Key Insights
- Panther Protocol is creating a decentralized, privacy-enhancing layer for decentralized finance (DeFi) that meets regulatory requirements while protecting user data.
- Panther has partnered with Eurobit to help them become the first VASP-licensed Zone Manager. Panther has also partnered with PureFi, a KYC/KYT provider, to expand their role in the Panther ecosystem and become a Zone Manager.
- UTXOs are fundamental to Panther’s privacy solution as they represent both digital assets (zAssets) and user accounts (zAccounts) within the Shielded Pools. By leveraging UTXOs and ZKPs, Panther ensures that the details of transactions, including the sender, receiver, and amounts, remain hidden from public view while still maintaining a verifiable and immutable record of activity on the blockchain.
- Shielded Pools in Panther are specialized smart contract environments where users can deposit assets, convert them into privacy-enhanced zAssets, and trade within the pool without their transactions being publicly visible. These pools are designed to enhance privacy in DeFi by leveraging ZKPs to obfuscate transaction details while allowing for selective disclosure of information for compliance purposes.
- DeFi adaptors will allow users to interact with external DeFi protocols directly from Panther’s Shielded Pools. This enables privacy-conscious users to engage in activities like swapping assets (using zSwap), providing liquidity, and staking, all while preserving the privacy of their transactions and identities.
Introduction
The lack of financial privacy is a problem that is commonly known but unaddressed, as people believe it cannot be fixed. Unlike traditional financial systems that rely on intermediaries to safeguard personal and transactional information, blockchain technology operates on a decentralized and transparent ledger, inadvertently exposing sensitive financial data and making individual transactions traceable. While fostering trust and accountability, this transparency poses significant risks such as surveillance, identity theft, and targeting by malicious actors. Achieving a satisfactory level of privacy must be carefully balanced with regulatory compliance to prevent illicit activities like money laundering and terrorism financing. This delicate equilibrium underscores the need for sophisticated privacy-enhancing technologies that offer robust user protection while adhering to necessary compliance standards.
Panther Protocol aims to strike this balance by leveraging advanced cryptographic techniques to provide a privacy-preserving framework across DeFi ecosystems. By integrating zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs), and other cutting-edge technologies, Panther addresses the critical need for privacy without compromising on transparency and regulatory compliance.
Background
Panther Protocol, founded in 2021, is a zero-knowledge cross-protocol layer unlocking compliant DeFi. Panther aims to create a fully decentralized, multi-chain, privacy-enhanced protocol that allows VASP-licensed entities to create customizable trading environments. Panther is building the infrastructure needed to realize this vision. Through the use of UTXOs, liquidity partitioned Zones run by Zone Managers, Shielded Pools, Compliance Tools, and DeFi Adaptors, Panther is well on the way to providing a privacy-preserving framework with onchain access and is currently on the 8th stage of its testnet, with the 9th stage (Panther’s canary network) coming soon.
Panther Protocol was co-founded by Oliver Gale and Dr. Anish Mohammed. Oliver Gale joined the crypto space in 2013, launched one of the first CBDC pilots in the Caribbean, and participated in policy discussions on the world stage with the UN, IMF, and many central banks. Dr. Anish Mohammed has spent over two decades in the security and cryptography space with an emphasis on researching cryptographic algorithms. Dr. Mohammed was also an early advisor to Ripple, Ocean Protocol, and part of the Ethereum Swarm (Orange) team, where he reviewed the Orange paper.
Since its inception, Panther has raised $31.80 million across three private funding rounds and one public token sale.
Technology
Panther Protocol is deploying a set of smart contracts onto EVM-compatible blockchains that will deliver a privacy-focused experience to end users. At the heart of Panther’s framework is the use of advanced cryptography. Panther leverages Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) in the form of Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge (ZK-SNARKs) – specifically the Groth16 variant – enabling (i) users to selectively disclose transaction histories and maintain control over their data, and (ii) Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) for efficient key agreements and secure digital signatures through the Elliptic-curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) protocol.
Beyond cryptography, Panther integrates various Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PETs) such as selective disclosure schemes. This technology ensures individual privacy is kept and allows users to reveal only necessary parts of their data as needed. This all combines to provide a cross-protocol layer to build DeFi solutions that meet customizable regulatory requirements while providing onchain data privacy.
UTXOs
UTXOs, Unspent Transaction Outputs, form the foundation of Panther Protocol’s privacy-enhancing solution. Unlike the account-based model used by many blockchains, where balances are associated with accounts, Panther leverages a UTXO model where each UTXO represents a specific amount of a zAsset. These UTXOs are stored as commitments in Merkle Trees, ensuring a verifiable and tamper-proof record of transactions. To spend a UTXO, a user needs to provide the correct cryptographic key, which is uniquely derived for each UTXO.
Panther utilizes UTXOs in several distinct ways, going beyond the traditional concept of “unspent” transaction outputs. UTXOs represent not only zAssets, which are shielded versions of deposited tokens, but also zAccounts, acting as private ledgers within the Shielded Pools. When users transfer zAssets, they are essentially transferring ownership of the associated UTXOs. This process involves creating new zAsset UTXOs for the transferred amount and any remaining change, as well as updating the recipient’s zAccount UTXO. This intricate system of UTXO creation, spending, and updates within the Merkle Trees allows for private and secure transactions within the Shielded Pools, while still maintaining a verifiable and auditable record onchain.
Non-interactive transfers in Panther are key to maintaining privacy for users while using UTXOs. The sender only needs the recipient’s zAccount ID, which is used to find the recipient’s public keys in a table kept by the smart contract. With these public keys, the sender can create a transaction that transfers ownership of a specific UTXO without the recipient needing to be online or take any action at the time of the transfer. This process protects the sender and receiver’s anonymity because their wallet addresses are not directly linked on the blockchain. The transaction details, like the amount being sent, are encrypted until the recipient uses their private key to decrypt them. Even if someone knows the public keys of the sender or receiver, they cannot connect different transactions to the same user because each UTXO has a unique spending key derived from the root spending key.
Panther Protocol´s split and join mechanism optimizes for clarity and efficiency by maintaining the user’s balance in a single large UTXO rather than multiple smaller ones. This allows users to transact any part of their balance with one transaction, avoiding needing an additional Multi-Asset Shielded Pool (MASP) transaction to consolidate UTXOs. However, UTXO merging is not always possible. For example, when Alice transfers zAssets to Bob, an independent UTXO is created for Bob regardless of his existing UTXOs. Additionally, zSwap transactions always generate a new UTXO for the received asset. In these cases, UTXO merging is bypassed.
For deposit transactions, the dApp merges the largest existing UTXO with the deposit amount, creating a new UTXO that reflects the combined total. Advanced settings allow users to select input UTXOs for merging in both deposit and regular transactions, which is especially useful when transferring tokens to CEX/DEX platforms, where proof of fund origin may be required. Only a user’s own tokens can be traced, and obtaining proof of tokens received from others would require the sender’s cooperation, which may not always be practical. Panther Protocol proposes marking incoming UTXOs for users to help maintain an accurate record.
zAssets
zAssets are private representations of assets deposited and locked in the Panther Vault and Shielded Pools. zAssets maintain a 1:1 collateralization ratio with the underlying assets. To maintain privacy, zAssets use ZK-SNARK proofs to store the UTXO data onchain and link the zAsset to specific zAccounts. Once users have their zAssets, they can take various actions within Shielded Pools (e.g., deposit, withdraw, swap, stake, and bridge). By obfuscating transaction histories and asset holdings, zAssets enhance user privacy within Panther Protocol, all while adhering to regulatory compliance overseen by Zone Managers.
zAccounts
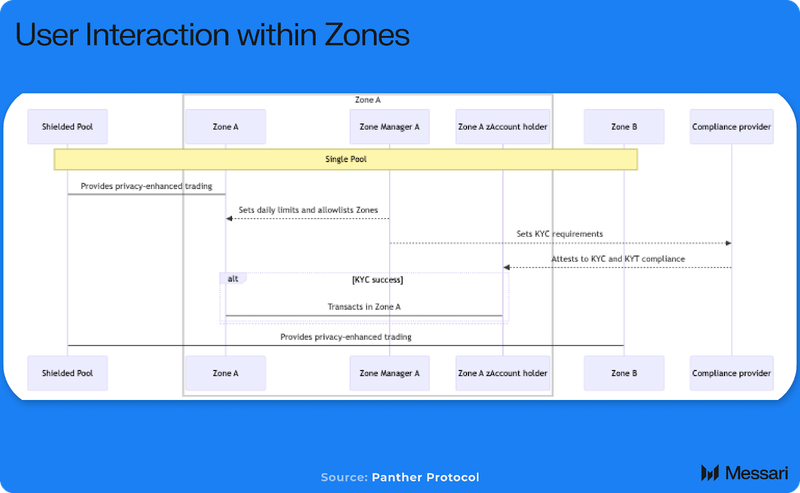
zAccounts in Panther Protocol serve as a user’s private gateway into a specific Zone within the Shielded Pools. zAccounts act as a private ledger that separates a user’s transactions from their publicly visible Externally Owned Account (EOA), allowing them to verify their trades and balances in a privacy-preserving manner. To create a zAccount, users must undergo a KYC verification process defined by the Zone Manager for that particular Zone. This verification is handled by third-party compliance providers, as the protocol itself does not process personal data. Once activated, the zAccount ID, linked to two root public keys (spending and reading), is publicly listed in a lookup table maintained by Panther’s smart contracts. These keys are needed to access and spend zAssets.
By integrating zAccounts with UTXOs, ZK-SNARKs, and non-interactive transfers, Panther allows users to engage in DeFi activities through DeFi Adaptors while maintaining control over their financial data, striking a balance between privacy and regulatory compliance within a secure and transparent framework.
Zone Managers
Zone Managers function as the gateway into Panther. The initial deployment of Panther Protocol requires Zone Managers to be VASP-licensed operators and are subject to the approval of the Panther DAO through a Panther Improvement Proposal (PIP). Each Zone Manager is able to customize the requirements to join their Zone to meet specific regulatory requirements, including blacklisting zAccounts. Zone Managers are the lynchpin for enabling compliant access to DeFi on Panther. The first VASP-licensed operator gearing up to apply to create their own Zone is Eurobit. If the Panther DAO approves, Eurobit will gain the designation of a Zone Manager and configure their Zone within Panther’s Multi-Asset Shielded Pool. PureFi, a KYC/KYT compliance tool, is also applying to become a Zone Manager in addition to its current role in the Panther ecosystem as a KYC/KYT provider.
How Zone Managers work:
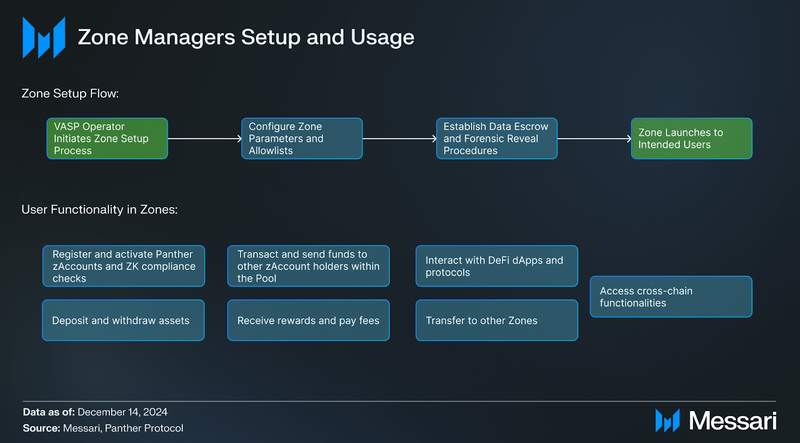
- Zone Managers determine the specific purpose of the Zone and its intended user base:
- User bases include institutional clients, retail users, or a specific niche within the DeFi space.
- This initial step is crucial for shaping the Zone’s compliance requirements, features, and operational parameters. For example, a Zone designed for institutional clients might require more rigorous KYC procedures and higher transaction limits than a Zone targeting retail users.
- Configure Zone Parameters and Allowlists:
- Zone Managers configure operational parameters, including transaction limits, trading fees, and supported assets.
- Zone Managers determine which other Zones users can trade with via the Shielded Pools.
- Zone Managers can create allowlists for specific users, assets, and trading pairs, enabling a controlled and compliant trading environment.
- Establish Data Escrow and Forensic Reveal Procedures:
- Zone Managers are responsible for setting up data escrow mechanisms to store encrypted transaction data for potential future disclosure to regulatory bodies.
- Zone Managers work with specialized data escrow providers and define the procedures for forensic reveals, ensuring that these comply with legal requirements and data privacy regulations.
- Integration with Panther Protocol and Go-Live:
- Once the Zone is configured, the Zone Manager integrates it into Panther.
- The Zone Manager tests the Zone’s functionality and compliance mechanisms before making it available to users.
Shielded Pools
Zones are created within Panthers Shielded Pool to facilitate the trade of zAssets by zAccounts and shield the external wallet addresses linked to accounts. At a high level, a Shielded Pool is a set of smart contracts where users can deposit tokens secured by ZK-SNARKS to be able to trade with privacy. A Shielded Pool is split into Zones, which are partitions of liquidity based on different entrance requirements set by Zone Managers.
Shielded Pools, currently only on Polygon, can be deployed on different Layer-1 or Layer-2 blockchains. Through the Multi-Asset Shielded Pool, these pools can support multiple asset types and the non-interactive transfer of zAssets in Zones, enabling two parties to transact without knowing or revealing their EOA’s. Transactions in a Shielded Pool are not observable directly onchain, allowing users to have optionality in what information they want to disclose based on compliance requirements.
zAccounts that meet the requirements to gain access to multiple Zones can transact and send funds to other zAccount holders within those pools, receive rewards and pay fees, interact with DeFi Adapters, and access other cross-chain functionality.
Relayers
The Panther Relayer is an optional service that enhances privacy in the Panther Protocol by obscuring the connection between the transaction initiator and the transaction itself. Relayers achieve this by bundling multiple transaction requests, signing them with their own public key, paying the gas fees, and submitting them to the Shielded Pool contract for processing by zMiners.
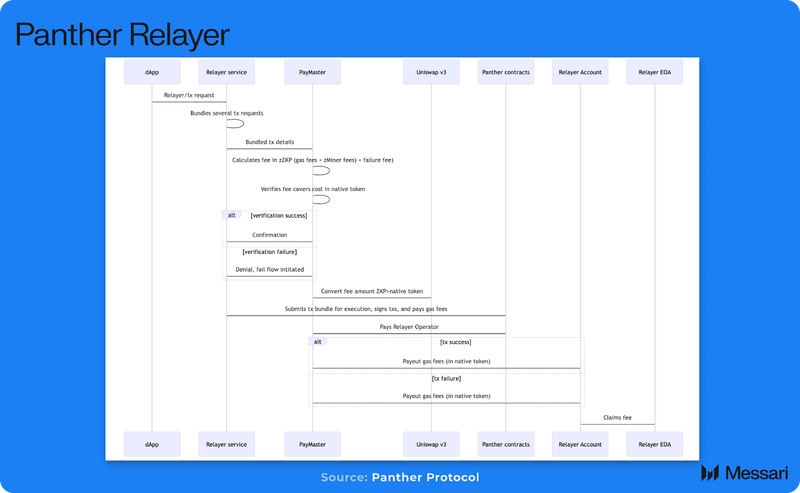
Panther Protocol uses account abstraction, introduced by ERC-4337, to simplify transactions and enhance privacy. This feature enables the Relayer service to mask user identities by bundling and signing transactions with its own keys, breaking links to onchain activity. The PayMaster contract automates transaction verification and fee calculation, streamlining account management. By separating account management from transaction execution, account abstraction further strengthens privacy within the Shielded Pool.
Compliance Tools
Zone Managers can determine what compliance looks like for their Zones. Panther Protocol does not process any user data; rather, the compliance provider(s) that the Zone Managers select do. Panther’s Compliance tools rely on three main features: (i) The Data Escrow, which is used for ‘ZK User Reveals’ and ‘Forensic Reveals’; (ii) Know Your Transaction (KYT), which is used for wallet screening and controlling deposit/withdrawal limits; and (iii) Extended KYT, which can be enabled by the Zone Manager, to provide additional compliance measures, including online transaction monitoring, suspicious transaction monitoring, and Travel Rule reporting.

Panther DAO
The Panther DAO is an entity responsible for guiding the direction of the Panther Protocol. In practice, the Panther DAO has already been useful in passing a few Panther Improvement Proposals (PIPs). The Panther DAO conducts its activity on Snaphot, with PIP-20 most recently being approved to increase the “Advanced Staking” reward pools. The Panther DAO has over 700 members and 100-200 votes per proposal.
Other areas the DAO has already contributed to include (i) the decentralized TGE of ZKP, (ii) selecting the multi-compliance vendors used, (iii) approving staking yield, and (iv) approving zAssets for allowlisting.
User Reveals
User Reveals enable users to selectively disclose specific information about their transactions and KYC status to authorized parties such as compliance providers, financial institutions, or other DeFi protocols. There are two types of user reveals: (i) ZK Reveals, which use Zero-Knowledge proofs to verify certain statements without revealing underlying data, and (ii) Non-ZK Reveals, which involve directly sharing specific data points like transaction details.
History CSV Export
History CSV Export allows users to download a comprehensive record of all transactions conducted through their zAccount without including any personally identifiable information (PII) or linking to their public blockchain addresses. Users unlock the ability to preserve their anonymity while providing a detailed and auditable transaction history if needed. Users retain full control over when and with whom they share this information, ensuring voluntary disclosure.
Forensic Reveals
Forensic Reveals in the Panther Protocol are specialized mechanisms designed for ad-hoc investigations into specific Shielded Pool transactions, enabling the disclosure of transaction details without compromising the privacy of routine activities. Utilizing the Forensic Data Escrow (FDE) system, each transaction is stored as an encrypted record secured with a unique ephemeral key. Decryption requires the cooperation of multiple stakeholders – including Zone Managers, Network and Zone FDE Assistants, and FDE Operators – ensuring that no single entity can access the private data independently. This multi-key decryption process allows authorized parties to uncover necessary transaction information for compliance or legal purposes while maintaining the anonymity of other users. Unlike User Reveals, which enable users to share specific information with chosen entities voluntarily, Forensic Reveals are initiated by Zone Managers or authorized entities to investigate particular transactions.
Tokenomics
Panther Protocol employs a structured fee system divided into Protocol Fees and Network Fees. Protocol Fees compensate Ecosystem Operators for their roles in transaction processing and include specific charges such as Relayer Fees for enhancing transactional privacy, Processing Fees for validating transactions, Withdrawal Fees to discourage reducing the privacy set, and KYC Fees for third-party compliance checks. Network Fees are the standard gas fees that the underlying blockchain requires for processing transactions, paid in the network’s native token. This fee structure not only covers operational costs and incentivizes Ecosystem Operators but also encourages users to keep their assets within Shielded Pools, thereby strengthening the overall privacy and security of Panther’s ecosystem.
To further incentivize participation and bolster the privacy set, Panther offers Panther Reward Points (PRPs). Users can earn PRPs by creating a zAccount, depositing assets into the Panther Vault, transferring zAssets within a Shielded Pool, and utilizing DeFi Adaptors like zSwap. PRPs encourage active engagement and ecosystem growth by rewarding actions that enhance privacy and expand the protocol’s functionality.
The native token of Panther Protocol, ZKP, has a maximum token supply of 1 billion and currently has 367 million tokens in circulation.

Protocol Usage
DeFi Adaptors
To bridge privacy with DeFi, Panther Protocol employs DeFi Adapters like zSwap, which connect Shielded Pools to popular DeFi protocols on networks such as Polygon. These adapters allow users to interact with decentralized exchanges (DEXs) using their private balances without compromising privacy. Additionally, Panther offers a Relayer service that enhances transaction anonymity by decoupling the transaction initiator from the transaction itself, leveraging ERC-4337 features like transaction bundling and account abstraction to obscure transaction origins.
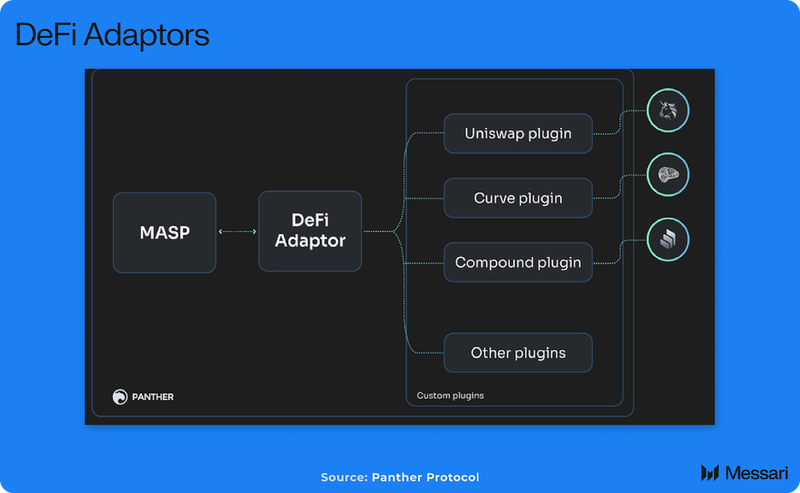
DeFi Adaptors integrate with Shielded Pools, allowing users to take actions like liquidity provisioning, and staking without the onchain activity being traced back to them.
zSwap
zSwap is the first use case for DeFi Adaptors, initially designed for DeFi protocols on Polygon like Uniswap, Curve, and QuickSawp.
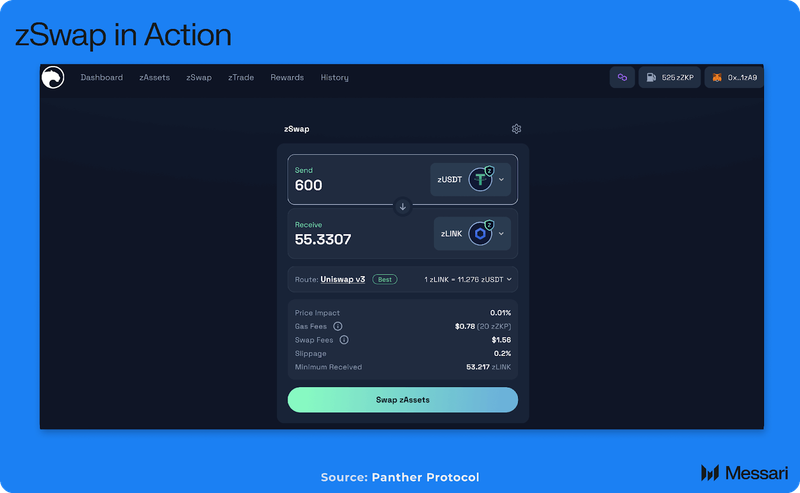
zSwap follows a simple flow that maintains the zAccount’s privacy throughout a swap:
- A zAccount initiates a swap through Panther and selects the desired trade (e.g., zETH to zUSDC).
- zSwap calculates the exchange rate and details the optimal route of execution.
- The zAccount confirms the swap, and a unique hashed time-locked contract (HTLC) is created.
- Within the set time limit of the HTLC, the zAccount reveals its secret keys to enable the DeFi Adaptor to execute the atomic swap; privacy is maintained as these details are never shown on the public blockchain.
- zUSDC is delivered to the zAccount along with PRP rewards.
Multi-Chain
Currently, Panther Protocol and many of its functionalities have been deployed on Polygon. Looking forward, the creation of zBridges will connect Shielded Pools that have been deployed on many blockchains, allowing for the transfer of zAssets across blockchains.
Ecosystem Roles
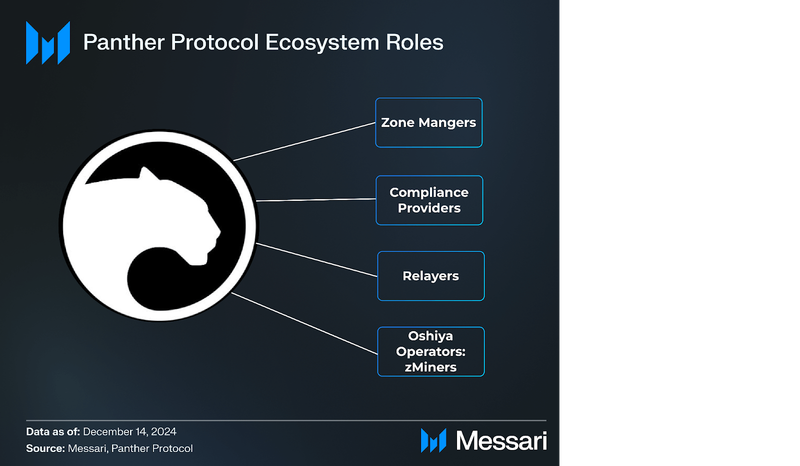
Panther Protocol has four main ecosystem roles:
- Zone Managers
- VASP-licensed operators who set up Zones, enabling entrance into Panther’s Shielded Pools
- Compliance Providers
- Dedicated service providers who ensure the Zone Manager’s KYC/T/B requirements are met by zAccounts
- Relayers
- Specialist Operators providing relaying and bundling service
- Earns fees for signing transactions, paying gas fees, and relaying bundles of transactions to Shielded Pool contract
- Oshiya Operators: ZMiners
- zMiners: operates Oshiya nodes
- Oshiyha node code fetches pending mining queue
- Updates Merkle Trees to append the UTXOs
- Creates SNARK proof to go onchain
- Provides offchain execution and submits proofs
- Receives rewards for processing all UTXOs in a queue (Guaranteed Reward & Premium Payment)
Closing Summary
By leveraging advanced cryptographic techniques such as ZK-SNARKs, and the UTXO framework, Panther Protocol offers robust privacy solutions through its core components: zAssets, zAccounts, and Shielded Pools. These elements work harmoniously to ensure users can engage in secure and anonymous transactions while maintaining full control over their financial data. Additionally, Panther’s innovative features, like DeFi Adaptors, facilitate seamless interactions with major DeFi platforms, enhancing both functionality and user experience. Panther’s compliance mechanisms, including History CSV Export, User Reveals, and Forensic Reveals help reinforce transparency and privacy, catering to both individual users and regulatory requirements. As Panther advances towards its mainnet launch, it remains committed to fostering a secure, compliant, and private financial environment, ultimately redefining privacy and compliance standards of the DeFi landscape.





















