Key Insights
- Total value locked (TVL) increased 14.6% QoQ, rising from $2.19 billion to $2.51 billion. The introduction of solvBTC, eBTC, and LBTC contributed to BTC on Venus overtaking BNB as the largest collateral category, with BTC-based collateral growing 44.4% QoQ to $957.1 million.
- Total value borrowed (TVB) rose 87.3% QoQ, from $456.0 million to $854.5 million. BNB borrowing saw the largest increase, up 821.3%, while BTC, USDT, and USDC borrowing also grew significantly. Increased demand for leverage contributed to the overall rise in borrowing.
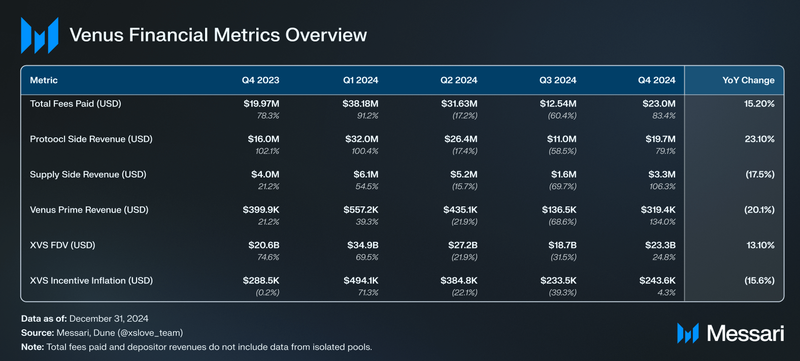
- Protocol-side revenue increased 79.9% QoQ, from $11.0 million to $19.7 million, while supply-side revenue grew 110.7% QoQ to $3.3 million. Higher borrowing activity and market speculation contributed to the revenue increase.
- Daily active users increased 27.9% QoQ, rising from 609 to 779. Deposits and withdrawals both more than doubled, increasing 128.5% and 125.9% QoQ, respectively.
- Staked XVS decreased 5.65% QoQ, from 8.17 million to 7.70 million, while its dollar value rose 14.64% to $70.60 million, reflecting price recovery.
Introduction
Venus (XVS) is a borrow/lend protocol built on BNB Chain, and recently launched on Base in Q4 2024. At its core, Venus enables users to deposit various cryptoassets as collateral, allowing them to borrow other assets based on their collateral value. Unlike traditional financial systems, Venus employs a unique algorithmic approach, where central entities often set interest rates. The interest rates for borrowing and lending on Venus are dynamically adjusted based on a jump rate model and a whitepaper rate model. These models leverage the utilization ratio, which is the proportion of collateralized deposited assets against the borrowed assets.
The utilization ratio is a critical component of the Venus Protocol. As borrowing demand rises, the ratio and interest rates increase. Conversely, lower demand decreases both, maintaining balance by incentivizing lenders in high demand and borrowers when demand wanes.
The Venus Protocol is governed by its DAO community and is enabled by the XVS governance token. Tokenholders can propose and vote on governance decisions. Furthermore, they can stake their tokens in a specialized vault to receive financial incentives, following the Venus tokenomics model. This model allocates a portion of the protocol’s revenue to stakers through a buyback and redistribution mechanism, rewarding active participation in governance. For a full primer on Venus, refer to our Initiation of Coverage report.
Website / X (Twitter) / Discord
Key Metrics
Performance Analysis
Financial Overview
Network Overview
Total Value Locked (TVL)
Total Value Locked (TVL) represents the total value of assets deposited into Venus Protocol across its supported markets. It serves as a key indicator of the platform’s size, liquidity, and overall user trust.
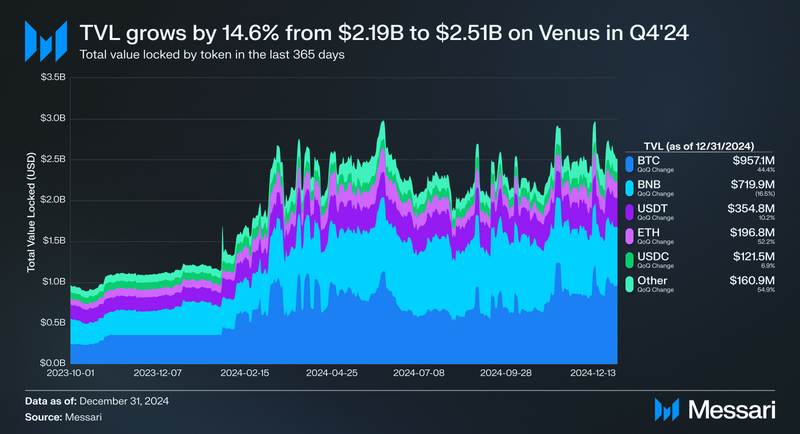
Venus Protocol’s total value locked (TVL) grew from $2.19 billion at the end of Q3’24 to $2.51 billion at the end of Q4’24, reflecting a 14.6% increase QoQ. This growth was primarily driven by the introduction of BTC-pegged assets, including solvBTC on October 27, eBTC on November 15, and LBTC on December 10, which collectively contributed to BTC on Venus overtaking BNB as the largest collateral category. BTC-based collateral surged to $957.1 million, a 44.4% increase QoQ, capturing 38.1% of the total market share. In contrast, BNB’s TVL decreased by 16.5% QoQ to $719.9 million, reducing its market share from 39.3% to 28.7%.
Stablecoin assets on Venus saw moderate growth, with USDT’s TVL rising 10.2% QoQ to $354.8 million and USDC increasing 6.9% to $121.5 million. Meanwhile, ETH experienced a notable recovery, with its TVL increasing by 52.2% QoQ to $196.8 million, rebounding from the declines observed in Q3’24. The “Other” category also saw significant growth, expanding by 54.9% QoQ to $160.9 million, likely due to the rising adoption of smaller collateral assets following cross-chain integrations and new listings.
The introduction of Bitcoin pegged assets not only contributed to the surge in BTC-backed collateral but also played a key role in diversifying the protocol’s asset composition. The increased adoption of these assets suggests a growing interest in Bitcoin pegged DeFi products on Venus. This growth highlights the demand for Venus protocol in the Q4’24 cycle.
Total Value Borrowed (TVB)
Total Value Borrowed (TVB) represents the aggregate value of all assets borrowed from Venus Protocol across its supported markets. It serves as a key metric for evaluating the protocol’s utilization and overall demand for its lending services. Unlike TVL, which measures deposits, TVB reflects the borrowing activity that drives revenue generation and lending efficiency.
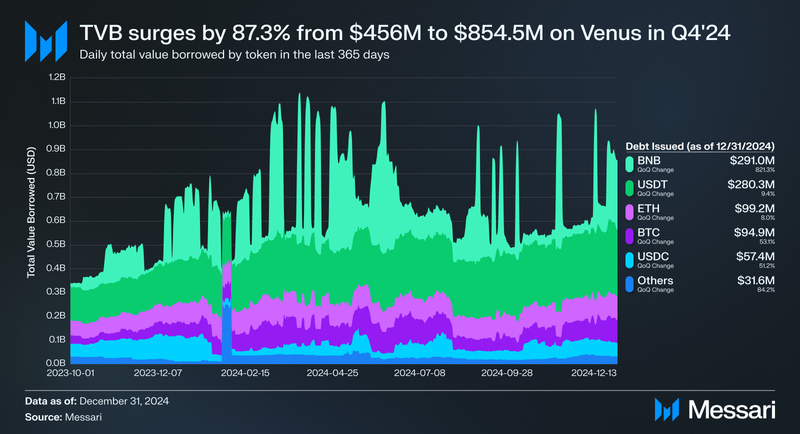
Borrowing activity on Venus Protocol increased significantly in Q4’24, with total value borrowed (TVB) rising from $456.0 million at the end of Q3’24 to $854.5 million, marking an 87.3% QoQ growth. BNB borrowing saw the most substantial rise, jumping from $31.6 million to $291.0 million—a surge of 821.3%—likely due to heightened demand for BNB-backed collateral to fund trading during the short-term December bull run.
USDT borrowing grew from $256.1 million to $280.3 million, a 9.4% increase, while ETH borrowing rose from $91.9 million to $99.2 million, up 8.0% QoQ. BTC borrowing also saw a significant jump, climbing from $62.0 million to $94.9 million, a 53.1% increase. USDC borrowing expanded from $38.0 million to $57.4 million, reflecting a 51.2% increase as users sought stable borrowing options.
Smaller assets, grouped under the “Other” category, experienced an 84.2% increase, rising from $17.1 million to $31.6 million, indicating a diversification of borrowing activity. The overall surge in TVB highlights growing demand for leverage and a more active trading environment on Venus Protocol, driven by new asset integrations and seasonal market dynamics.
User Activity
User activity refers to the total volume of user-driven transactions on Venus Protocol, including asset deposits, withdrawals, loan repayments, and new borrows. These activities directly impact metrics like TVL and TVB, offering a clear picture of the protocol’s utilization and user engagement trends.
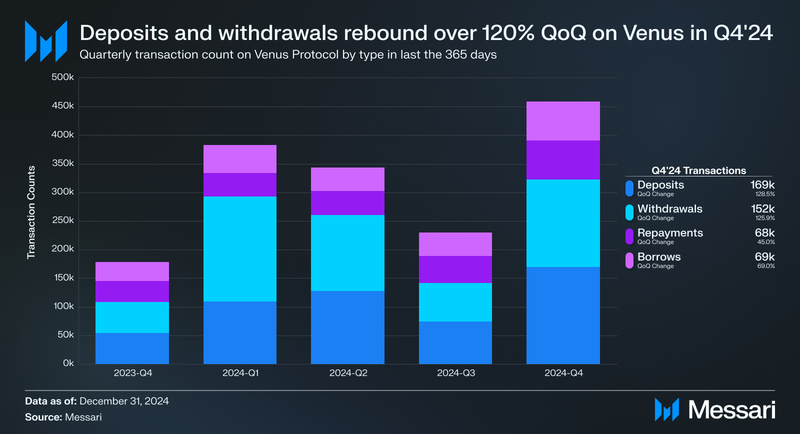
Deposits on Venus Protocol rose significantly in Q4’24, increasing by 128.5% QoQ from 74,000 to 169,231. Withdrawals also grew substantially, rising 125.9% QoQ from 67,694 to 152,932. This rebound suggests renewed user activity following the post-Ethereum launch cooldown observed in Q3’24. Repayments increased by 45.0% QoQ, reaching 68,342, indicating a stronger focus on debt management. Meanwhile, borrows grew by 69.0% QoQ, rising from 40,668 to 68,738, likely reflecting increased confidence in leveraging opportunities amid improved liquidity conditions.
Daily Active Users
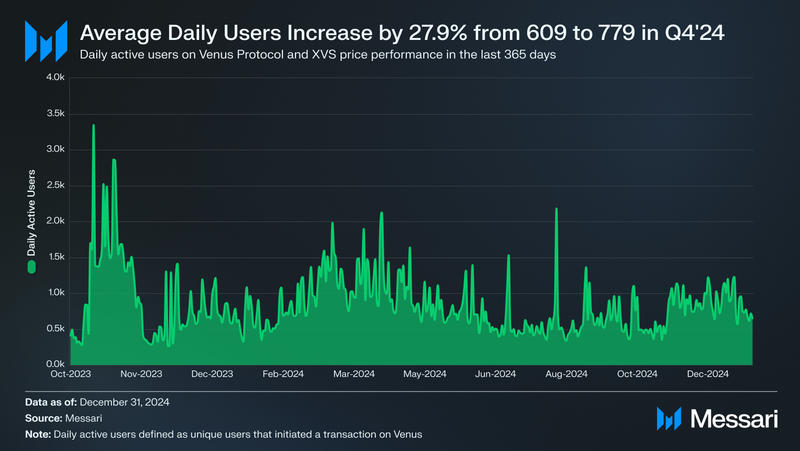
The average daily number of users on Venus Protocol rose by 27.9% QoQ, increasing from 609 in Q3’24 to 779 in Q4’24. This growth suggests a recovery in user engagement following the declines observed in previous quarters.
Revenue Metrics
In the context of Venus Protocol, revenue is categorized into two primary types: protocol revenue (often referred to as “fees”) and supply-side revenue (commonly referred to as “revenues”). These metrics provide insight into the financial performance of the protocol and its participants.
- Protocol Revenue (Fees): This represents the portion of total revenue retained by the protocol itself. Protocol revenue includes fees collected from borrower interest payments and penalties accrued during liquidations. It is retained to support protocol operations, governance, and treasury reserves.
- Supply-Side Revenue (Revenues): This refers to the revenue earned by users who supply assets to the protocol. Supply-side revenue is generated from interest paid by borrowers and distributed to lenders as compensation for providing liquidity.
Within Venus, interest revenue is the interest paid by borrowers on loans, which is split between supply-side and protocol revenue. Liquidation revenue arises when borrowers fail to maintain the required collateral ratio, triggering liquidations that generate additional funds for the protocol. Liquidation revenue typically contributes entirely to protocol revenue, as it stems from penalties rather than interest payments.
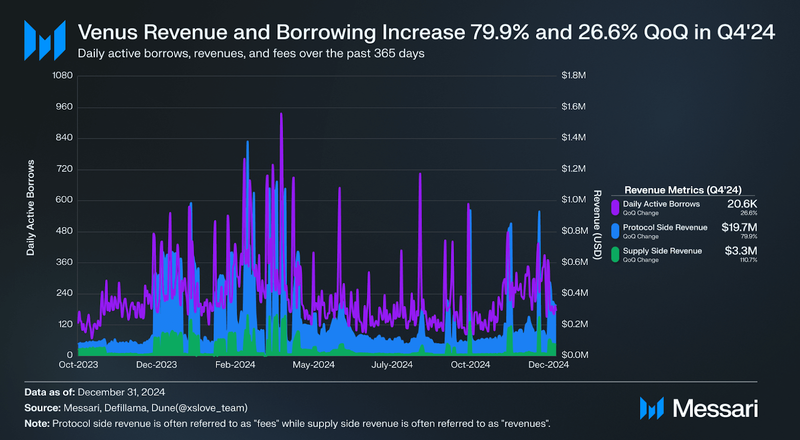
The resurgence in borrowing and revenue coincided with the euphoric meme cycle and heightened anticipation for an alt-season, both of which likely fueled speculative activity and increased leverage across DeFi markets.
Staked XVS
XVS staking on Venus allows tokenholders to participate in the protocol’s governance and earn rewards. By staking XVS, users gain voting power to influence Venus Improvement Proposals (VIPs), which guide protocol development, treasury management, and risk parameters.
Additionally, staked XVS contributes to the protocol’s buyback and redistribution mechanism, with 20% of the protocol’s revenue allocated to buying back XVS tokens for distribution to vault stakers. This ensures that stakers receive a share of the platform’s earnings while also supporting token demand. Beyond direct rewards, the Venus Prime Token Program offers additional incentives by providing enhanced APYs and exclusive benefits for long-term participants, further aligning staking with the protocol’s sustainability.

Staked XVS on Venus decreased by 5.65% QoQ, falling from 8.17 million in Q3’24 to 7.7 million in Q4’24. In contrast, the dollar value of staked XVS increased by 14.64%, rising from $61.58 million to $70.60 million, likely due to price recovery in the latter part of the quarter. Despite fluctuations, staking participation remained steady, reflecting continued engagement with Venus’s staking and governance mechanisms.
Introducing Bad Debt Metrics
Bad debt refers to the portion of outstanding loans on a protocol that cannot be repaid, typically due to failures in the liquidation process. Lending platforms like Venus rely on a Loan-to-Value (LTV) threshold, which ensures a borrower’s collateral maintains sufficient value to cover their debt. If an account’s LTV breaches the allowable ratio, liquidators—such as bots—step in to sell the collateral and repay the debt. However, in cases where liquidations are delayed or fail (e.g., due to sudden market crashes, low liquidity, or blockchain congestion), the collateral may not cover the borrowed amount, leaving the protocol with unrecoverable losses classified as bad debt.
Now in Q4’24, Venus has multiple quarters of bad debt data to reference, allowing for a clearer view of trends in liquidation efficiency and risk management. This metric will continue to provide insight into how well the protocol safeguards lender and platform funds, particularly in response to changing market conditions and borrower activity.
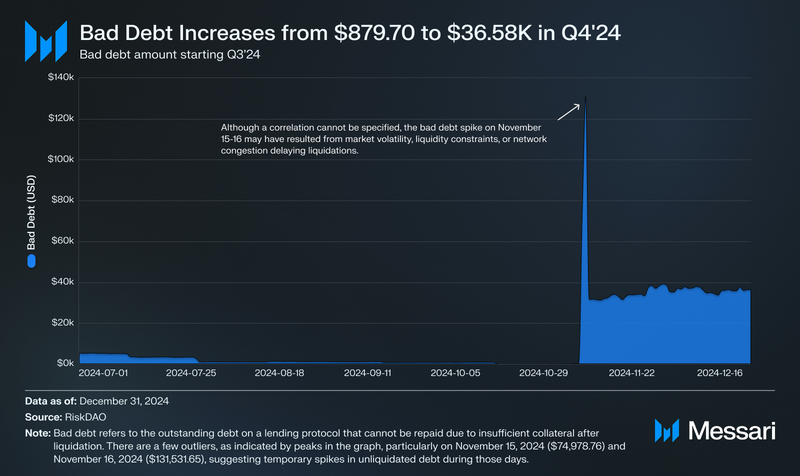
Bad debt on Venus Protocol increased from $879.70 at the end of Q3’24 to $36,582.86 at the end of Q4’24, marking a 4,058.6% QoQ increase. This rise suggests a higher incidence of failed or delayed liquidations, potentially due to increased market volatility or temporary inefficiencies in liquidation processes. The bad debt-to-TVL ratio rose from 0.00004% in Q3’24 to 0.0014% in Q4’24, reflecting the increase in absolute bad debt. However, despite this uptick, the overall impact remains minimal relative to the protocol’s $2.6 billion in total value locked (TVL) at the end of Q4’24.
Qualitative Analysis
Protocol Updates
Venus Prime and Tokenomics
In Q4 2024, Venus Protocol expanded the Venus Prime program to Arbitrum, enabling eligible users to claim Prime Status and access premium features starting Dec. 2, 2024. This move was part of a broader strategy to enhance user retention and engagement across its ecosystem by offering consistent benefits for active users.
Managing token emissions was a key focus during this period. VIP 410, approved on December 27, 2024, reduced total XVS emissions by 55%, lowering them from 67,166 XVS to 30,372 XVS per period across all supported chains, including BNB Chain, Ethereum, Arbitrum, and ZKSync. This adjustment aimed to curb inflationary pressures and create a more sustainable emission schedule.
On the same day, VIP 413 specifically addressed XVS emissions on BNB Chain, updating the XVS Vault distribution to 1,211 XVS per day (39,330 XVS per month). While VIP 410 reduced total emissions, it did not fully update the distribution within the XVS Vault on BNB Chain, requiring a follow-up proposal to align rewards with the adjusted emission structure. VIP 413 corrected this by ensuring consistency in emissions allocation.
Cross-Chain Asset Integration
Venus Protocol’s cross-chain strategy in Q4 2024 aimed to enhance liquidity and broaden asset diversity across its supported networks. A significant focus was on integrating Bitcoin-pegged assets, with solvBTC added on October 27, eBTC on November 15, and LBTC on December 10. These integrations allowed Bitcoin holders to access DeFi applications within Venus without liquidating their positions, diversifying the protocol’s range of collateral options.
The protocol also expanded its stablecoin offerings, with Sky Ecosystem’s USDS and sUSDS approved as collateral in the Venus Ethereum Core Pool. Additionally, the proposal to integrate Yearn Finance vaults as collateral was approved, allowing assets like yvUSDC and yvUSDT to be used within the protocol. The inclusion of these yield-generating assets was aimed at enhancing liquidity options and providing users with diversified strategies for leveraging their holdings. By broadening its cross-chain asset support, Venus sought to create a more interconnected DeFi ecosystem with increased liquidity and user choice.
Risk Parameter Adjustments
Risk management was a significant focus for Venus Protocol in Q4 2024, with multiple governance proposals aimed at adjusting risk parameters to maintain financial stability. VIP 385, approved on Oct. 19, 2024, introduced adjustments for BNB to mitigate volatility risks and align collateral factors with market conditions.
VIP 415, passed on Dec. 30, 2024, focused on risk adjustments for stablecoin markets, ensuring adequate liquidity and reducing systemic risks. There were also efforts to adjust risk parameters for LTC, AAVE, and TWT, covered under VIP 388 and VIP 389. These proposals required multiple rounds of voting before gaining approval, highlighting the complexities of managing risks for a broad range of assets.
To strengthen its risk management framework, Venus collaborated with Chaos Labs, which provided recommendations on risk parameters, including those for newly integrated tokens like EIGEN. This partnership was intended to enhance Venus’s ability to manage risks effectively through informed adjustments and a proactive approach.
Governance
Venus Protocol governance revolves around the XVS token, a BEP-20 token that grants holders voting power to participate in decision-making. Tokenholders can stake XVS on the Venus application to create and vote on Venus Improvement Proposals (VIPs), which guide the protocol’s development and operations. Governance encompasses treasury management, collateral parameters, stablecoin minting fees, and more.
Venus Improvement Proposals (VIPs) serve as the mechanism for implementing changes within the protocol. They are categorized based on their scope, ranging from adjustments to token emissions and liquidity to the introduction of new features and integrations. Each XVS token equals one vote, and decisions require community approval through on-chain voting. Q4’24 introduced 388 new VIPs, of which 37 were executed, and 1 was defeated.
Omnichain Governance Implementation
In Q4 2024, Venus Protocol made significant progress in implementing Omnichain Governance to streamline decision-making across its multichain ecosystem. The process began with VIP 391, approved on Nov. 1, 2024, which granted the Timelock contracts on these networks the same privileges as on BNB, while revoking permissions from the Guardian wallets, except for contract upgrades. Additionally, 5 BNB was transferred from the Venus Treasury to fund cross-chain governance execution.
The next phase involved VIP 399, passed on Nov. 23, 2024, which extended Omnichain Governance to zkSync Era and Optimism. This proposal enabled remote VIP creation and execution of privileged commands by authorized guardian wallets, reducing administrative overhead. VIP 403, approved on Dec. 7, 2024, further refined governance mechanisms to ensure balanced power distribution across networks.
By decentralizing governance processes, Venus aimed to enhance operational efficiency and maintain consistent standards across different chains. These updates were part of a broader strategy to manage its expanding network footprint effectively.
Partnerships and Integrations
In Q4 2024, Venus Protocol expanded its multichain presence by deploying on the Base network following the approval of VIP 408. The deployment, completed on Dec. 19, 2024, introduced initial support for cbBTC, WETH, and USDC, aiming to leverage Base’s scalability and low-cost transaction environment. This move marked Venus’s presence on its seventh network, further diversifying its ecosystem.
The protocol also focused on optimizing Layer-2 solutions to enhance user experience and reduce transaction costs. On Oct. 18, 2024, Venus integrated gasless transactions on zkSync via the Zyfi.org paymaster, enabling users to conduct approvals, supplies, withdrawals, borrowing, and XVS Vault operations without incurring gas fees. This feature processed approximately 400 sponsored transactions daily, lowering barriers to entry and usage. By the end of September 2024, XVS Vault on zkSync reached over 140,000 XVS staked, growing at an average weekly rate of 150% without withdrawals, indicating user confidence in the protocol’s L2 implementation.
In addition to zkSync, Venus expanded to other L2 networks like Optimism and Arbitrum. Deployments on these networks were guided by governance proposals, which configured tailored risk parameters and market settings. For instance, VIP 382 established markets on Optimism and set up key infrastructure components, including the ProtocolShareReserve contract for managing protocol fees and the NativeTokenGateway for ETH transactions. These L2 deployments aimed to alleviate the challenges of high transaction costs and network congestion on Ethereum, making Venus’s DeFi offerings more accessible and efficient.
On-Chain Initiatives and Community Engagement
Venus Protocol partnered with Tokocrypto, an Indonesian cryptocurrency exchange, to launch the “Tanding Trading Tokocrypto” competition aimed at boosting XVS token activity. Held from Oct. 27 to Nov. 7, 2024, the event featured a prize pool of 150 million Indonesian Rupiah (approximately $9,600 USD). The competition’s structure incentivized higher trading volumes and frequent transactions for XVS pairs, using dynamic marketing strategies to sustain interest. This initiative was part of Venus’s broader efforts to expand its presence in Southeast Asia, attract new users, and enhance XVS liquidity on regional exchanges.
Closing Summary
Venus Protocol experienced strong growth in Q4’24, with TVL increasing 14.6% QoQ to $2.51 billion, driven by the introduction of BTC-pegged assets that helped BTC on Venus surpass BNB as the largest collateral category. Borrowing activity rose 87.3% QoQ, with BNB borrowing increasing over 800%, contributing to higher lending demand. Revenue rebounded from Q3 declines, with protocol-side revenue growing 79.9% to $19.7 million and supply-side revenue increasing 110.7% to $3.3 million.
User engagement also improved, with daily active users increasing 27.9% QoQ, while deposits and withdrawals more than doubled. XVS staking declined 5.65% in token count but increased 14.64% in dollar value, reflecting price appreciation. Governance activity remained strong, with multiple risk parameter adjustments, cross-chain integrations, and the expansion of Omnichain Governance across new networks. As Venus continues to scale its operations and refine its risk management framework, its positioning within the DeFi lending market remains strong.





















