New Economy Movement (NEM) is an enterprise-grade solution to power the impending blockchain economy. Originally intended to be a fork of NXT, the community decided to go with a completely new codebase with an alpha version released June 25, 2014, and the first stable release March 31, 2015. The platform is currently being rewritten in C++ and will be released as the “Catapult” update sometime in early 2018.
The Smart Asset System
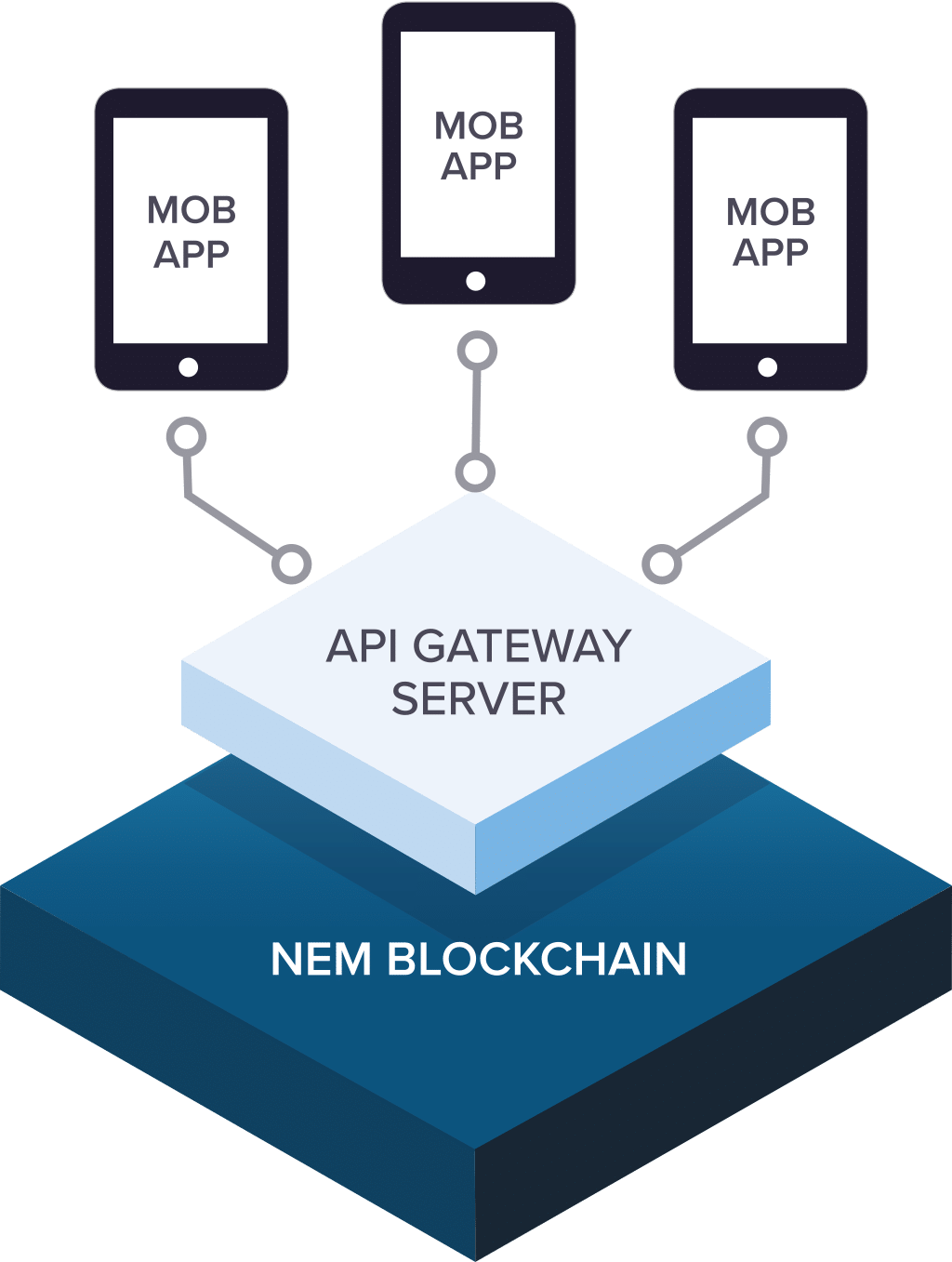
The NEM blockchain powers what they call the Smart Asset System. This system is intended to be an open, customizable blockchain solution for any number of use cases built on top of simple, powerful API calls. The blockchain is secured and transactions are processed by a global network of nodes running the NEM core software, and the network is used as an API Gateway server.
This means developers looking to build blockchain powered apps don’t need to run any special NEM software as all of the NEM functionality is available by accessing API calls.
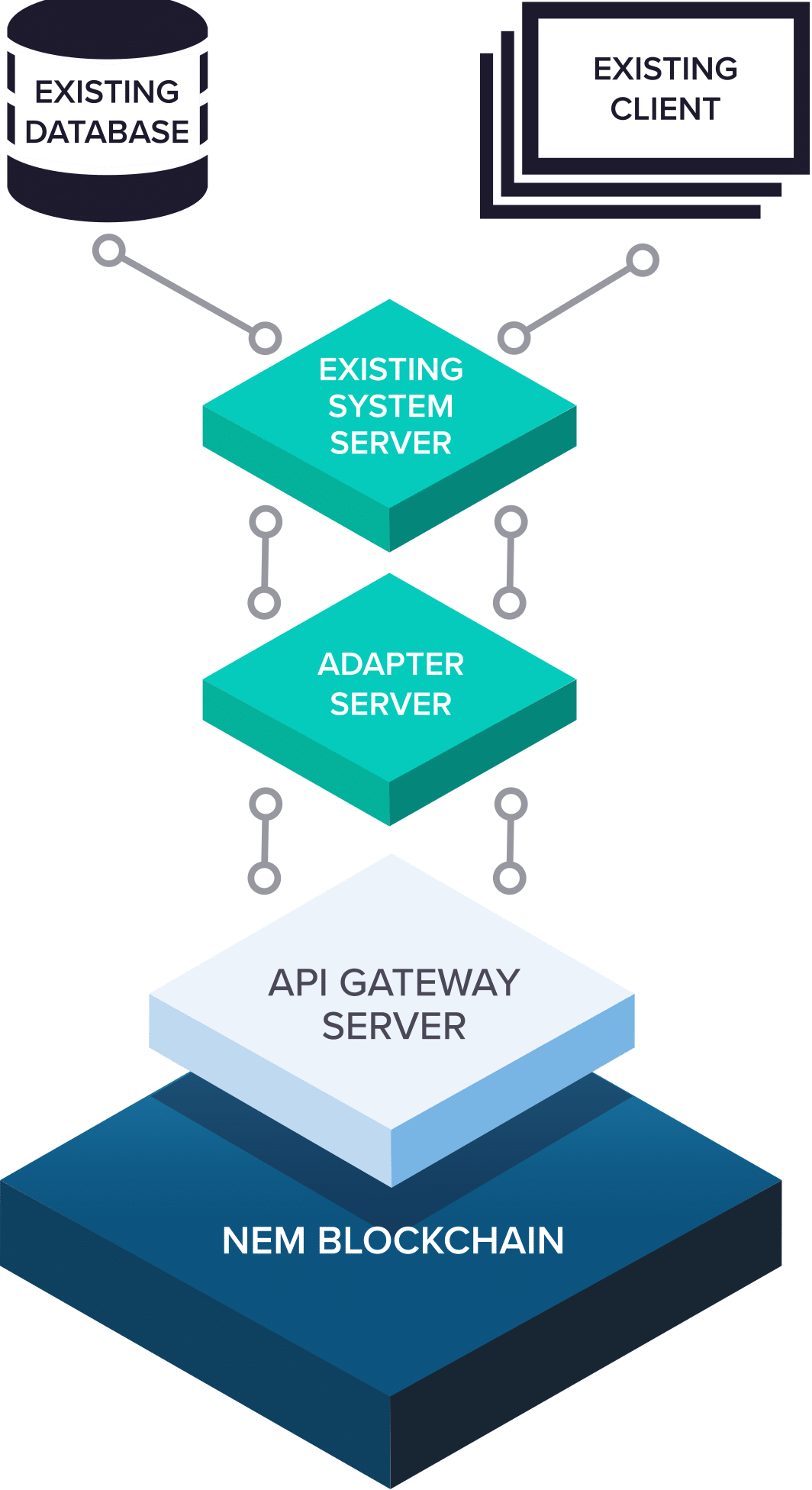
This allows for a lot of flexibility when it comes to system design and how various apps are making use of the NEM network. Apps can access the NEM API directly, access a separate server in addition to making NEM requests, or existing servers can be adapted to make use of NEM in the background.
Developers define NEM Addresses that act as containers for assets and can be updated and changed over time. An Address could represent simply a wallet holding coins or something more complicated like a document that requires signatures or an election that is collecting votes.
The developer would then create Mosaics: identical, transferable assets that represent the coins, signatures, or votes that will reside in the Addresses. This system of flexible addresses and configurable mosaics is viable for countless use cases, and since all of the NEM functionality is accessed through the NEM API, anyone can build any sort of system they dream up and hook it into the NEM blockchain with relative ease.
Proof-of-Importance and Harvesting
The NEM Blockchain employs a Proof-of-Importance algorithm (as opposed to Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work or PIVX’s Proof-of-Stake) to achieve consensus through a process that incentivizes active participation in the network. This makes for a decentralized, nimble network of well-behaved nodes. Each node has an importance score that determines how often it can harvest (think mining or staking in PoW or PoS systems) XEM, NEM’s native token.
Part of this system works by vesting coins: when you place coins in your wallet, they start out as unvested coins.
Over time, your coins will begin to vest or count toward the importance of your account. In order to be eligible for an importance score, your account must have at least 10000 vested XEM.
This part of the system acts just like staking coins in PoS setups but is only one part of calculating your importance.
In addition to tracking vesting, the transaction graph of the NEM network is constantly analyzed to provide information on which nodes are contributing and which are not. This means that the more transactions you send to other users and the more you use the network normally, the more important you become. The vesting process and transaction metrics result in an importance score for each node, and these scores are used to scale the likelihood of your node harvesting XEM.
Since PoI is not hardware intensive, it allows full nodes to be run on almost any machine regardless of power, preventing centralization of harvesting to those with the biggest machines.
Since it requires a time commitment via the vesting process, it prevents the “rich get richer” effect of many staking systems wherein those with the most money immediately become the biggest earners and cannot be outpaced.
In some systems like Bitcoin, mining blocks and running a network node are separate. In the NEM system, running a node to secure the network and harvesting coins is done by the same software, incentivizing running a full node and leading to more decentralization over time as harvesting becomes more profitable.
Overall, the PoI system is unique and seems promising, an excellent alternative to traditional consensus methods that all comes with their share of strengths and weaknesses.
Other Blockchain Features
NEM uses a custom version of the Eigentrust++ algorithm that implements a “reputation system” for nodes on the network. Basically, each node keeps track of the information it receives from other nodes (new blocks, transactions, etc.) and then verifies this information.
If the information proves valid, the reputation of the providing node will increase, and if it’s bad info the reputation will decrease. The reputations of all nodes are then passed around the network and updated within each node. This allows for automatic load balancing and removing bad nodes from the network, keeping the network running as smoothly and quickly as possible.
Additional Features:
- Built-in spam filters that prevent garbage transactions from flooding the network and clogging up the works
- A P2P time synchronization system that allows the network to maintain accurate timestamps without relying on any outside servers for checking the time
- Encrypted messaging on the blockchain without hacking transaction fields to carry data like other coins
- Multisignature addresses allow developers to define shared addresses and multiparty control over assets and containers
Information on the technology described here and can be found on the NEM technology page and in more technical detail in their technical reference.
Public vs. Private
Anyone can use the public NEM blockchain by making use of the API calls as described above, but for applications that require more privacy or wish to keep things in-house, a private version of the NEM blockchain can be provisioned to run on internal servers and only make use of predefined nodes of the users’ choosing. On these trusted, private node networks, some features of the public network that are in place to prevent bad nodes from causing problems can be removed or reused in scope, allowing for even faster transactions (into the thousands/second) in a closed box setup.
These private blockchain deployments can be used to power anything from loyalty points programs to shipping fleet logistics, all without ever exposing the transaction data and providing unparalleled speed and security. This makes a lot of sense for companies that want to use the blockchain to power up their existing internal tools and don’t need the added functionality of the public chain. Use cases for the NEM system public and private are explored on their website at https://nem.io/enterprise/.
Final Thoughts
NEM offers a truly impressive system that promises to be a major player in the coming blockchain powered economy. The ease of development, flexibility, and unique PoI system make NEM a very attractive platform for any developer or company that’s looking to build out a blockchain solution.
As time moves on, I think we’ll see more and more interesting projects being built on top of NEM. Keep an eye on it!
The post What is NEM Cryptocurrency? | Beginner’s Guide appeared first on CoinCentral.