Key Insights
- In October 2024, Velo transitioned from its initial focus on digital credit issuance to the tokenization of Real-World Assets (RWAs), while also integrating the Omni Point loyalty program through its consumer super app, Orbit.
- Velo operates on Stellar and Nova’s blockchain infrastructure, with planned additional multichain support to reduce transaction costs, increase speed, and ensure a seamless user experience.
- As of October 2024, Velo Finance reports a Total Value Locked (TVL) of $19.22 million, while Nova has processed 17,367 transactions across 3,404 wallet addresses.
- The VELO token supply was reduced by 6 billion in 2022, adjusted from an initial 30 billion to 24 billion through strategic burns and swaps.
- Partnerships with industry giants such as Visa, Securitize, and the Solana Foundation highlight Velo’s commitment to expanding RWA offerings and cross-border payment capabilities.
Introduction
While blockchain technology has matured, it has also faced challenges in scaling, interoperability, and integration with traditional finance systems. Various decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms have introduced innovative ways to transact, yet remain fragmented, complex, and inaccessible to the average user. Velo addresses these issues by providing a seamless solution that simplifies cross-border transactions, enables the tokenization of Real World Assets (RWAs), and enhances everyday payments through its Orbit platform and Omni Point loyalty program.
Notably, Velo has undergone significant strategic shifts since its inception in 2018. Initially, in 2020, the platform focused on its Digital Reserve System (DRS) and digital credit issuance mechanism, aiming to facilitate secure cross-border settlements. By December 2023, Velo shifted its focus toward becoming a decentralized Web3 payment network (e.g., VeloDAO), while also introducing their Identity Framework as an additional feature. In October 2024, the project expanded its focus to include the tokenization of Real World Assets (RWAs) and introduced Orbit, a consumer super app.
Background
Since its launch in 2018, Velo has evolved from building a decentralized financial payment network to advocating for broader blockchain adoption, with finance as its first targeted industry. Velo integrates traditional finance with Web3 solutions, improving transaction speeds and reducing fees without altering the user experience or replacing the system itself. End-users will not directly interact with the blockchain but will benefit from more efficient and cost-effective transactions. To do so, Velo has released a suite of products and tools, which include Universe (a hybrid DEX), Warp (bridging platform), Nova (EVM-compatible blockchain), Quantum (remittance network), PLG (tokenized gold), and Orbit (consumer payment super app).
With these tools, Velo solves fragmentation in global payment systems, especially in regions lacking banking infrastructure, by enabling seamless, cross-border transfers of fiat, digital, and real-world assets. According to a 2022 study from the IMF, remittance costs associated with sending money worldwide were as high as 16.60%. Many corridors still have fees above 5.00%, far exceeding the UN’s sustainable development goal of keeping average fees below 3.00% by 2030. Led by CJ (Founder) and TA (Vice Chairman) and advised by Jed McCaleb (Founder of Stellar), Prof. David Mazières (CSO of Stellar and Stanford Professor), Prof. Robert Townsend (Economics at UC, MIT, and CMU), John Ng Pangilinan (Founder of Signum Capital) and Paul Veradittakit (Partner at Pantera) – Velo has acquired partnerships with large companies (e.g., Visa and Copper) and has recently raised $60+ million from investors DWF Labs, LDA Capital (for Lightnet, a partner company), and UOB Venture Management.
Technology
Velo is a blockchain-powered financial infrastructure that connects traditional finance with Web3 applications. Velo uses Stellar for fast, low-cost transactions and Nova for EVM-compatible smart contracts, simplifying cross-border value transfers, while also supporting multiple chains. The Warp bridge accompanies this, allowing effortless token transfers across multiple blockchains. At the same time, Orbit powers a decentralized loyalty program that integrates Web2 and Web3 rewards via the Omni Point loyalty program and a robust merchant network. This framework supports various financial activities, from tokenizing RWAs to driving DeFi mechanisms.
Base Transaction Infrastructure
Velo uses both the Stellar and Nova blockchains to facilitate seamless cross-chain interactions. Initially, Velo was built on Stellar due to its high transaction speed, efficiency, and low-cost operations. However, until February 2024, Stellar lacked smart contract functionality, limiting its ability to handle complex operations. To address the limitations of Stellar’s lack of smart contract functionality, Velo expanded to the BNB Smart Chain. While BSC offered more affordable transaction fees, the cost still posed a significant hurdle for users. To solve this, Velo introduced Nova in 2022 – an EVM-compatible blockchain specifically designed to eliminate gas fees and provide a more efficient blockchain infrastructure for the Velo ecosystem.
Cross-Chain Architecture and Warp Bridge Mechanism
The core technology that allows this interaction between Stellar and BSC, or any other smart contract-compatible blockchain (e.g., Nova, TRON, Solana, or TON) in the future, is Velo’s Warp bridging system. This system employs Stellar’s hash timelock contracts (HTLC) to enable cross-chain asset transfers.
Warp securely and efficiently moves VELO tokens between Stellar and a smart contract chain (e.g., BSC) as follows:
- A trusted partner, a vetted and authorized business entity that can issue and manage digital credits within the platform, initiates the transfer of VELO tokens from Stellar to BSC using Warp via the user interface.
- HTLC creates a cryptographic hash that serves as a unique identifier for the token transfer.
- VELO tokens are locked on Stellar, allowing Warp to generate a corresponding smart contract on BSC.
- The smart contract incorporates the cryptographic hash, ensuring the transfer can be traced and linked between Stellar and BSC.
- Warp unlocks an equivalent number of VELO tokens on BSC, locking them with the provided hash.
- The trusted partner uses the hash to call the “mint” method function on the smart contract, converting the VELO tokens into digital credits on BSC, allowing them to be utilized with the ecosystem.
- A trusted partner uses the hash to call the “redeem” method function on the smart contract, allowing them to re-access the VELO tokens on BSC. Once the hash is verified, the tokens are unlocked.
To move the tokens back to Stellar, the trusted partner can initiate the “redeem” method function. This locks the VELO on the smart contract chain, while Warp facilitates the unlocking of the corresponding VELO on Stellar.
Orbit’s Omni Point Loyalty Program
In Velo’s RWA-focused litepaper, they discuss a loyalty program that combines traditional Web2 and Web3 systems, creating an ecosystem for earning and redeeming rewards (i.e., Omni Points and OM tokens) through various Web2 and Web3 activities.
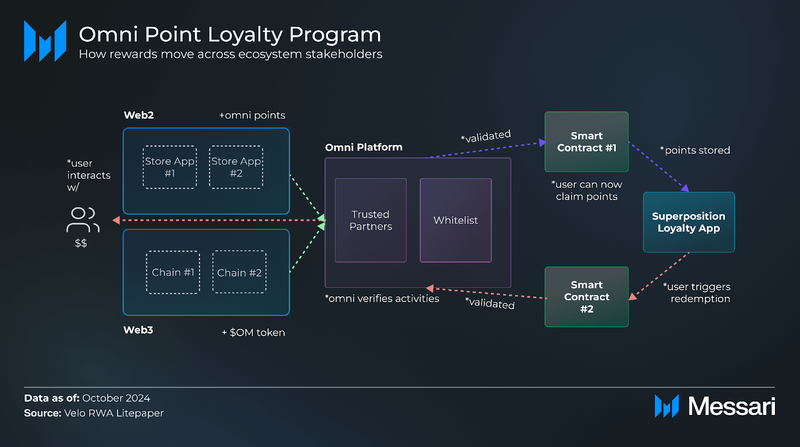
Here’s how the system works to facilitate the flow of Omni Points and OM tokens:
- To earn said points and tokens, users can engage in Web2 (e.g., marketing campaigns and loyalty programs) and/or Web3 (e.g., staking and trading) activities.
- The Orbit platform/server validates the user’s participation and eligibility for rewards based on trusted partners and/or airdrop whitelists.
- Once validated, “Smart Contract #1” is triggered, enabling the user to claim points and tokens. During this, Velo will cover the user’s gas fees.
- Points and tokens are stored in the user’s Superposition Loyalty Point app, which supports multichain wallets for managing points across blockchains.
- When users wish to redeem points and/or tokens for vouchers/rewards, they initiate the redemption process via the Superposition Loyalty Point app.
- This triggers “Smart Contract #2,” which facilitates redemption and adjusts the user’s point balance on the app.
- The Orbit platform/server validates the vouchers/rewards, ensuring legitimacy.
- The user receives the vouchers/rewards, which can be applied within Velo’s multi-market merchant network.
Throughout this process, users interact with Orbit’s easy-to-use app interface without being exposed to the complex underlying technology.
Identity Framework
In the most recent litepaper, Velo outlines its identity framework – a solution that combines the advantages of KYC and KYB verification with blockchain’s inherent anonymity. This framework is designed to find a balance between regulatory compliance and users’ private identity through a two-tiered system:
- KYC/KYB Verification Blockchain: Ensures all ecosystem participants are validated entities.
- Anonymous Blockchain Layer: Enables self-custodian interactions using encryption techniques and wallet address identity-preserving protocols, while maintaining the network’s integrity and security.
Additionally, the framework supports different types of interactions based on varying levels of privacy:
- KYB/KYC to KYB/KYC: Ideal for financial institutions wanting to onboard new corporate clients. Institutions can securely verify the business credentials of new clients, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements with improved efficiency.
- KYB/KYC to Anonymous: Ideal for e-commerce platforms, allowing verified sellers to transact with buyers through their Web3 identity, ensuring that sellers are verified while buyers can maintain anonymity.
- Anonymous to Anonymous: Allows users on decentralized platforms to communicate, share content, or transact entirely anonymously, ensuring privacy is maintained, while still benefiting from Velo’s infrastructure.
Staking, Rewards, and Governance Structure
Network Rewards
Velo offers different ways in which users can earn rewards.
- Users can lock VELO tokens in staking pools for a set period. Notably, previous staking efforts have involved CEXs such as KuCoin and OKX.
- Users can provide liquidity to liquidity pools (LPs) on Velo Finance. Yield farming rewards are distributed in VELO and can be found here.
Based on a commercially reasonable search, further details regarding the mechanisms behind each method are not publicly available.
Putting It All Together
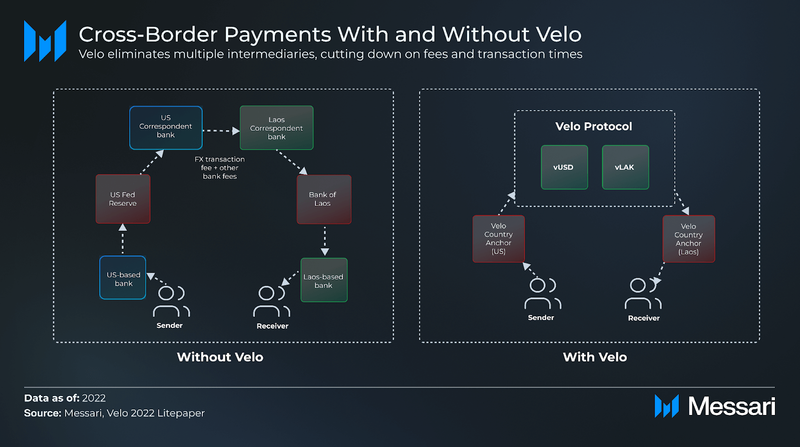
To understand Velo’s broader impact beyond RWAs, it’s important to see how its infrastructure optimizes cross-border payments. The diagram below displays the difference between traditional systems and Velo, highlighting how the ecosystem reduces intermediaries, fees, and speeds up the process.
While the above has covered the network’s unique functions, Velo is also actively creating a suite of products to enhance the ecosystem’s utility, as mentioned in this report’s “Background” section. Some notable products are:
- Universe: A hybrid DEX platform that uses both an automated market maker (AMM) and a dynamic market maker (DMM) mechanism, which also integrates tools such as the Lightyear trading bot. The platform uses two secondary tokens:
- USDV functions as a stablecoin pegged 1:1 with USDT and serves as the primary trading token within the DEX. It is overcollateralized by VELO, digital gold, Blackrock’s BUIDL fund, and OpenEden’s tokenized Treasury Bills.
- USDG is used for trading simulations within Universe. It allows users to practice trading strategies in a risk-free environment and is distributed for free when users first connect a wallet to the platform.
- Universe Wallet: A decentralized trading wallet that integrates with the Universe DEX, allowing users to connect with multiple blockchains, manage assets, and execute trades securely.
- Nova: An EVM-compatible blockchain with high transaction speeds and low gas fees. Notably, the system utilizes a new secondary token, NOVA, which serves as the onchain gas fee. Unlike VELO, Nova has no monetary value and is distributed through faucets to users.
- Velo Finance: The broader platform for DeFi solutions, which includes yield farming, staking opportunities, and decentralized lending options.
- RWA: Tokenizing U.S. Treasury Bills, accounts receivable, and gold into blockchain ecosystems, along with a staking program.
- PLG: In partnership with the Laos government, Velo has introduced the Physical Gold (PLG) tokenization project. This involves tokenizing physical gold reserves, providing users with a stable, gold-backed asset. Previous RWA efforts have included tokenizing real estate but were disbanded due to low demand.
- Orbit: A consumer super app that seamlessly transacts between Web2 and Web3 environments. Users can make payments, earn Omni Points or OM tokens, and exchange these points within Velo’s multi-market merchant network.
- Quantum (Remittance Network): A blockchain-powered remittance platform where traditional financial institutions connect with vetted businesses, known as Trusted Partners – allowing end users of each partner to benefit from faster transactions, lower fees, and broader coverage.
VELO Token
Token Functions
VELO is the native token of the Velo ecosystem and was originally issued on Stellar, making it compatible with Stellar native wallets. VELO also exists as a BEP-20 token on BNB Smart Chain through a wrapped version. This wrapped VELO is compatible with EVM-native wallets such as MetaMask and can be acquired through CEXs and DEXs. It serves multiple purposes within the ecosystem, including:
- Acting as collateral for digital credits (e.g., the USDV stablecoin);
- Staking in return for rewards;
- Covering transaction fees across the platform; and
- Reducing fees and earning rebates via Orbit.
Tokenomics
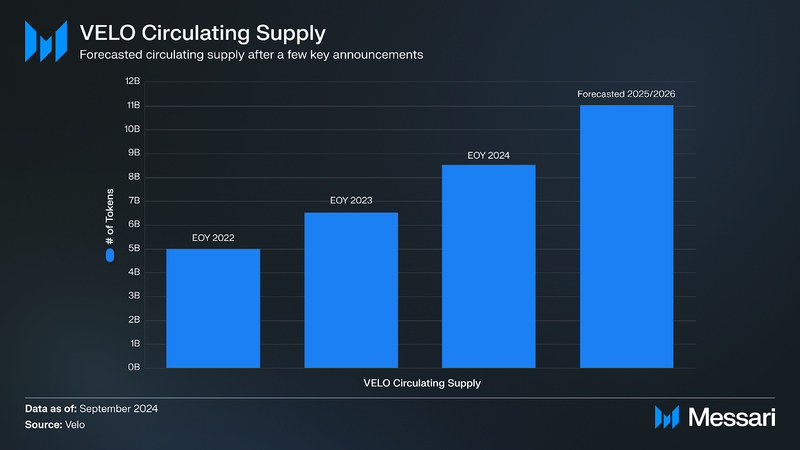
VELO originally had a maximum token supply of 30 billion, but it was reduced to 24 billion after a 6 billion token burn in 2022 spread across six months. A commercially reasonable search found no disclosure(s) of other planned token burns. The circulating token supply as of September 20, 2024, is ~7.39 billion, reduced from a projected ~10.78 billion due to:
- A token swap with Stellar where VELO was exchanged for XLM; and
- Distribution delays, where the vesting schedules for founders, select investors, and advisors were extended for up to two years.
To support ecosystem expansion, the circulating token supply is forecasted to reach ~11.04 billion by 2025/2026, as depicted in the chart below.
VELO Token Allocations
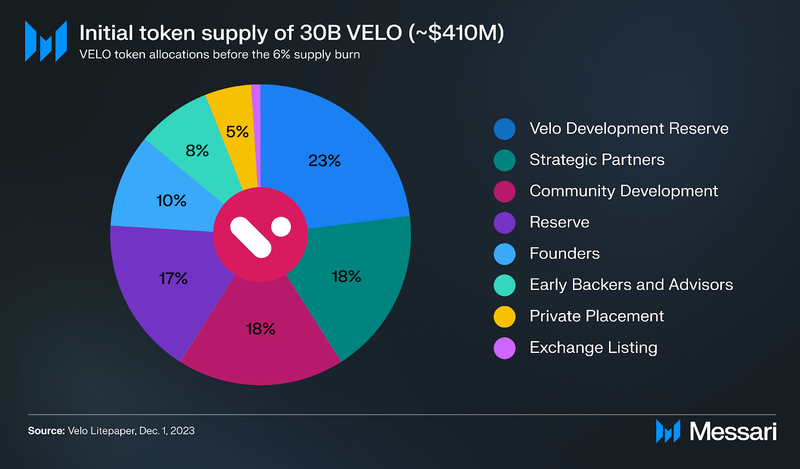
Notably, the above pie chart depicts the initial token allocations. However, after the token burn, percentages of the new 24 billion VELO maximum token supply have changed as follows (valued at approximately $328.08 million USD, as of October 18, 2024, with VELO priced at $0.014):
- Velo Development Reserve: 20.83% (5.00 billion VELO, $68.35 million)
- Strategic Partners: 22.85% (5.48 billion billion VELO, $74.97 million)
- Community Development: 14.51% (3.48 billion VELO, $47.62 million)
- Reserve: 12.50% (3.00 billion VELO, $41.01 million)
- Founders: 12.50% (3.00 billion VELO, $41.01 million)
- Early Backers and Advisors: 9.88% (2.37 billion VELO, $32.40 million)
- Private Placement: 6.10% (1.46 billion VELO, $20.03 million)
- Exchange Listing: 0.83% (199.20 million VELO, $2.72 million)
Vesting
As mentioned above, vesting schedules for founders, select investors, and advisors were extended by up to two years. Furthermore, reserve tokens are perpetually locked.
- Private Placement: Vesting is complete
- Founders: Unlocked over five years (10%, 10%, 25%, 25%, 30%, respectively)
- Early Backers and Advisors: Vesting at 25% every six months over two years
- Strategic Partners and Community Development: Vesting in 1/60th increments monthly over five years
- Velo Development Reserve: Same as founders, 10-30% over five years
Roadmap
The 2024 roadmap for Velo has been updated as of September 2024 to reflect the latest developments and future plans. Below are the key milestones:
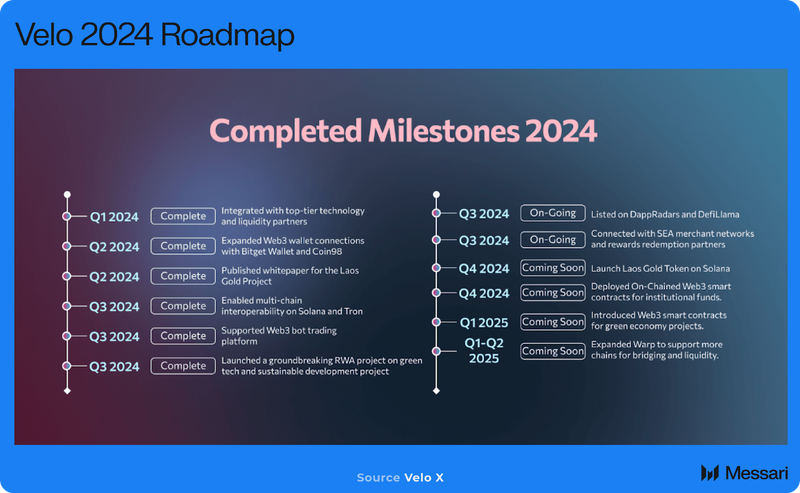
Additionally, here are a few recent announcements from Velo:
- October 2024: Collaboration with Sofinx, specifically integrating their social and copy trading tools to improve the user experience of Velo’s Universe hybrid DEX.
- September 2024: Assets backing Velo’s USDV stablecoin now include (i) BlackRock’s tokenized short-term treasury fund (BUIDL), tokenized by Securitize, and (ii) OpenEden’s Treasury Bills. This follows Velo’s recent partnership with the Laos government to tokenize the country’s gold reserves (Laos Bullion Bank).
- May 2024: Integration of Centroid Solutions’ multi-asset bridge technology, which connects brokers to various liquidity sources and optimizes trading activities across markets.
- April 2024: Velo and its partner Lightnet signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the Solana Foundation for the Laos gold project. Solana will serve as the blockchain settlement layer, while Velo provides the infrastructure and acts as a clearing house for digital gold transactions.
- January 2024: Velo signed an MOU with Laos conglomerate, PTL Holdings, to drive Web3 finance in Laos. They also integrated Uppsala Security’s digital asset tracking and AML protection solutions into their ecosystem. This includes adding Chainkeeper, an AML tool, to enhance compliance and security.
Closing Summary
Since its launch in 2018, Velo has pivoted its strategy toward tokenizing real-world assets (RWAs), including U.S. Treasury Bills, accounts receivable, and gold. Innovations like (i) Universe, a hybrid DEX, (ii) Warp, a cross-chain bridge solution, and (iii) Nova, an EVM-compatible blockchain, are central to its mission of improving global financial transactions. Recent partnerships with the Solana Foundation and the Laos government highlight Velo’s growing influence in digital and traditional finance sectors. With plans to expand its ecosystem through projects like Orbit and its Omni Point loyalty program, Velo is ready to continue enhancing cross-border payment efficiency and accessibility.




















