Key Insights
- Polkadot has completed and shared the official release of Polkadot 1.0, marking the completion of the Polkadot whitepaper. The next iteration of Polkadot, referred to by the community as Polkadot 2.0, will be determined by community discussions and consensus.
- The percentage of DOT staked rose by 12% QoQ to 49%. The close alignment of Polkadot’s staking rate with the ideal rate reflects the effectiveness of its mechanism.
- Wormhole integrated Moonbeam Routed Liquidity. With the implementation, every parachain can now access liquidity from Wormhole-connected ecosystems.
- Native USDC went live on the Polkadot asset hub unlocking access across the entire Polkadot ecosystem.
- Sub0, Polkadot’s annual developer conference, unveiled notable network enhancements. The conference highlighted Asynchronous Backing, significantly boosting Polkadot’s throughput and scaling, alongside Open Zeppelin’s library of parachain runtimes and Moondance Labs’ Tanssi ContainerChains for simplified appchain deployment.
Primer on Polkadot
Polkadot is a distributed blockchain computing platform that acts as a base layer for other sovereign blockchains, called parachains, for validation and shared security. Polkadot was built using Substrate, a blockchain developmental framework. Furthermore, Polkadot’s base layer is known as the Relay Chain, which utilizes a Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) consensus mechanism, and its state machine is compiled to WebAssembly (Wasm).
Polkadot Relay Chain’s core function is to validate and provide security to its parachains. Parachains are added to the Relay Chain through Parachain Slot Auctions. The auction process is a candle auction that lasts for one week. During this week, potential parachains “bid” DOT tokens to secure a parachain slot. The DOT associated with the winning bid is locked for the duration of the slot lease (96 weeks). At the end of the slot lease, the DOT tokens are unlocked. Bids by potential parachains can be either self-funded or crowdfunded through a crowd loan campaign. Parachains on Polkadot utilize Collators to order transactions and send data to the Relay Chain.
Lastly, parachains on Polkadot can communicate with one another through the Cross-Consensus Mechanism Format (XCM). The XCM is a messaging format that standardizes messages between Polkadot’s parachains, allowing for greater interoperability.
Key Metrics
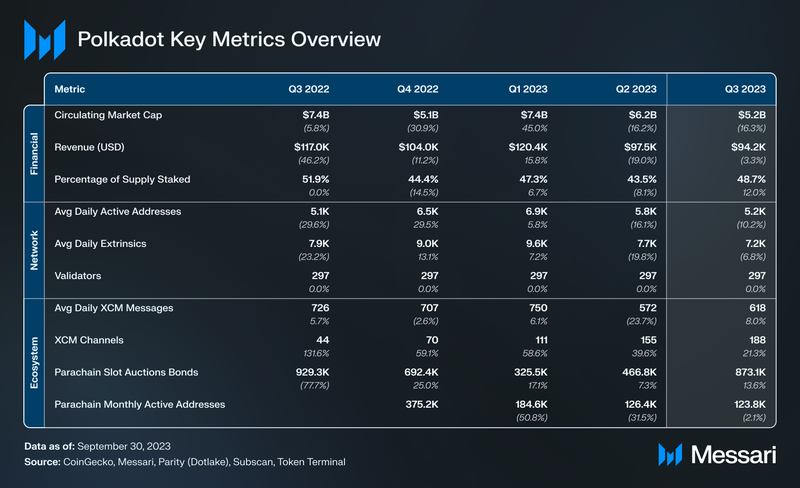
Financial Analysis
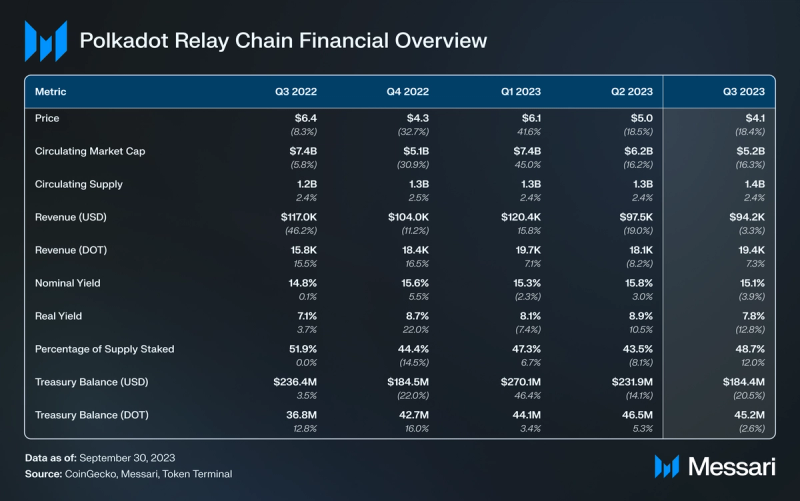
Market Capialization
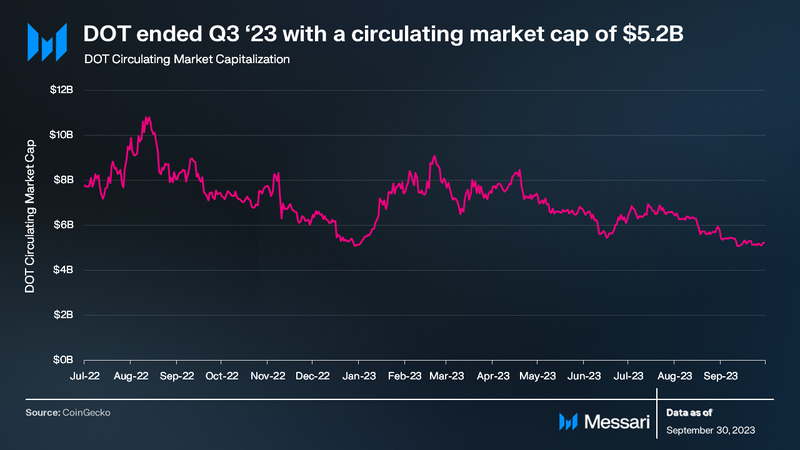
In Q3 2023, despite favorable court rulings for XRP and Grayscale, the overall crypto market experienced a moderate downturn. The total crypto market capitalization decreased by 5.8%, while BTC and ETH fell by 7.5% and 10.0%, respectively. DOT’s market capitalization declined by 16% QoQ, closing at $5.2 billion, making it the 13th largest crypto asset by market cap.
Revenue
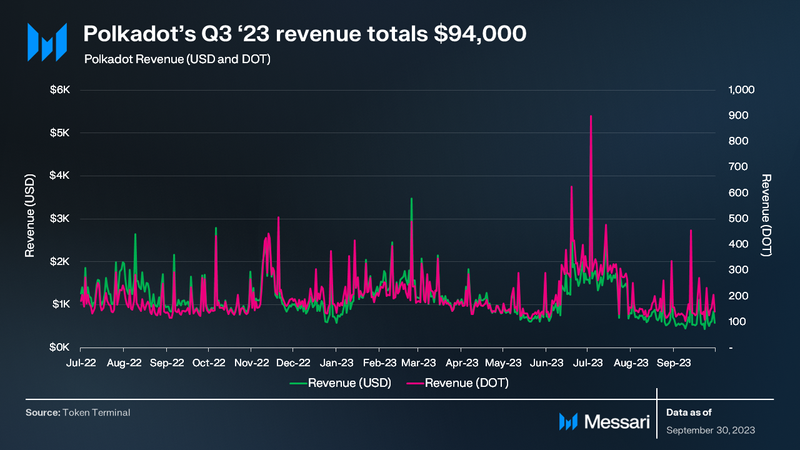
Polkadot’s financial structure is based on a weight-based fee model, where transaction fees are determined and charged prior to execution, distinguishing it from the gas-metering model. The fee calculation encompasses three components: a weight fee reflecting computational resources, a length fee based on transaction size, and an optional tip to incentivize block authors. These fees originate from various activities such as token transfers, staking, validator elections, governance voting, and parachain slot auctions. It’s important to note that transaction fees do not apply to parachain transactions.
In Q3, Polkadot’s revenue amounted to $94,000, representing a 3% decrease QoQ. Polkadot’s revenue tends to be relatively lower compared to its competitors due to the network’s structural design.
Supply
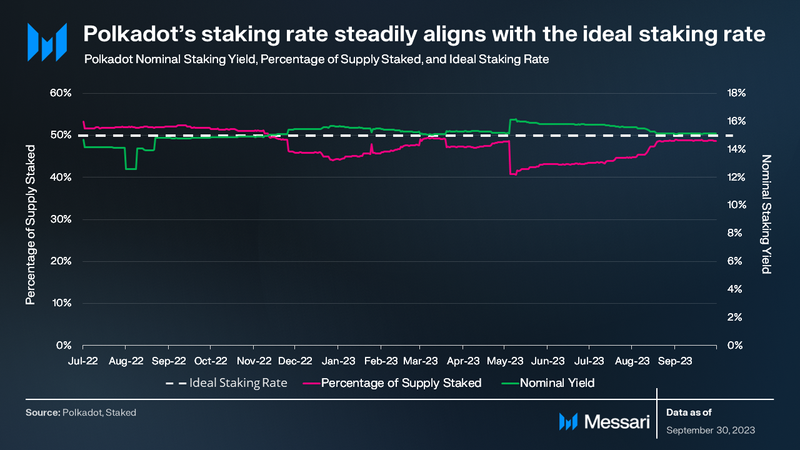
Polkadot’s native token DOT serves three primary purposes: governance, staking, and parachain bonding. As of the end of Q3, Polkadot had a staking rate of 49%. DOT has an inflationary monetary policy and no maximum supply. DOT’s monetary policy is determined by its compliance to an ideal staking rate, which accounts for the sufficient backing of DOT to prevent possible security compromises while keeping the native token liquid. If the staked amount falls below the ideal rate, staking rewards for nominators increase, encouraging more staking. Conversely, if the rate exceeds the ideal, staking rewards decrease.
By the end of Q2 2023, Polkadot’s staking rate was 44%, prompting higher staking rewards as it was below the ideal rate. In Q3 ’23, the DOT staking percentage rose by 12% QoQ to 49%, leading to reduced staking rewards and a 12% QoQ decline in annualized nominal yield to 15%. The close alignment of Polkadot’s staking rate with the ideal rate reflects the effectiveness of its mechanism.
Zodia Custody, a leading digital asset custodian whose shareholders include Standard Chartered, SBI Holdings and Northern Trust, announced institutional custody and staking services on Polkadot.
Treasury
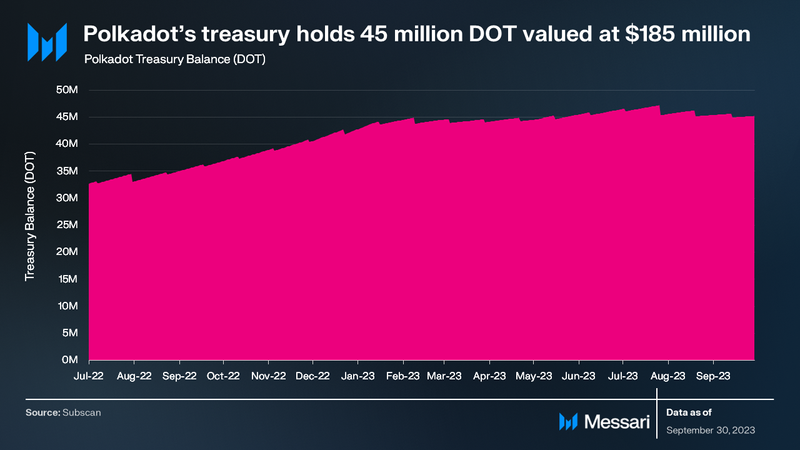
The Polkadot treasury is financed through block rewards, validator slashing, transaction fees, and staking inefficiencies. The treasury funds, held in a system account, are allocated for expenditures within a 24-day spend period, with any unspent funds subject to a 1% burn. Notably, all treasury expenditures are executed automatically on-chain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
In Q3 ‘23, the Polkadot treasury supported various initiatives, including software development, bounties, client upgrades, and community events like meetups and hackerspaces. The introduction of OpenGov on June 15 represented a significant milestone, revolutionizing treasury management and enabling concurrent proposals with distinct requirements. OpenGov’s implementation is expected to drive increased usage of the treasury, delivering substantial benefits to the Polkadot community. As of the quarter’s end, the Polkadot treasury held approximately 45 million DOT ($185 million).
Network Analysis
Usage
The Polkadot Relay Chain has several primary functions, including securing and connecting the parachains. As such, its end users typically transact and use the network primarily through the parachains.
Today, the Relay Chain does support some end user functionality, including token transfers, staking, validator elections, governance voting, and parachain slot auction participation. However, with RFC-0032: Minimal Relay, it is proposed to migrate several subsystems into system parachains. By minimizing state transition logic on the Relay Chain by migrating it into system chains the Polkadot Relay Chain can maximize its primary offering: secure blockspace.
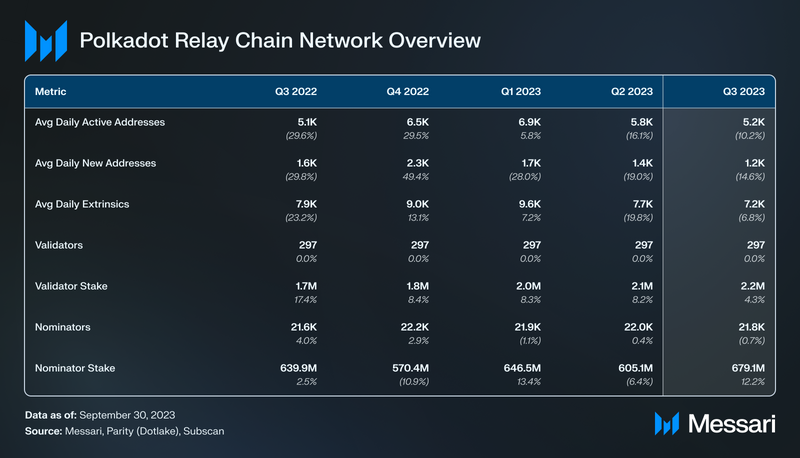
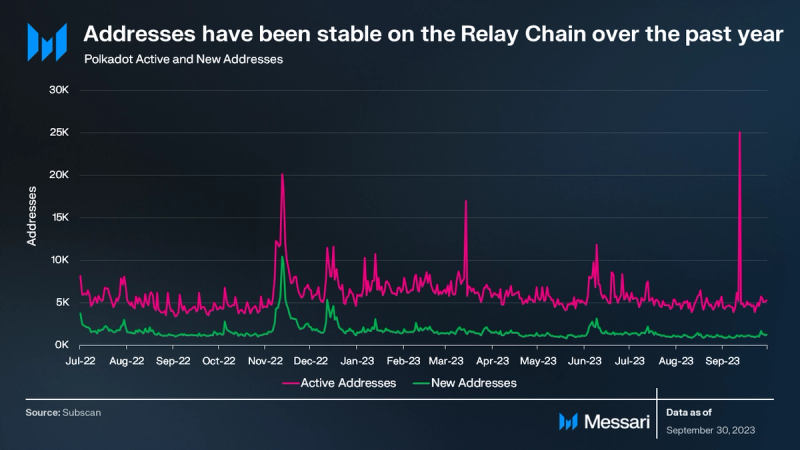
Following the launch of OpenGov in June, the Polkadot Relay Chain experienced an increase in account activity. This surge can be attributed to heightened governance activity, as the Relay Chain plays a crucial role in facilitating governance processes. Throughout Q3, the Relay Chain witnessed an average of 5,200 daily active accounts, marking a 10% QoQ decrease. Across the Polkadot ecosystem, there were 4,312,113 million unique accounts (public key addresses) by the end of September, up 9.3% QoQ and 34.9% year-to-date.
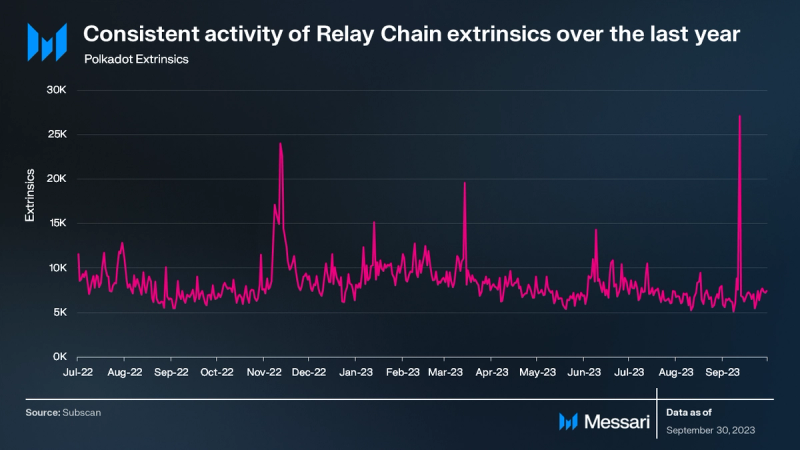
In Polkadot’s blockchain framework, an extrinsic is a crucial element that facilitates state transitions within the Relay Chain. It acts as a generalized transaction, encapsulating external data that the network needs to validate and track. Commonly, extrinsics carry a signature and references to specific functions, enabling interactions such as token transfers between accounts. Through extrinsics, Polkadot efficiently handles external inputs, ensuring a seamless operation of its blockchain network. Over the past year, the Relay Chain has seen a stable trend in extrinsics, averaging 7,000 daily extrinsics in Q3 ’23.
Development
Polkadot boasts one of the largest developer bases in the crypto industry. According to Electric Capital, Polkadot averaged nearly 2,000 monthly active developers in the third quarter, making it the second largest ecosystem by developers.
Polkadot provides comprehensive developer support through its open-source tech stack, encompassing various categories such as user interface, tools, APIs and languages, smart contracts, chains and pallets, network maintenance tools, consensus, networking, and more.
Third quarter highlights include:
- The Polkadot Developer Heroes Program introduced to foster collaboration and recognize exceptional developers.
- Polkadot Blockchain Academy Wave 3 concluded at UC Berkeley, California, where a new entrepreneur-focused Founders Track was introduced. Waves 4 and 5 will visit Hong Kong and Singapore respectively, in January and May 2024.
- Polkadot revealed significant scaling updates at the sub0 Developer Conference. These updates included Asynchronous Backing, new architectural components and concepts, a parachain runtime library by OpenZeppelin, a new ledger app that will support any parachain by Zondax, and a Snowbridge Deployment.
- Google Cloud added support for Polkadot on BigQuery.
- Moondance Labs has introduced Tanssi ContainerChains, a new solution for deploying application-specific blockchains (appchains) that aims to simplify the deployment process
Decentralization and Security
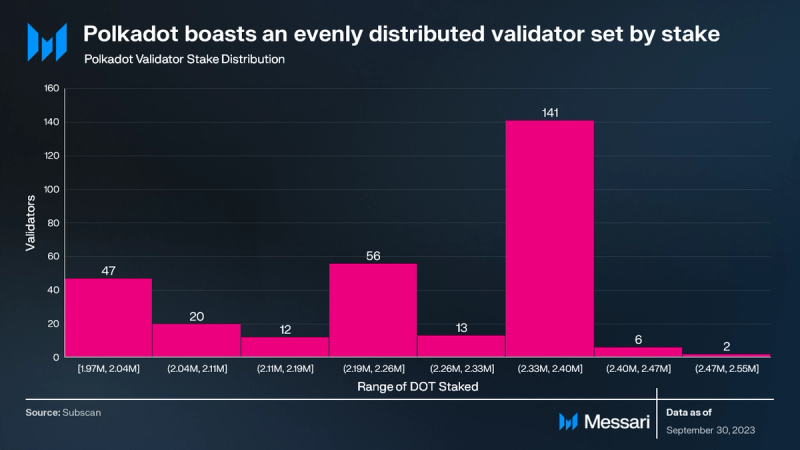
Polkadot employs a unique consensus mechanism called Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS). Validators receive payments every 24 hours based on their completion of payable actions, known as era points. Every four hours, a subset of validators is randomly selected to validate all parachains with a multiplier applied to their era points. This combination of era points and random parachain validation creates a probabilistic guarantee that validators earn rewards that are nearly identical. Because validators earn near-equal rewards and distribute these rewards pro-rata to their nominators, nominators are incentivized to stake with lower-staked validators to earn higher rewards. The validator-nominator reward model is designed to decentralize Polkadot’s validator set.
The active validator set on Polkadot has been stable at 297 for years, with no immediate plans for changes. During Q3 ‘23, the validator reward model continued to demonstrate its effectiveness in promoting validator stake decentralization. All 297 validators fall between 1.97 million to 2.55 million DOT staked.
The even reward distribution of the validator model incentivizes node operators to operate multiple validators. This strategy has been adopted by multiple entities.
Governance
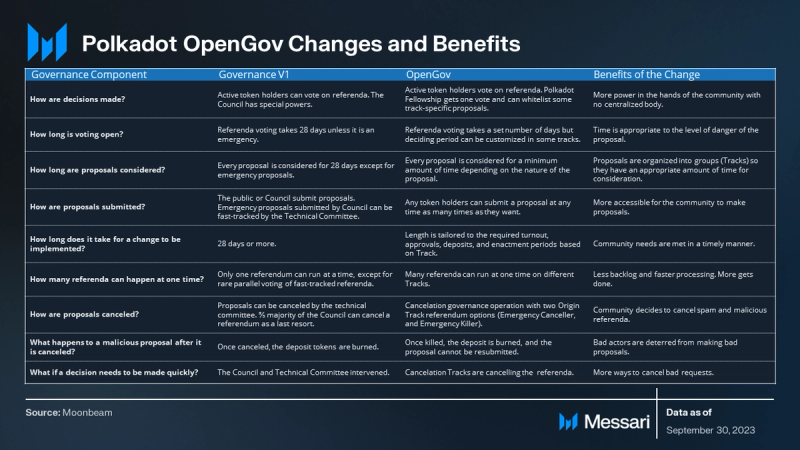
OpenGov, the new governance model for Polkadot launched in Q2 2023, marking an important milestone after months of anticipation. Referendums in the OpenGov system undergo a structured life cycle for enactment, including the Lead-in Period for proposal submission, the Decision Period for voting and approval, and the Enactment Period for execution. Open Gov allows multiple referenda to run concurrently, allowing for the faster passage of motions. During the initial six months of OpenGov operating on Kusama, the number of proposals increased more than four-fold compared to the previous year.
In the OpenGov system, the Council and Technical Committee have been replaced by the Fellowship, which acts as a developer DAO and ensures decentralization through community voting and checks and balances. Additionally, the new model introduces flexibility for delegation, allowing users to delegate their voting power based on conviction and the number of tokens committed.
Following the launch, Parity Technologies shared details on its ongoing relationship with Polkadot and the evolution of its role within the network. Parity has stated that “go-to-market will be more effectively driven by the broader Polkadot community” and is therefore “sunsetting its go-to-market functions to make room for the emergence of new ecosystem leaders beyond Parity.” According to the team, future initiatives will focus on “delivering Polkadot’s next-gen technology, improving the developer experience, and fostering a strong developer community.”
Roadmap
Polkadot has completed and shared the official release of Polkadot 1.0, marking the completion of the Polkadot whitepaper. Additionally, the network’s codebase has been fully transitioned to a repository managed by the community through Polkadot OpenGov and the Technical Fellowship.
The next iteration of Polkadot, Polkadot 2.0 as deemed by the community, will be determined by community discussions and consensus. Polkadot founder Gavin Wood proposed ideas such as “additional, more flexible and capital-efficient mechanisms for allocating Polkadot’s blockspace beyond the parachain model, and an idea for creating opt-in’ treaty-like’ agreements between multiple blockchains called “accords”.
Ecosystem Analysis
XCM
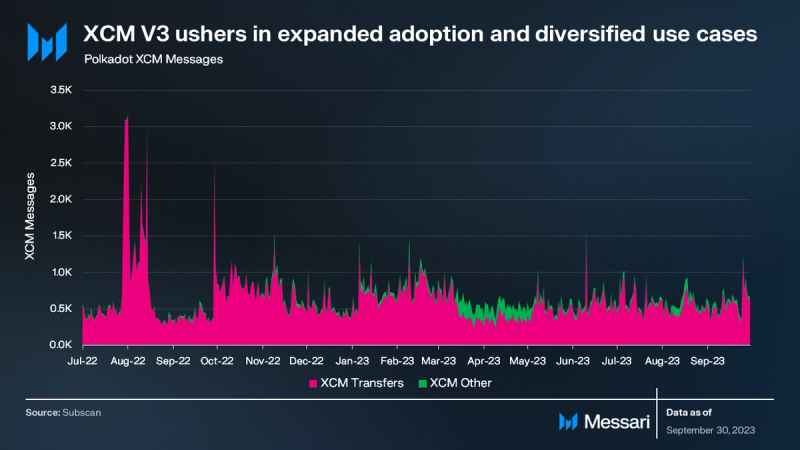
The Cross-Consensus Message Format (XCM) is a standardized messaging format and language that enables seamless communication between parachains and other consensus-driven systems. XCM plays a crucial role in facilitating interoperability and complex cross-consensus interactions. It allows blockchains to exchange messages, perform operations, and transfer assets, among other use cases.
The recent launch of XCM V3 on June 15 has generated significant excitement. This new iteration of the messaging format introduces advanced programmability, bridging capabilities with external networks, cross-chain locking, improved fee payment mechanisms, and support for non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
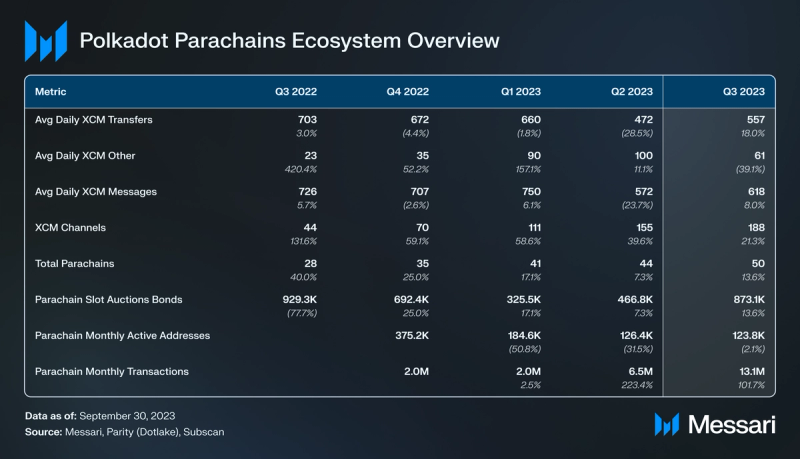
Non-asset transfer use cases accounted for 10% of total XCM messages, a 39% drop QoQ. The number of active XCM channels expanded from 155 to 188.
Parachains
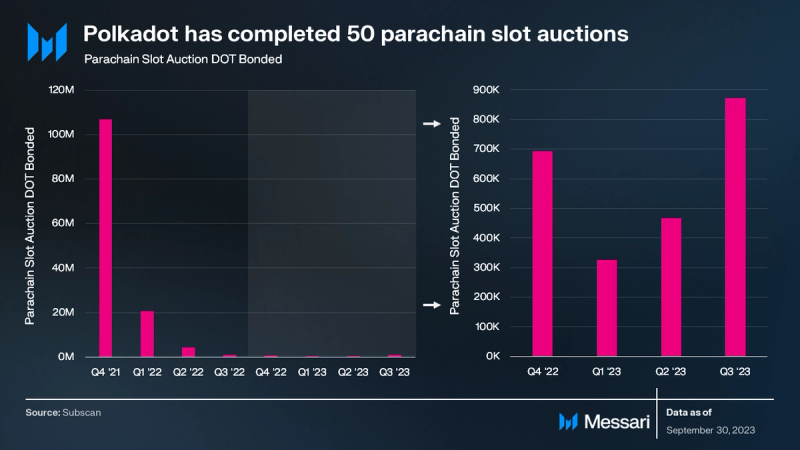
During Q3 ‘23, Polkadot completed six more parachain auctions, bringing the total number to 50.
- Peaq – Enables people to build Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (#DePIN) – incentivizing communities to connect hardware and earn from it.
- Bit.Country – A platform for user-created metaverses, allowing users to launch their own metaverse in 12 seconds, and streamlining the creation process with a library of existing content.
- InvArch – A multichain DAO infrastructure project which features a dynamic multisig solution capable of servicing the entire Polkadot ecosystem.
- Astar (re-sign) – A smart contract platform aimed at enhancing cross-chain interoperability and protocol development across various blockchains.
- Energy Web – Uses Web3 technology to help major names like Shell, Vodafone, and Volkswagen to accelerate their decarbonization strategies.
- Nodle (re-sign) – A connectivity provider for the Internet of Things, building a network powered by Bluetooth low energy to help companies and cities connect.
Overall, 873,000 DOT was bonded (+14% QoQ). Through 50 auctions, 135 million DOT has been bonded.
As part of Polkadot 2.0, the parachain auctions and general model will be overhauled. It introduces a marketplace for allocating “core time” via NFTs, allowing more agile and on-demand access to resources. The new approach aims to address drawbacks and encourage seamless application deployment and collaboration across chains. The transition would shift from chain-centric to application-centric focus within the Polkadot ecosystem.
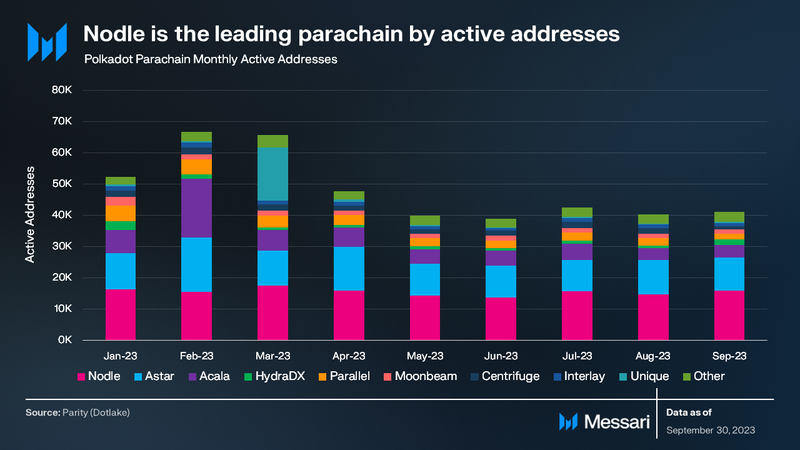
In Q3 ’23, Polkadot’s diverse leading parachains by active addresses showcased a range of specialties. Nodle topped the list with 15,400 monthly active addresses. Smart contract platform Astar followed with 10,600 addresses. Notably, Astar announced it is developing a zkEVM Layer2 using the Polygon CDK. DeFi parachains Acala and Parallel Finance occupied the third and fourth positions with 4,300 and 2,200 addresses respectively. Real World Asset parachain Centrifuge rounded up the top five with 1,600 monthly active addresses.
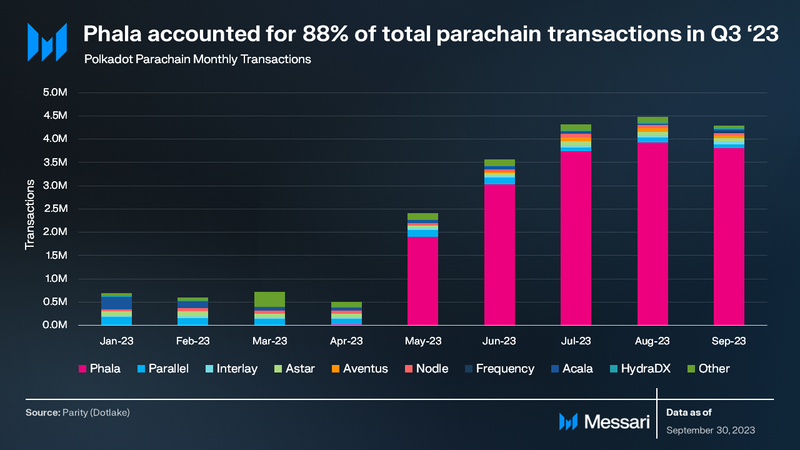
In Q3 ’23, Phala Network led in monthly average transactions with 3.8 million, offering privacy-centric cloud computing. Following were Parallel Finance, Astar, and Aventus with 91,000, 72,000, and 70,100 transactions respectively. Despite Nodle’s lead in active addresses, it ranked sixth in transactions with 66,000 monthly average transactions, underscoring the varied focus and performance across different parachains,
Additional notable parachain announcements from the third quarter include:
- Kilt is contributing to the transformation of the energy sector in Germany by providing the infrastructure for DIVE, a project commissioned by the German Energy Agency (dena).
- Beatport, the renowned music platform, launched a new NFT marketplace called Beatport.io in collaboration with design studio Define Creative on Aventus.
- Sony Network Communications, a subsidiary of Sony, announced a joint venture with crypto tech firm Startale Labs (joint venture firm of Astar) to develop a new blockchain platform.
- Circle launched native-USDC on the Polkadot Asset Hub.
- Moonbeam introduced Moonbeam Routed Liquidity (MRL). This allows parachains to tap into bridge liquidity from ecosystems, including Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, and Avalanche, without the need for a Moonbeam account or its direct involvement. HydraDX was the inaugural parachain to utilize MRL, facilitating the cross-chain transfer of Wormhole-based tokens and streamlining liquidity movements from Ethereum to HydraDX through Moonbeam.
Closing Summary
In Q3 ’23, Polkadot witnessed significant advancements on several network development fronts. The milestone of completing Polkadot 1.0 was announced by Parity, marking the fulfillment of the Polkadot whitepaper. The community now anticipates the next iteration, which it is calling Polkadot 2.0, to be shaped through community discussions and consensus. The annual developer conference, sub0, unveiled critical network enhancements. Key highlights included Asynchronous Backing which will significantly bolster Polkadot’s throughput and scaling – specifically in terms of flexibility in blockspace coordination and the introductions by Open Zeppelin and Moondance Labs aimed at simplifying appchain deployment.
The quarter also saw a 12% QoQ rise in DOT staked, reflecting the efficacy of Polkadot’s staking mechanism. Integration milestones included Wormhole’s routed liquidity via Moonbeam and the launch of Native USDC on Polkadot’s Asset Hub. Additionally, with an average of 2,000 active developers monthly, Polkadot continued as the second-largest ecosystem by developer count.
Overall, Polkadot has completed 50 auctions with 135 million DOT bonded. Nodle was the leading parachain by monthly active addresses with 15,400, and Phala Network was the leading parachain by monthly transactions with an average of 3.8 million.
Looking ahead, Polkadot 2.0 aims to further decentralize development and governance. These strides underscore Polkadot’s ongoing evolution, setting the trajectory for continued network growth and development.






















