compliance for a suspected airdrop. While data collection of this sort can be avoided by setting custom RPC configurations, it’s important for privacy to be the default setting, which can be achieved by integrating a mixnet with a network’s transport layer.
In Bitcoin, for example, the transport layer is already subject to surveillance. LinkingLion is an entity that has been working to deanonymize Bitcoin since 2018. Its behavior involves opening connections to many Bitcoin nodes using specific IP address ranges and listening to transaction announcements. This activity may allow LinkingLion to associate newly broadcasted transactions with the IP addresses of the nodes responsible for broadcasting them.
Monero, the largest crypto privacy protocol by market cap, is a project that takes steps to address this transport layer issue. Bitcoin and Monero’s Dandelion++ technique enhances transport-layer privacy by temporarily obscuring the source of transactions, making it harder for observers to trace. This enshrined version of onion routing is helpful for keeping transaction broadcasts private by changing the IP address but is not as private as a mixnet that re-orders the packets and adds cover packets. An adversary like a chain analysis company that can watch the entire p2p network could easily de-anonymize Dandelion++, but this is not the case with a mixnet.
Decentralized secure communication strategies like onion routing are a great start, but they still need to be improved upon. Secure communication infrastructure is generally composable with any message-passing network through an interface and can, therefore, be most efficiently implemented as a modular solution. Nym’s mixnet is just that, a solution for arbitrary private (and by extension, secure) communication that can be either enshrined into a protocol or added on with an interface. In addition, Nym is complementary and composable with almost all other privacy and security technologies, rather than rivalrous.
Nym Overview
There are three components to the Nym ecosystem:
- The Nym mixnet — a modular, private communication network
- Zk-nyms — an anonymous credential system
- The NYM token — a cryptocurrency
These technologies are supported and leveraged by Nyx, a sovereign, general-purpose Layer-1 (L1) blockchain with a CosmWasm VM. Nyx supports Nym in several ways:
- By ensuring that the mixnet network directory is decentralized and permissionless.
- By operating the tokenomics of the mixnet to incentivize and reward operators for providing privacy instead of grabbing user data.
- By facilitating the vesting of the NYM token.
Nyx’s main feature, the Nym mixnet, is a general-purpose piece of infrastructure that can be used for any kind of online communication, such as browsing the internet, messaging on Telegram, or broadcasting transactions to blockchain networks. Nyx smart contracts keep track of the decentralized directory authority of Nym mix nodes on the network.
The Mixnet
The Nym mixnet is a solution for private and secure transport-level communication. Secure communication infrastructure keeps online activities private and secure, bypasses geo-restrictions, protects sensitive information, and shields against eavesdropping. Such privacy tools are essential for many online activities; otherwise, passwords and credit card numbers would be floating around the internet in plaintext, able to be read by anyone.
Common types of secure communication infrastructure include:
- Virtual private networks (VPNs): Secure communication tools that create an encrypted tunnel between your device and a remote server via the VPN’s node. Examples include Surfshark and NordVPN.
- Onion routers: Similar to a VPN, but onion routers route encrypted data traffic through a series of nodes rather than a single node. The name “onion router” is inspired by the multiple layers found in an onion, which correspond to the various stages of encryption and decryption the data undergoes. Examples include Tor and decentralized VPNs (dVPNs).
- Mixnets: Similar to an onion router, but mixnets also mix data traffic at the individual packet level, creating a homogenous output of data that cannot be differentiated from each other. This renders mixnets private even when against global passive adversaries (adversaries that monitor all data/packets).
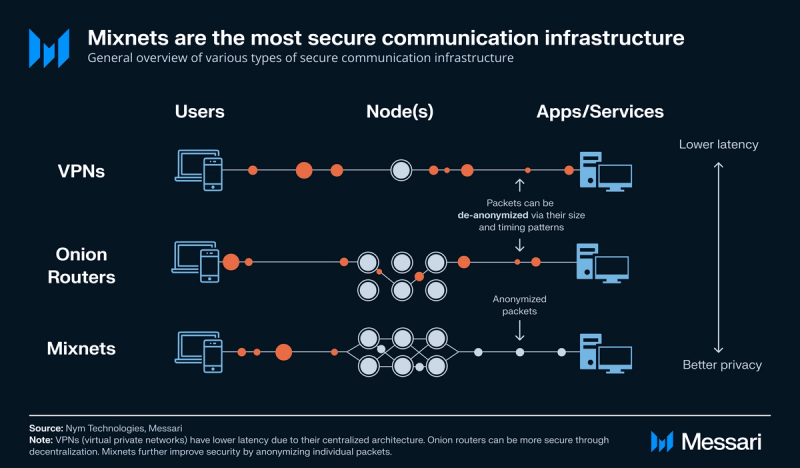
The Nym mixnet improves on the security offered by VPNs and onion routers primarily through three features:
- Indistinguishable packets: All traffic is encrypted to look the same so adversaries can’t follow individual traffic.
- Mixed packets: All traffic is reordered so that adversaries can’t simply count what goes in and what comes out to statistically de-anonymize users.
- Cover traffic: Adversaries will always see a constant flow of traffic, supplemented by fake packets, to avoid revealing patterns about when a user is sending real packets.
Privacy (and by extension, security) can be increased by using a decentralized network of nodes rather than a single node for routing traffic. The mixnet is supported by a decentralized network of mix nodes, which can be run by anyone. Mix nodes facilitate the secure transportation of data across the Nym mixnet. They receive packets, mix them, and strip the outer layer of encryption to forward them to their next destination. Given these extra steps, mix nodes limit the speed at which data can be transmitted. This increased latency is an inherent tradeoff in designing a secure communication tool. However, the Nym mixnet implements strategies to remedy any increases in latency enough to not affect user experience. These techniques are explored further in the Scaling Anonymity section.
Encryption
The Sphinx packet format serves as a secure and efficient method for encapsulating and encrypting data while it navigates through the mixnet. Sphinx encompasses encryption, packet structuring, and onion routing functionalities. Data is subjected to Sphinx-format encryption before it reaches mix nodes, and, importantly, all encrypted packets appear indistinguishable to the mix nodes. Bitcoin’s Lightning Network also uses Sphinx, although it does not implement mixing or routing entropy, limiting its privacy.
Mixing
Nym is built upon the Loopix anonymity system, a mixnet designed to balance high anonymity levels and low latency. Loopix employs “continuous mixing,” where messages are continuously processed and forwarded, reducing latency compared to conventional mixnets.
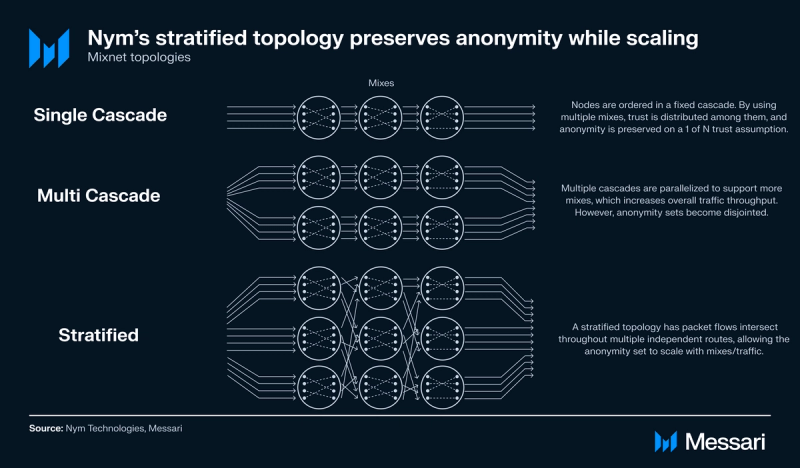
Traditional Chaumian mixnets, using single cascade topologies, introduce significant latency as traffic volume grows. While adding parallelized cascade layers (mixes) can support more traffic, it compromises anonymity by creating disjointed sets of packets.
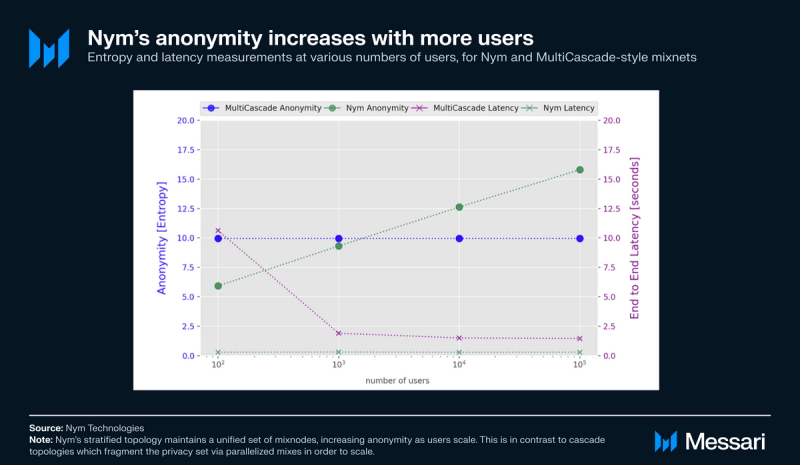
Breaking a single large cascade layer into smaller ones does not effectively increase a mixnet’s throughput. However, Nym’s stratified topology ensures that all packet routes intersect, regardless of multiple independent routes, thereby maximizing the anonymity set for all packets.
Cover Traffic
Under Nym’s “continuous mixing” approach, messages are continually processed rather than waiting for fixed batch sizes. If packets were not continuously mixed, there exists a potential vulnerability for adversaries to discern user patterns. Consistent messaging timings or cadences could allow adversaries to probabilistically deduce user information over time. To counteract this, dynamic cover traffic is introduced throughout the network.
Users within the mixnet automatically transmit cover traffic in the Sphinx packet format. Each cover traffic packet is binary-indistinguishable from others, just as real packets are. When users transmit actual data, it becomes concealed amid the continuous flow of decoys.
The dynamic nature of cover traffic means it diminishes as real traffic enters the network. This setup prevents adversaries from detecting linear increases in packet output that could reveal genuine communication patterns.
Scaling Anonymity
The size of an anonymity set directly influences its effectiveness, and anonymity can be empirically gauged using traffic and entropy metrics. Traffic quantifies the total packet volume traversing the network, while entropy measures the unpredictability or randomness in traffic distribution. Doing so makes it challenging to associate specific packets with their source within an anonymity set. These measurements are grounded in Shannon Entropy.
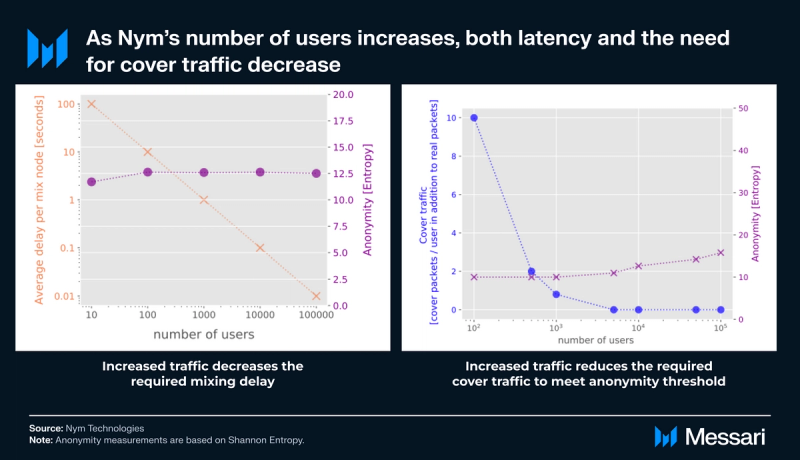
Nym’s horizontal scalability is a key feature that allows anonymity to expand alongside an increasing user base. This scalability doesn’t come at the cost of latency either; in fact, latency (i.e., the time packets spend waiting in mix nodes before forwarding) can be decreased as more users join, and cover traffic can be logarithmically reduced.
Compared to centralized VPNs, Nym’s mixnet introduces additional steps, rendering it slower. Its current data transfer time is 500 ms, as opposed to as low as 20-50 ms for VPNs. While Nym is an order of magnitude slower than its competitors, 500 ms remains relatively performant. Half a second is generally inconsequential, especially for broadcasting payment transactions. Core contributors are working to further reduce Nym’s latency. The Nym team’s goal is to bring latency down to 300 ms. Doing so would align it more closely with the requirements of existing cryptocurrency networks, such as Ethereum validators. This would enhance Nym’s compatibility and usability within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Zk-nyms
Zk-nyms are a form of anonymous credentials that empower users to selectively disclose information while safeguarding their privacy. These credentials, rooted in Coconut Credentials, enable users to prove statements about themselves or their attributes without revealing sensitive information. This balance between privacy and authentication ensures users can demonstrate their eligibility or specific attributes while maintaining their personal data’s confidentiality.
These credentials allow users to prove certain statements about themselves or their attributes without revealing their actual identity or sensitive information. They’re designed to strike a balance between privacy and authentication, enabling a user to demonstrate specific attributes while keeping their personal details confidential.
The initial application of zk-nyms involves Nym mixnet’s bandwidth credentials. They enable users to showcase their authorization for utilizing the mixnet without disclosing wallet addresses, payment details, account balances, or other data. Looking ahead, zk-nyms have promising applications in private transactions including offline privacy preserving ecash and across various cryptocurrencies and secure voting processes. These use cases can be implemented on the Nyx blockchain, where zk-nyms are readily available for developers.
Nyx Blockchain Overview
Nyx is a sovereign, general-purpose Cosmos Layer-1 (L1) blockchain with built-in privacy features. It was built with various open-source Cosmos technologies, such as the Cosmos SDK.
Nyx is currently permissioned, with a Proof-of-Authority consensus mechanism run by current validators, but it is planned to move to a permissionless Bonded-Proof-of-Stake (BPoS) mechanism. When it changes mechanisms, Nyx will feature a BPoS Byzantine-Fault-Tolerant (BFT) consensus mechanism, as it is built with CometBFT, a fork of Tendermint Core.
Nyx’s application layer, built with the Cosmos-SDK, features the CosmWasm virtual machine (VM). CosmWasm supports Rust and Go, as they compile to Web Assembly (WASM). This choice was made to lower the barrier of entry for developers, as many popular languages compile to WASM. Nyx’s use of the Cosmos tech stack also ensures compatibility with Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC). Nyx inherently offers privacy through zk-nyms, allowing confidential execution of payments, voting, and other transaction types. Its IBC connectivity facilitates seamless access to privacy features for users across various Interchain networks.
Nodes
Nym Mix Nodes
The Nym mixnet is supported by a decentralized and permissionless network of mixing nodes, known as mix nodes. The network uses a client-server architecture and is not P2P. The primary purpose of mix nodes is to securely route and mix traffic through the mixnet.
Mix nodes use a novel Proof-of-Work (PoW) scheme called Proof-of-Mixing (PoM). PoM samples the network randomly and rewards mix nodes for mixing traffic using a VRF-based cryptographic scheme. The system guarantees fairness by taking advantage of the Sphinx packet format, which makes all packets, even those from cover traffic, indistinguishable from each other.
As of September 2023, there are ~600 total Nym mix nodes. Of those total nodes, 240 are selected as active for every epoch in order to maximize the rewards and efficiency of the system. The number of active nodes scales as demand scales. The selection of active nodes is fully decentralized and is based on a mix node’s reputation (measured by their total stake in NYM tokens) and performance.
Nyx Validators
Once de-permissioned, the Nyx blockchain will be supported by a decentralized and permissionless network of validating nodes, known as validators. The primary purpose of validators is to order transactions and reach consensus on the state of the network. The state of the network is a directory (or “map”) of all mix nodes and their reputations. While mix nodes mix traffic, validators maintain consensus of the topology and token economics of the mixnet. These Nyx validators will be similar to PoS validators on other Interchain networks and PoS blockchains in general. Nyx validators will run a BPoS consensus mechanism built with CometBFT. Holders can delegate their NYM tokens to Nyx validators with no bonding or unbonding period.
As of September 2023, the Nyx network is still permissioned, and the PoA validators are run by Nym Technologies and its partners. At the moment, there are 34 active Nyx validators.
The NYM Token
The NYM utility token serves the following functions for the Nym mixnet and the Nyx blockchain:
- Access to the mixnet.
- Paying Nyx transaction fees.
- Pledging to mix node operators as an initial reputation score.
- Paying Proof-of-Mixing rewards to mix node operators.
NYM was initially distributed as an ERC-20 token and still exists as so. Ethereum ERC-20 NYM can be bridged to native Cosmos NYM through centralized exchanges, but Nym Technologies is also building a swap functionality in the Nym Wallet.
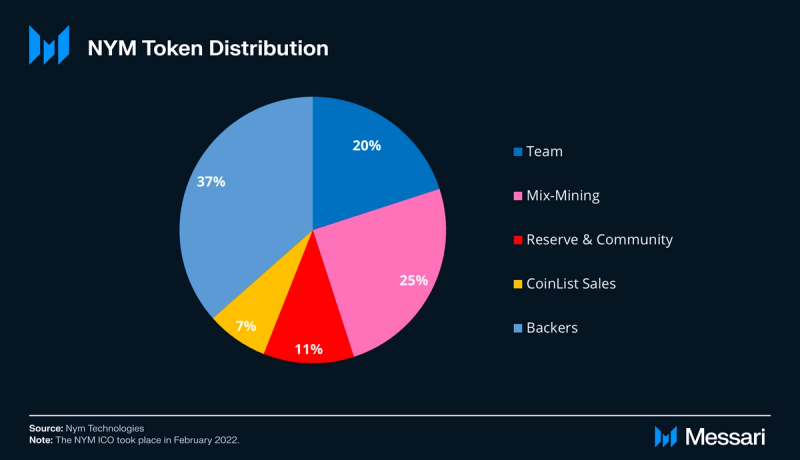
NYM has a total supply of 1 billion and a circulating supply of ~550 million as of September 2023. Two Coinlist sales took place in February 2022 and accounted for 75 million NYM, 7.5% of the total supply. Mix-mining rewards account for 250 million NYM, 25% of the total supply. The remaining 675 million NYM went to the team, backers, and a mix-mining reserve to bootstrap mixnet rewards.
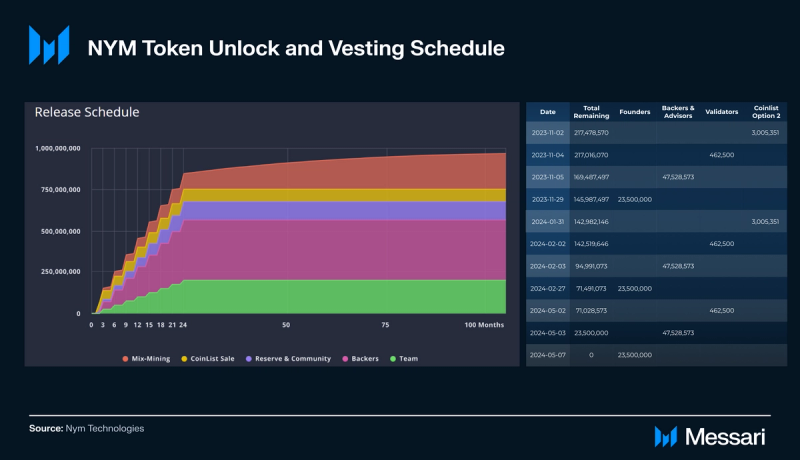
NYM that was set aside for founders, backers, validators, and Coinlist buyers will be fully vested in May 2024. At that point, the only new NYM entering circulation will come from mix-mining rewards. Those rewards will continue to be distributed to mix nodes from the mix-mining pool for several years until the maximum supply of 1 billion NYM is in circulation. As mix-mining rewards decline, mix node incentives progressively depend more on user fees due to the growing user base and demand for privacy services within the network.
State of the Nym Ecosystem
For end users, the Nym mixnet can generally be leveraged in one of two ways. The Nym mixnet can be leveraged through a general-purpose interface layered on top of your applications, such as with NymConnect, or, the mixnet can be enshrined in a protocol, as it will be with Aztec. Any wallet or application can integrate with Nym, abstracting away any implementation details from the end user for a seamless UX.
NymConnect
NymConnect is a simple interface that enables users to privacy-enhance their apps by routing traffic from third-party applications through the Nym mixnet. This means that a user’s IP address is protected from their app providers, and their metadata and communication patterns are protected from any observer of the network. NymConnect is a Beta application, used to stress test the mixnet and test features that will be included in the NymVPN set to launch in Q1 2024. This means NymConnect should not be fully relied on for strong privacy protections quite yet.
Through the Nym mixnet, NymConnect allows users to securely broadcast messages to interact with various applications. It is currently compatible with:
- Keybase: a cryptographic platform and messaging application. Users can link their online identities (such as social media profiles) to their Keybase account, helping to establish trust and verify their identity.
- Electrum: an open-source Bitcoin wallet that enables users to manage their holdings, create and store multiple wallets, and send transactions.
- Telegram: a cloud-based instant messaging platform. It offers end-to-end encryption for chats, voice messages, and calls.
- Monero: a private cryptocurrency network focused on payments.
- Element: Element is a messaging platform and collaboration tool similar to Discord that is built on the Matrix network. Matrix is an open, decentralized communication protocol for secure, real-time messaging and collaboration.
- Blockstream Green: a Bitcoin wallet.
- Any wallet or app that can run SOCKS5: SOCKS5 is a general network protocol used by many crypto wallets, including Wasabi and Samourai.
In some cases, NymConnect enhances existing privacy. For example, Monero already onion routes transactions before broadcasting them, but it could improve this by sending them through the mixnet. In other cases, NymConnect adds privacy where there is none. For example, without a mixnet or VPN, Telegram could be censored by a government, as it was in Iraq, which prevents anyone in that region from using the platform.
Usage of the NymConnect interface can be configured to meet the needs of a specific application or user. NymConnect’s Speedy Mode allows users to forego cover traffic in favor of faster speeds.
Aztec
Aztec is a privacy-focused, Layer-2 (L2) Ethereum rollup. Aztec developers are integrating the Nym mixnet directly into the protocol to privately route message broadcasts to the Aztec network.
In a fully private blockchain, all state must be end-to-end encrypted, including commitments and encrypted note preimages that hold assets, values, and sender information. This private state, as well as the global public state, must be accessed in order to prove ownership of specific parts and build valid transactions. However, users inadvertently leak information by requesting the state from the network. Users must either hold the entire state themselves (which does not scale well) or find a way to privately request the necessary data.
By partnering with Nym, Aztec users will be able to securely and privately request data necessary from the state to interact with private functions. This alleviates the burden of users needing to own the whole state to avoid the risk of deanonymizing themselves.
NymVPN
NymVPN is a VPN service developed by Nym, designed to offer users enhanced privacy and security. It employs the Nym mixnet and provides options for users to balance speed and privacy. It also enables payments with NYM tokens, ensuring anonymity in transactions. The Nym VPN app aims to meet the growing demand for privacy protection in the familiar and user-friendly form of a VPN while maintaining a surveillance-resistant business model.
The NymVPN’s general-purpose scope has the potential to onboard many more users than previous Nym integrations (i.e., NymConnect and specific B2B Nym integrations). To increase accessibility, it will automatically convert payment across a wide variety of payment methods, including Bitcoin and fiat, to NYM tokens in order to purchase access to the VPN product. The NymVPN payments will then fund the mix nodes in the same way transaction fees work in other networks.
Competitive Landscape
VPNs are separate services from mixnets, as they are centralized and prioritize different core principles. Decentralized VPNs (dVPNs) and onion routers, such as Tor, are closer to direct competition for a mixnet but are ultimately inferior in terms of packet-level privacy. While Tor does not provide privacy against an adversary that watches an entire network, mixnets like Nym do. Also, unlike Tor, as mixnets scale to more users, they increase the privacy of everyone by increasing the anonymity set. Other mixnets that use P2P architectures or parallelized topologies are generally not as private or scalable. There are a handful of competing decentralized technologies on the market, including
- Lokinet: an incentivized private communication network built on the Oxen blockchain and supporting applications such as Session. Lokinet uses Garlic Routing (also known as Invisible Internet Project / I2P), an extended version of onion routing, and is therefore technically not a mixnet
- HOPR: a mixnet that uses a P2P architecture rather than a layered topology, which Nym claims is less private.
- Elixxir: a postquantum secure mixnet that parallelizes cascade layers. Nym compares and contrasts their network here.
- dVPNs: Orchid, Sentinel, and Boring Protocol are all incentivized decentralized VPNs that offer less privacy than a mixnet.
In general, there’s very little usage of these kinds of technologies. Most people are not aware of how much information their patterns of communication reveal about them, even when using end-to-end encryption. VPNs are the most widely used tool in this category. Nearly two-thirds of US adults have used VPNs for either work or personal reasons. Many VPN use cases are not privacy-focused and are as simple as connecting to an office network from home or streaming content from another country’s server (e.g., watching a show on Netflix that is not available in your country).
Tor is by far the most popular onion router and is a choice tool for avoiding censorship or maintaining privacy. Tor consistently exceeds 4 million daily active users and 250 GB/s of consumed traffic as of September 2023. These values are up roughly 100% and 1,000% from May 2020, respectively. While these metrics are low compared to overall internet usage, they’re certainly growing. Tor has no official token.
Nym has to overcome the network effect of more established services such as VPNs and Tor. Additionally, Nym has to provide a UX without too much friction, which it’s already making steps towards with interfaces like NymConnect and private credential systems like its zk-nyms. In the crypto industry, Nym actually has the first-mover advantage of being early to launch and partner with other cryptocurrency projects, such as Aztec. The full launch of the Nyx blockchain may also act as a catalyst to bring more users and use cases to the Nym mixnet.
Conclusion
Nym addresses a frequently neglected component of the technology stack: the transport layer. True privacy is achieved from the bottom up, starting with the transport layer. Both conventional Web 2.0 applications like Telegram and blockchain-related applications such as wallets — and even entire networks — can benefit from Nym’s modular network stack. Unlike other privacy solutions, Nym’s mixnet employs a unique architectural approach that enhances anonymity proportionally with the growth in network participation.
The Nym mixnet serves as a modular addition to any internet application, introducing transport layer privacy for a diverse user base. Coupled with the Nyx blockchain, it’s a DePIN project focused on fostering private, secure communication infrastructure. Given the rising prevalence of private communication technologies (e.g., VPNs), along with the sustained emphasis on privacy within the cryptocurrency sphere, Nym is strategically poised to offer genuine anonymity to a broad range of end users.



















