Key Insights
- Bitcoin’s limited programmability, lack of non-custodial infrastructure, and native yield have hindered BTC DeFi (BTCFi), but developments like sidechains, non-custodial staking, and BitVM are changing that.
- Core’s ecosystem is designed to unlock BTC yield and extend BTC’s utility through programmability and DeFi, creating a path to unlock $1.8T in idle liquidity.
- Core’s ecosystem offers a range of DeFi applications, including lending, restaking, DEXs, and liquid staking. Notable apps include Colend, BitFLUX, Glyph Exchange, and b14g.
- Core launched Dual Staking in Q4 2024, allowing users to stake BTC and CORE tokens simultaneously for higher rewards. Over 25% of BTC stakers on Core currently participate.
- Core will launch lstBTC, a liquid staking token representing locked BTC, alongside Maple Finance, BitGo, Copper, and Hex Trust. lstBTC enables users to earn additional yields across multiple DeFi opportunities while maintaining liquidity.
Primer
The Core blockchain (CORE) is a scaling and programmability solution for Bitcoin powered by its Satoshi Plus consensus, EVM execution environment, BTCFi, and Core governance. Launched in early 2023, the Core community is building an ecosystem of Bitcoin-focused apps, leveraging Bitcoin security, such as consensus resources, wherever possible.
Satoshi Plus consensus involves staking CORE, hash rate delegation from Bitcoin miners, and locking up BTC through non-custodial BTC staking. This combination of security resources results in a hybrid model that leverages Bitcoin mining, rewards miners, and separates block production to mitigate censorship and MEV risks. The network’s EVM compatibility allows Core to run smart contracts and apps by leveraging existing Ethereum developer tools and the Ethereum ecosystem.
In Q2 2024, Core introduced non-custodial BTC staking. BTC holders can lock their tokens using absolute time-locks; in return, holders receive voting power on Core, which they delegate to elect validators, earning users CORE token rewards. Relayers in the Core ecosystem monitor the BTC network for valid lockup transactions and forward approved transactions to Core’s Consensus Engine. Holders are then rewarded via CORE tokens on the Core network. BTC holders do not need to transfer their tokens from the Bitcoin network or give up custody of their private keys. The Fusion Upgrade introduced higher CORE token rewards via dual staking of BTC and CORE, and lstBTC, a BTC liquid staking token that enables users to earn yield while retaining BTC liquidity in Core’s fully expressive execution environment. For a complete primer on Core, refer to our Initiation of Coverage report.
Introduction to BTCFi
As of March 2025, BTC’s market cap is $1.7 trillion, yet 99% of BTC is idle capital not used in DeFi to secure additional networks or generate yield. BTC holders and developers have faced challenges building an onchain economy on Bitcoin, primarily due to the following:
- Minimal Programmability: Bitcoin’s limited scripting language restricts smart contracts and apps, forcing users offchain or to L2s for nuanced transactions.
- Lack of Non-Custodial Support: Bitcoin launched in 2008 as a trustless alternative to TradFi, but custodial options have undermined its core ethos. Current DeFi apps suffer from counterparty and smart contract risk.
- Unsustainable Yield: Bitcoin offers no native yield mechanism; centralized apps carry higher risk, and onchain options are limited by its lack of programmability.
Core aims to tackle these challenges and foster an onchain DeFi ecosystem utilizing Bitcoin (BTCFi).
Ethereum’s TVL-to-market cap ratio is 22%, while Bitcoin’s is only 0.1%. Because of Bitcoin’s limited programmability, it’s hard to imagine DeFi could achieve similar adoption. Even so, it’s evident that a small percentage of BTC would be more than enough to fuel a rich BTCFi ecosystem. Sidesystems are currently the best route to leverage BTC, as they provide a route to lock up tokens similarly to staking. Core takes this further with non-custodial BTC staking, so users can participate in BTCFi without leaving the BTC network.
Despite Bitcoin’s TVL-to-market cap ratio being significantly lower than Ethereum’s, even modest BTCFi adoption could unlock substantial capital. Core is positioned to capitalize on several catalysts (e.g., rising BTC dominance, OP_CAT, increased adoption) should they cause an uptick in BTCFi participation.
What is BTCFi
BTCFi enables users to leverage their BTC holdings through non-custodial onchain products.
For BTCFi to achieve broad adoption, it must appeal to institutional users, which requires the following:
- Security: Institutions require the highest security standards. Custodians like Coinbase and Fireblocks protect large holdings and mitigate hack risks while vetting DeFi protocols for yield.
- Deep Liquidity: Essential for capital markets, market makers like Citadel provide liquidity for high-volume BTC, ETH, and SOL trades with minimal slippage.
- Abstraction: A single, intuitive app simplifies access and management, aiding Bitcoin integration into financial strategies.
Core Staking Products
Staking on Core is non-custodial, provides yield opportunities for BTC stakers, and includes a wide range of liquidity options, from liquid staking to institutional custody providers. BTC holders lock tokens with time-locks, delegate corresponding voting power to Core validators, and earn CORE tokens. At the same time, relayers monitor and forward valid transactions to Core’s Consensus Engine for rewards.
Within the Core network, CORE stakers, BTC delegators (known as stakers), and Mining Power all contribute to a hybrid score to elect validators each round. Validators earn CORE tokens from transaction fees and block rewards, sharing a portion with miners and stakers after taking a commission (set by each validator). Rewards are distributed daily.
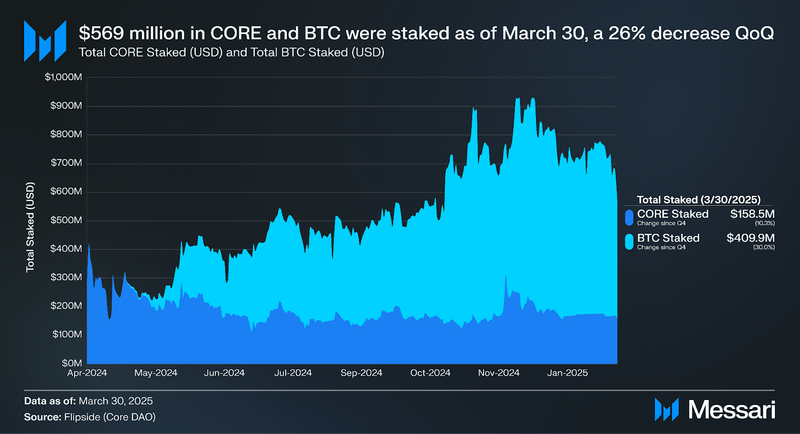
Over $731 million of CORE and BTC were staked in Q4, a 31% increase QoQ. BTC staked on Core increased 54% QoQ. With dual staking, BTC and CORE stakers can capitalize even further on this alignment by earning higher yields with more staked CORE. As of March 31, When BTC is staked alone, it earns roughly 0.2% APY, whereas when BTC is dual-staked with CORE, it can earn anywhere from 0.3%-9% APY.
CORE Staking
CORE staking operates within the Core network’s Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) model, a key component of its Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism. In DPoS, tokenholders vote to select a small group of trusted delegates to validate transactions and secure the blockchain rather than everyone participating directly.
stCORE is Core’s liquid staking token, enhancing CORE’s utility by keeping staked assets liquid within the Satoshi Plus consensus. Liquid staking enables users to stake assets on a Proof-of-Stake blockchain and receive a receipt token (LST) representing their staked funds, keeping them liquid for trading or use on other DeFi platforms.
Non-Custodial BTC Staking
Non-custodial BTC staking launched in Q2 2024, allowing users to delegate BTC, secure the Core network by contributing to consensus, and earn CORE token rewards in return. Non-custodial staking enables a trust-minimized way to hold BTC while participating in network validation.
The underlying technology that supports non-custodial BTC staking is a CheckLockTimeVerify (CLTV) Timelock. This Bitcoin-native cryptographic feature allows users to set a specific time or block before processing a transaction. When users stake BTC, they apply a CLTV timelock to the transaction. This timelock specifies a future block height or time that staked BTC cannot be moved or spent. The BTC is effectively “locked” until the timelock expires. A simple analogy would be a safe with a built-in timer: even while your belongings are stuck in the safe until the timer runs out, they have not transferred ownership and are still your belongings. This process is often called “staking” by Core, even though it is technically different from traditional proof-of-stake.
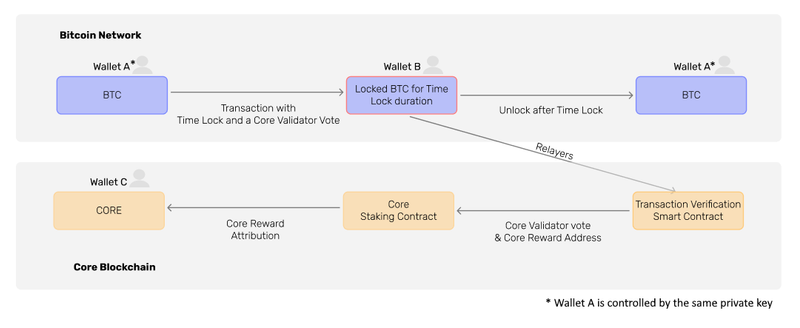
Source: Core Documentation
To participate in non-custodial BTC staking, users need a Bitcoin wallet funded with BTC and a Core wallet address to receive rewards. A minimum of 0.01 BTC must be locked up for at least 10 days. Users must determine how long they’d like to lock up their BTC in the CLTV Timelock when staking. After a user’s tokens are locked on the Bitcoin network, they can delegate their voting power to validators to help get them elected. Once the timelock has expired, users can redeem their locked BTC on the delegator page. There is no additional wait period to withdraw. Because of the CLTV Timelock, BTC holders can support Core’s security without bridging BTC to Core. As such, a user’s BTC holdings cannot be compromised by the Core network.
Non-custodial BTC staking is particularly interesting to institutions and ETF providers, as it is one of the only ways to unlock idle BTC without counterparty or smart contract risk. This makes it an appealing alternative to WBTC, which has been criticized for its centralized nature and changes in multi-sig management.
Dual Staking
Dual Staking rewards users who stake BTC and CORE tokens simultaneously, maximizing rewards while diversifying their participation in the network. By staking both assets, users can contribute to the stability and security of the Core network, earning rewards that reflect their combined contributions.
The staking process is unchanged; users stake their BTC and CORE through the same contracts. Depending on how much CORE the user stakes, they can achieve even higher yield thresholds. CORE token rewards are transferred to users through a new pool.
Dual Staking benefits the Core network by incentivizing deeper economic alignment between Bitcoin and Core. By offering higher BTC staking yields to participants who stake both BTC and CORE, the system encourages BTC stakers to further their commitment to the network by also staking CORE tokens. Additionally, increased value staked/locked up is economically attractive for the Core Network, as it creates alignment by rewarding BTC tokenholders for contributing to the Core network.
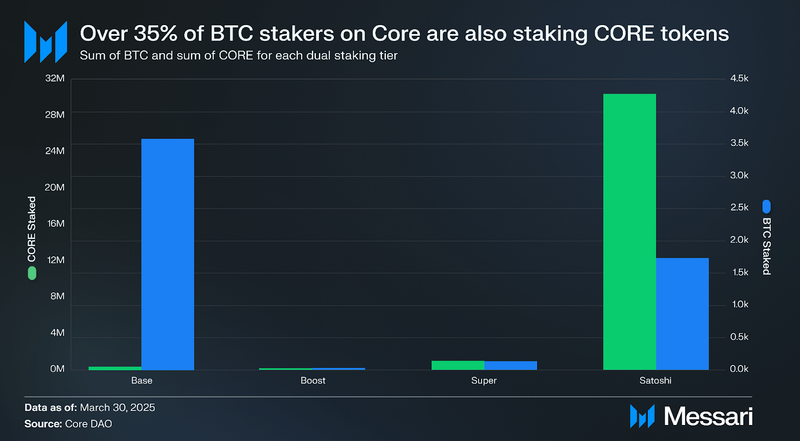
Over 35% of BTC stakes are dual staking. These dual-stakers can choose from three tiers—Boost, Super, or Satoshi—based on the amount of CORE they stake in relation to their staked BTC. Users can access higher tiers by staking more CORE to achieve greater yields.
Although just 9% of BTC dual-stakers have attained the elite Satoshi tier, their combined CORE stakes account for 59% of all dual-staked CORE. This disparity highlights a strong interest in dual staking to boost BTC yields, suggesting users are comfortable holding CORE to maximize their returns.
Core announced they were raising the amount of staked CORE necessary for each tier following an approved governance proposal, increasing the incentive for BTC stakers to stake more CORE. The tier requirements have been updated to:
- Satoshi Tier (Highest Rate) – 24,000:1
- Super Tier – 9,000:1
- Boost Tier – 3,000:1
Dual staking allows BTC holders to strengthen returns and network stability.
Core Ecosystem
Core offers an ecosystem of DeFi apps tailored towards unlocking BTC and supporting CORE. The most popular apps on Core include lending and restaking various BTC wrappers, with Colend and Pell Network leading in TVL.
In Q2 2024, Core introduced Sparks to reward active participants on the network. Similar to points, Sparks can be earned through participation in apps within Core’s ecosystems, and there are often various campaigns with multipliers, rewarding active Core participants. Core announced Season 3 of the Sparks campaign in Q1 2025, which included a leaderboard reset and new multipliers.
Notable protocols
Colend
Colend is a lending and borrowing platform on the Core network. It allows users to lend wrapped BTC assets and CORE, among other tokens, as collateral to earn interest or borrow funds. For Core, Colend adds value by enhancing the network’s BTCFi ecosystem, providing a practical way to activate idle BTC and increasing TVL, supporting the network’s aim to improve capital efficiency for individual and institutional users. Colend had their TGE in November, rewarding users who had earned points lending.
BitFLUX
BitFLUX is a DEX on the Core network, functioning as a stableswap platform tailored for BTC-pegged assets, enabling users to swap with minimal slippage. BitFLUX supports single-sided liquidity provision, allowing BTC holders to deposit assets and earn yield without the risk of impermanent loss. BitFLUX is significant because it strengthens the network’s BTCFi infrastructure by providing a reliable mechanism to enhance BTC liquidity. It supports Core’s goal of activating idle BTC, offering a practical solution for users and institutions to generate returns on BTC holdings while keeping them active in DeFi.
Copilot Insights: What is a stableswap platform?
Glyph Exchange
Glyph Exchange is a DEX built on the Core network to facilitate trading BTC-based assets and inscriptions. It operates as an automated market maker (AMM) with features like concentrated liquidity through its V4 engine and a modular structure, supporting low-fee, fast transactions. Compared to BitFLUX, Glyph offers more asset diversity, driving trading volume and ecosystem connectivity.
A distinctive aspect is its integration of inscription trading via the FairC-20 standard alongside traditional DeFi offerings using ve(3,3) tokenomics, which incentivizes liquidity provision. With a TVL exceeding $160 million as of early 2025, Glyph has established itself as a key trading hub within Core’s ecosystem.
b14g
b14g is a Bitcoin Merge Staking platform on the Core network that enables BTC Holders to access Dual Staking yields with just locked-up BTC. Unlike typical staking platforms requiring users to hold multiple assets, b14g introduces a collaborative model through its Merge Marketplace, where BTC and CORE holders can pair their assets to unlock higher staking rewards. Users stake BTC non-custodially via Core, receiving virtual BTC (vBTC) as a receipt token. Stakers can earn additional points, which will eventually be redeemable for $B14G tokens. This system lowers entry barriers, allowing users who lack one asset to participate still and earn higher yields by collaborating, with funds securely stored in Core’s staking contract. For Core, the Merge Marketplace increases BTC inflow, supports ecosystem balance, and broadens participation in its BTCFi framework by making dual staking more accessible and efficient.
In Q1, b14g introduced dualCORE, a liquid dual-staking token on the Core network issued by b14g. dualCORE is created by staking CORE into a vault where b14g automatically matches it with BTC for dual-staking rewards. Unlike the Merge Marketplace, which requires users to manually pair their BTC or CORE with another party’s assets through a smart contract to unlock rewards, dualCORE automates the process, eliminates the need for matchmaking, and provides a tradable asset that can be used in DeFi apps like liquidity pools for additional yield.
Stablecoins
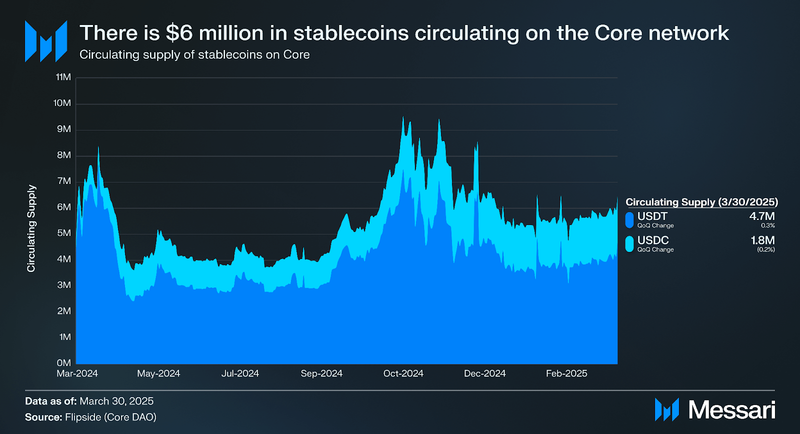
At the time of writing, there were $6.5 million in stablecoins circulating on Core, down from its peak of $9.5 million in Q4 2024. While stablecoins are a valuable part of the Core ecosystem, much of the reward system is designed to incentivize holding BTC on Core, so users opt for the latter as a store of value.
This shift toward BTC staking could reflect user confidence in BTC’s long-term value compared to stablecoins. Additionally, the decline in stablecoin circulation might suggest reduced trading or liquidity needs on the platform, as users are incentivized to provide liquidity through BTC.
Core-Enabled Products
The Core network supports a range of products designed to integrate Bitcoin into DeFi and institutional frameworks. These products enable institutions to improve the utility of BTC holdings, supporting activities like collateral use and liquidity provision within a regulated environment.
lstBTC
lstBTC is an upcoming liquid staking token issued on the Core network representing staked BTC. Users who lock BTC on the Bitcoin network receive lstBTC on Core in return. Maple will borrow against that BTC for CORE tokens, which they will use in dual staking.
Core Foundation has partnered with Maple Finance and custodians BitGo, Copper, and Hex Trust to expand lstBTC opportunities to institutional clients. Institutional BTC holdings often fall short of capital efficiency; profits are eroded by custody, leverage, and/or management costs. By adopting lstBTC, institutions can earn yield on top of their BTC, unlocking potentially greater returns for themselves and their stakeholders. This enables participation in activities like lending, liquidity provision, borrowing stablecoins for trading, or engaging with various BTCFi apps.
lstBTC’s future success lies in its ability to unlock BTC liquidity for broader DeFi opportunities in the retail market and for institutions to adopt liquid staking. Core must capture market share from competition such as WBTC, cbBTC, and other BTC derivatives to receive meaningful adoption.
Valour’s Yield-Bearing BTC ETP
In Q2 2024, Valour leveraged the Core Network to launch a BTC Exchange Traded Product (ETP) on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange in Germany. Valour, which runs a validator on Core, accumulates CORE token rewards through Non-Custodial BTC Staking. Valour then converts CORE into BTC and adds it to the ETP’s net asset value.
While the solution is non-custodial while onchain, users give up custody of their base currency (Euros in the case of Valour) while invested in the ETP. Fortunately, ETFs and ETPs are subject to more stringent regulations than crypto custodians, such as filing a prospectus.
TradFi has recently become more involved with crypto; major companies like BlackRock, Fidelity, JP Morgan, and Morgan Stanley now issue and promote BTC ETFs. Crypto ETF issuers have looked for new ways to create structured, yield-bearing crypto ETFs, such as incorporating staking in ETH ETFs. If the option for a yield-bearing BTC ETF exists, issuers may seek ways to include it to remain competitive. Core is well-positioned to provide ETF issuers with a yield-bearing strategy and can highlight the success of the Valour ETP.
CoreFi Strategy
In November, DeFi Technologies announced the launch of CoreFi Strategy, a leveraged, regulated approach to BTC and CORE yield through Dual Staking on Core, providing high-beta exposure to BTCFi. The initiative was formed to provide investors with a regulated entry into BTCFi, inspired by successful models like MicroStrategy. CoreFi Strategy aims to generate sustainable yield with a higher upside than BTC.
DeFi Technologies is Valour’s parent company, which manages a CORE ETP and a BTC staking ETP using Core’s non-custodial BTC staking mechanism. DeFi Technologies is well positioned to leverage dual staking for CoreFi internally since Valour runs a validator on Core.
Closing Summary
Core has positioned itself to unlock BTC’s latent potential as an asset by integrating BTC staking, structured products, and DeFi protocols. Through internal staking products such as non-custodial BTC staking, dual staking of CORE and BTC, and the forthcoming lstBTC liquid staking token, the platform enables BTC holders to unlock idle tokens and generate yield. Furthermore, Core has facilitated the development of various products tailored to institutional needs, paving the way for more capital-efficient Bitcoin management that aligns with traditional finance standards. This approach diversifies yield sources and reinforces network resilience by combining the strengths of both BTC and CORE tokens.
As BTC matures, these innovations could provide an attractive alternative for investors seeking additional returns beyond merely holding Bitcoin. For Core to succeed in the market and maintain its edge in BTCFi, It must capture institutional clients and capitalize on upcoming catalysts for BTCFi growth. Through lstBTC and Dual Staking, Core can generate sustainable native yield that may appeal to institutional traders and BTC holders looking for additional returns, especially if BTC experiences diminishing price appreciation as it matures.






















